January 2026

The global liquid biopsy market size is projected to reach USD 27.42 billion by 2035, growing from USD 7.08 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035, as a result of technological advancements in cancer diagnostics, and rising preference for minimally invasive cancer diagnostics.
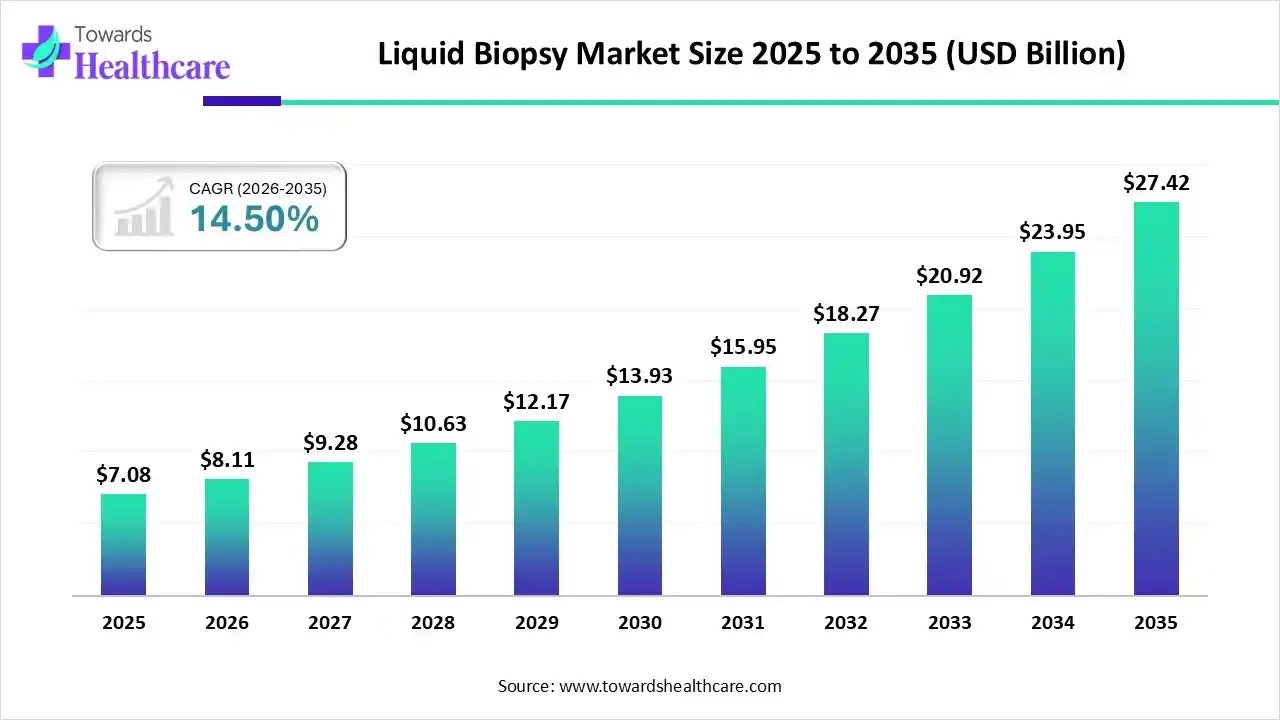
| Metric | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 7.08 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 27.42 Billion |
| CAGR (2026 - 2035) | 14.5% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Market Segmentation | By Sample Type, By Biomarker, By Technology, By Application, By Clinical Application, By Product, By End-Use and By Region |
| Top Key Players | Bio-Rad Laboratories and Biocept Inc., Guardant Health and Illumina, Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. and Johnson & Johnson, Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings and MDxHealth SA, and QIAGEN N.V. and Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. |
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana is a government-funded medical care initiative established to provide important support for cancer treatment and management, particularly targeting the underprivileged, which causes the growth of the liquid biopsy market.
The liquid biopsy market refers to the market for non-invasive diagnostic tests that use a patient's blood, urine, or other bodily fluids to detect cancer or other diseases. The liquid biopsy market is growing rapidly due to a number of factors, including the increasing incidence of cancer, advances in genomics and proteomics, and the need for non-invasive diagnostic tests. One of the significant drivers of the liquid biopsy market is the increasing incidence of cancer worldwide. Liquid biopsies offer a less invasive and more convenient way to detect cancer and monitor disease progression compared to traditional tissue biopsies, making them an attractive option for patients and healthcare providers.
The advent of liquid biopsy has connected targeted treatments and molecular diagnostic tests in a highly synergistic way. Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive diagnostic method that involves the analysis of various biomarkers in bodily fluids such as blood, urine, and saliva to detect the presence of cancer and other diseases. This method has gained increasing attention in recent years due to its potential to provide a less invasive and more accurate diagnosis and monitoring of cancer than a traditional tissue biopsy. One of the latest trends in the liquid biopsy industry is the development of multi-analyte liquid biopsy tests that can detect multiple types of biomarkers in a single test. These tests can improve the accuracy of cancer diagnosis and monitoring by providing a more comprehensive analysis of the disease. The integration of liquid biopsy with AI is another trend in the market. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data generated by liquid biopsy tests to identify patterns and biomarkers that may not be detectable by traditional analysis methods, improving the accuracy and precision of diagnosis and monitoring.
One of the main advantages of liquid biopsy over traditional tissue biopsy is its non-invasive nature, which makes it a more comfortable and less risky procedure for patients. Another advantage is the ability to monitor disease progression and treatment response over time, which can help doctors make more informed decisions about treatment options. Liquid biopsy has several potential applications, including cancer diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and early detection. Liquid biopsy can also detect other diseases, such as infectious, autoimmune, and cardiovascular diseases.
Advances in genomics and proteomics have also played a significant role in the growth of the liquid biopsy sector. With the advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies and other advanced molecular techniques, it is now possible to detect and analyze cancer-specific mutations and biomarkers in a patient's blood or urine. This has enabled the development of highly sensitive and specific liquid biopsy tests that can detect cancer at early stages and monitor disease progression.
The need for non-invasive diagnostic tests has also contributed to the growth of this global market. Traditional tissue biopsies are invasive and often require hospitalization, anesthesia, and lengthy recovery times. In contrast, liquid biopsies are minimally invasive, can be performed in an outpatient setting, and often provide faster results, making them an attractive option for patients and healthcare providers. Thus, the liquid biopsy market is expected to continue to grow rapidly in the coming years, driven by advances in genomics and proteomics, increasing incidences of cancer, and the need for non-invasive diagnostic tests. However, there are also challenges facing the market, including the lack of standardized testing protocols and regulatory oversight, as well as the high cost of liquid biopsy tests.
The U.S. National Library of Medicine studied the effect of liquid biopsy using AI in triple-negative breast cancer, in May 2021.
Artificial intelligence has presented promising diagnostics to deliver incredible treatment outcomes. Several government and private organizations are engaged in conducting exhaustive research to study and advance the use of AI in liquid biopsy. Additionally, several companies are developing liquid biopsy platforms that incorporate AI algorithms for data analysis. These platforms are designed to automate the liquid biopsy workflow, from sample preparation to data analysis, and provide clinicians with actionable insights in real time. Furthermore, AI-driven liquid biopsy analyses are helping identify specific mutations and biomarkers that are unique to an individual's cancer, allowing for more personalized treatment approaches. AI algorithms potentially analyze liquid biopsy data to identify drug targets and predict treatment response.
Liquid biopsy is a less invasive technique for identifying non-hematological cancers, and it has gained popularity due to technological advancements in ongoing research on circulating biomarkers. A liquid biopsy involves analyzing circulating tumor DNA, circulating tumor cells, exosomes, and extracellular vesicles, which have the potential to transform cancer management and treatment dynamics. Moreover, the market is expected to grow by providing precise and personalized treatment in the coming years.
Liquid biopsy is an advanced testing technology for detecting tumor-related genetic alteration. It has also been used to stratify tumors and provide appropriate precision oncology treatment. These recent advancements, innovations, and expansions in the industry promoting liquid biopsy are driving the market's growth.
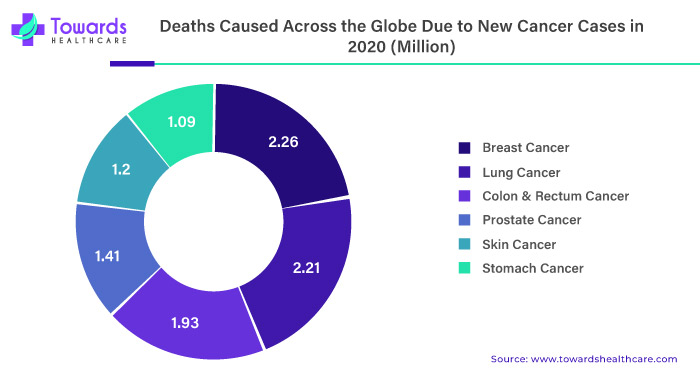
The rising prevalence of cancer is a significant driving factor for the growth of the liquid biopsy market. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer is one of the leading causes of death globally, and it is estimated that approximately 10 million people die from cancer every year. Additionally, the incidence of cancer is increasing, primarily due to factors such as population growth, aging, and lifestyle changes. This has led to an increased demand for accurate and efficient cancer diagnostics and treatment options, including liquid biopsy.
Liquid biopsy offers several advantages over traditional tissue biopsy, such as less invasiveness, the ability to perform real-time monitoring, and the potential to identify genetic alterations that may not be detected by tissue biopsy. Liquid biopsy can also be used for early cancer detection and monitoring of treatment response, which can lead to improved patient outcomes. As a result, liquid biopsy has become an increasingly important tool in cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Liquid biopsy technologies have made considerable headway in recent years, showing a significant boom in adoption and clinical applications. Liquid biopsy is a rapidly evolving tool of precision oncology, enabling longitudinal monitoring and minimally invasive molecular diagnostics for treatment purposes. For managing advanced-stage lung cancer, quantifying and detecting circulating DNA are now commonly adopted as clinical practice. Moreover, liquid biopsy technology is delivering a new source for cancer biomarkers and adding new dimensions to clinical trials. A liquid biopsy helps diagnose cancer at an early stage, identify resistance mechanisms of therapies, and customize treatment for disease detection, which is expected to contribute to market growth.
Although conventional tissue biopsies involve invasive methods for detecting tumor cells, liquid biopsies involve using peripheral blood, which is easily accessible, allowing for more common use, primarily in patients who cannot undergo surgery. As a result, it takes less time for treatment based on tumor detection, enhancing staff & resources efficiency, and is used to screen other diseases. It can also help avoid potential complications associated with conventional biopsies, removing the risk of tumor spread, severe bleeding, and injury to surrounding tissue. Thus, liquid biopsy is widely accepted and expected to drive market growth soon.
For various applications such as non-small-cell lung cancer, breast, prostate, colorectal, and ovarian cancer, liquid biopsy is used for diagnostic and screening purposes, making it an essential tool. After various studies and speculations, it has been derived that the liquid biopsy technique could provide an improved diagnosis outcome. Data shows that screening techniques should be used on high-risk patients with an ancestral cancer history. Currently, community practices and academic centers use liquid biopsy as their complementary technique compared to standard tissue biopsies, which is expected to drive the market globally.
Biopsy procedures have long been considered the gold standard for cancer diagnosis, but they are not without their challenges. One of the main challenges is the lower sensitivity of certain biopsy procedures, which can lead to false-negative results or inconclusive diagnoses. This can delay proper treatment and lead to poorer outcomes for patients.
The lower sensitivity of certain biopsy procedures is one of the restraints for the liquid biopsy market. While liquid biopsy offers many advantages over traditional tissue biopsy, such as being less invasive, faster, and allowing for real-time monitoring, it may not be suitable for all types of cancers and all stages of cancer. Some cancers, such as brain cancer, may not shed enough DNA or cells into the bloodstream for liquid biopsy to detect accurately. Moreover, a liquid biopsy may not be able to identify the precise location of cancer, which may be necessary for surgical planning.
Additionally, some liquid biopsy techniques, such as the analysis of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), may have a lower sensitivity compared to tissue biopsy, particularly in early-stage cancers or small tumors. False negatives or false positives may also occur due to technical issues, such as the degradation of the DNA during the collection or analysis process, or due to the presence of non-cancerous DNA mutations. These limitations may impact the accuracy of liquid biopsy results, and some patients may still require tissue biopsy to confirm a cancer diagnosis or treatment plan.
Therefore, the lower sensitivity of certain biopsy procedures remains a significant challenge for the liquid biopsy market. However, ongoing research and development in liquid biopsy technology and the identification of new biomarkers may address some of these limitations and improve the accuracy and reliability of liquid biopsy for cancer diagnosis and treatment monitoring. Furthermore, the growing demand for personalized and precision medicine may drive the development of liquid biopsy techniques that can detect a wider range of biomarkers and offer more comprehensive diagnostic and treatment options for cancer patients.
To address this challenge, researchers are exploring the use of liquid biopsy as a complementary tool to traditional biopsy procedures. Liquid biopsy involves the analysis of biomarkers such as circulating tumor DNA, circulating tumor cells, and exosomes in a patient's blood or other bodily fluids. These biomarkers can provide valuable information about the presence and characteristics of cancer, even at early stages or in hard-to-reach locations.
The liquid biopsy market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation in the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment. One key opportunity is the potential to improve the accuracy and efficiency of cancer diagnosis, particularly in cases where traditional biopsy procedures may not be feasible or effective.
Liquid biopsy allows for the detection of circulating tumor DNA, circulating tumor cells, exosomes, and other biomarkers in a patient's blood, urine, or other bodily fluids. This enables real-time monitoring of the tumor's genetic profile and disease progression, as well as the ability to detect cancer at an earlier stage than traditional biopsy methods.
Another opportunity is the potential for liquid biopsy to be used in personalized medicine approaches. By analyzing a patient's genetic profile through liquid biopsy, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to the individual's specific needs and characteristics. This can lead to more effective and targeted therapies, resulting in improved outcomes for patients.
Moreover, liquid biopsy also presents opportunities for cost-effective cancer management. The non-invasive nature of liquid biopsy procedures eliminates the need for surgery or other invasive procedures, which can be expensive and time-consuming. In addition, the ability to detect cancer at an earlier stage through liquid biopsy can lead to earlier interventions, which can be less costly and more effective than treatments at later stages of the disease.
Thus, the liquid biopsy market presents numerous opportunities for growth and innovation in the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment. The continued development of new technologies and expanded applications of liquid biopsy in clinical settings is expected to drive market growth in the coming years.
By technology, the multi-gene-parallel analysis (NGS) segment held a dominant presence in the market in 2024. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies are used to detect tumors from bodily fluids. Body fluids such as plasma and blood are used as a substrate for NGS. The NGS process includes cell-free nucleic acid purification and sample preparation from a single tube of blood. NGS leads to faster and more accurate diagnosis, enhancing precision.
By technology, the single gene analysis (PCR microarrays) segment is predicted to witness significant growth in the market over the forecast period. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is another widely used technique for detecting cancers. The demand for PCR technology is increasing due to technological advancements, leading to higher precision and sensitivity. The advent of digital PCR techniques augments the market growth. These assays are simple, precise, and rapid for tracking potential responses.
By biomarker, the circulating nucleic acids segment led the global market in 2024. Circulating nucleic acids involves DNA or RNA molecules that are passed or actively released from tumor cells. These nucleic acids cannot be detected through conventional biopsy tests. Hence, they are detected using high-precision liquid biopsies. Circulating tumor RNA is an emerging biomarker providing unique information that is not found in circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. The growing demand for personalized treatment potentiates the need for assessing circulating nucleic acids through liquid biopsy, augmenting the segment’s growth.
By biomarker, the exosomes/microvesicles segment is anticipated to grow with the highest CAGR in the market during the studied years. The growing research and development activities signify the role of exosomes and microvesicles as potential biomarkers in cancer. They can monitor cancer progression and treatment efficacy as they contain cancer-related proteins, RNA, and DNA fragments. Exosomes are involved in cancer progression and metastasis between cells.
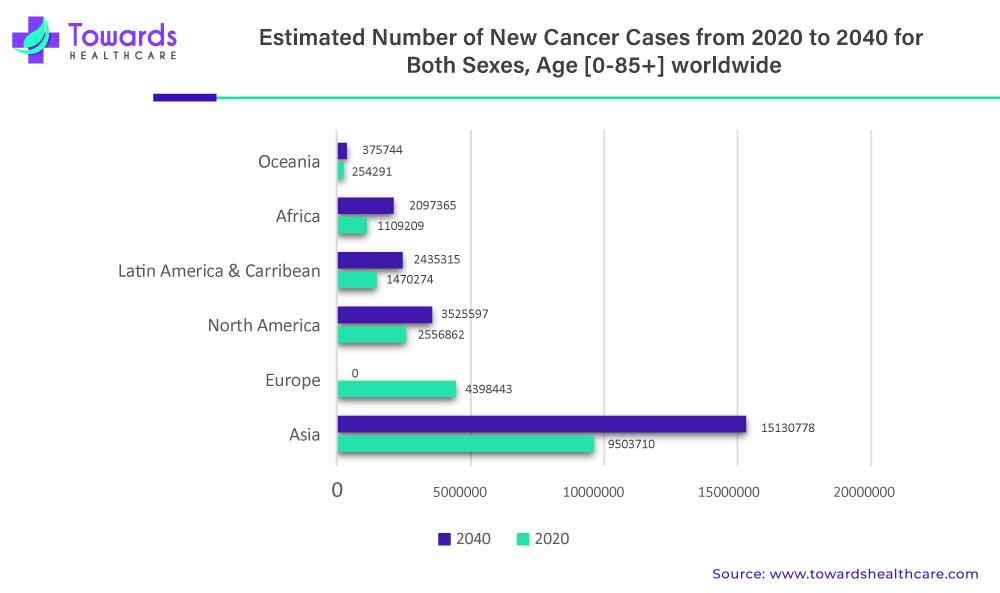
By application, the cancer segment held the largest share of the market in 2024. The increasing incidences and prevalence of cancer and its complexity boost the segment’s growth. The WHO estimated 20 million cases in 2022 and projects over 35 million new cancer cases in 2050. The growing research and development activities identify numerous novel and emerging biomarkers involved in cancer progression. These biomarkers are difficult to detect through conventional biopsies. Liquid biopsies can help detect minute quantities of such biomarkers.
By application, the reproductive health segment is projected to expand rapidly in the market in the coming years. Liquid biopsies have widespread applications in prenatal testing, preimplantation genetic testing, and monitoring pregnancy-related conditions. The rising incidences of reproductive disorders and a major focus on fetus health potentiate the use of liquid biopsies. Liquid biopsy can detect fetal conditions and pregnancy-related disorders, eliminating the need for invasive procedures.
By clinical application, the therapy selection segment registered its dominance over the global market in 2024. Therapy selection refers to the process of choosing the most appropriate treatment option for a patient based on their medical condition. Liquid biopsies help in the early detection of cancer, enabling healthcare professionals to provide more advanced and personalized treatment. Thus, liquid biopsies aid in clinical decision-making for healthcare professionals, improving overall treatment outcomes.
By clinical application, the early screening segment is projected to expand rapidly in the market in the coming years. Several government organizations release guidelines and initiatives to encourage screening and the early detection of cancer and other disorders. Favorable government policies fuel the segment’s growth. The need for effective treatment strategies and the growing demand for personalized treatment also contributes to the segment’s growth.
By product, the instruments segment held a major share of the market in 2024. Instruments are essential parts of liquid biopsy experiments, and they include centrifuges, flow cytometers, etc. Technological advancements and increasing investments drive the installation of liquid biopsy instruments in research institutions and diagnostic laboratories. Favorable regulatory frameworks also positively impact the segment’s growth, leading to new product launches.
By product, the kits and reagents segment is estimated to show the fastest growth in the market over the forecast period. Kits and reagents, including buffer solutions and extracellular vesicles, are necessary for liquid biopsy experiments. They are preferable due to their affordability and low infrastructural requirements. Many companies offer kits and reagents as they need to be refilled to conduct numerous experiments.
By sample type, the blood sample segment dominated the global market in 2024. Blood samples are usually collected for liquid biopsy diagnostic tests as they are easy to collect. Blood contains several biomarkers released from tumor cells, which makes it easier for pathologists to detect them. Blood can also be segregated into different components, such as plasma and other components, for more precise detection. Thus, isolating blood for liquid biopsy tests helps physicians to identify cancer early, plan treatment, and monitor their condition.
By end-use, the hospitals and laboratories segment accounted for a considerable share of the market in 2024. The segmental growth is attributed to suitable infrastructure and the presence of trained professionals. Patients mainly trust hospitals and laboratories for diagnostic tests due to high precision and the availability of specialized equipment. Suitable capital investments and the increasing number of hospital admissions due to increasing cancer cases also propel the segment’s growth.
By end-use, the specialty clinics segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of the market during the forecast period. The presence of skilled professionals and the availability of specialized equipment are likely to contribute to the segment’s growth. Advancements in technology and the growing demand for affordable and advanced treatment services have increased the demand for specialty clinics.
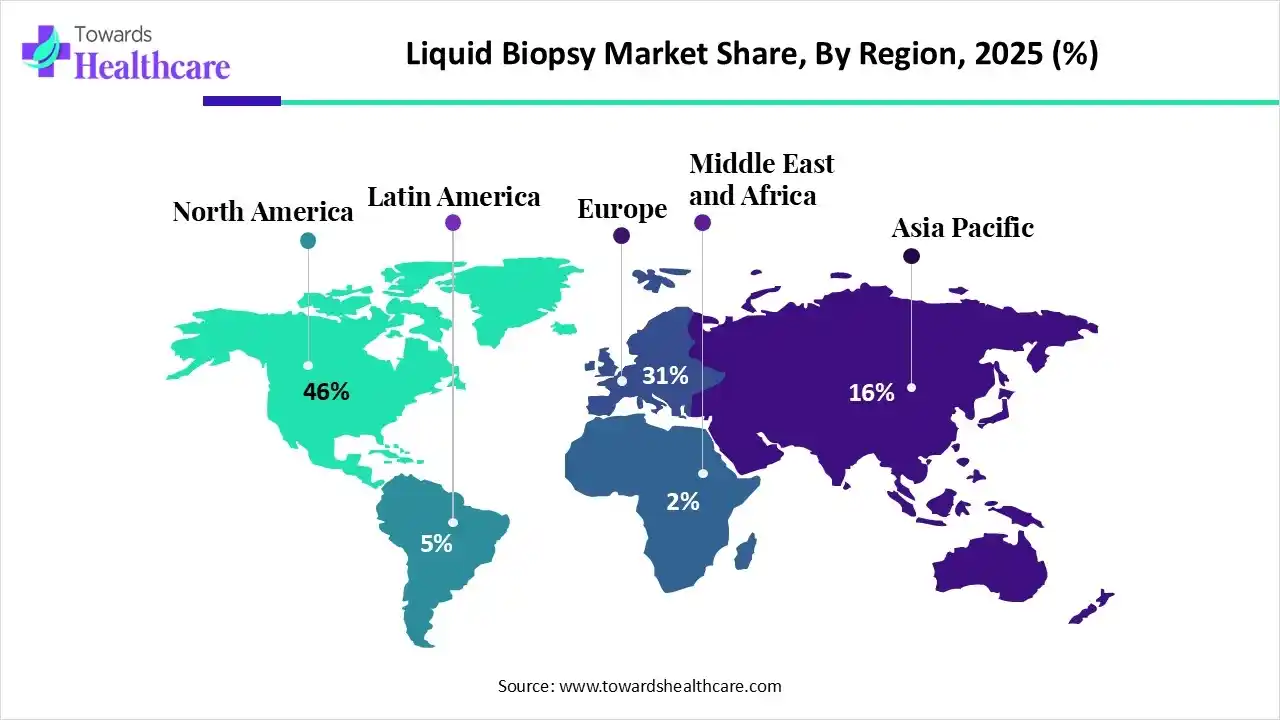
North America dominated the global market in 2025. The rising incidences and prevalence of cancer and technological advancements drive the market. American Cancer Society estimated that more than 2 million new cancer cases will be reported in the U.S. in 2025. Key players such as Bio-Rad Laboratories, Guardant Health, and Thermo Fisher Scientific hold the major share of the North American market. Favorable government support and regulatory frameworks potentiate the market. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approves liquid biopsy tests for detecting and monitoring cancer. The increasing investments by several government and private organizations boost the market. The New Brunswick Department of Health announced a total of $175,000 in funding toward liquid biopsy testing.
Canada Market Trends
The demand for liquid biopsy testing is increasing in Canada, with the growing cancer patients. The Canadian Cancer Society estimates that 2 in 5 Canadians will be diagnosed with cancer in their lifetime. In July 2024, William Osler Health System became the first Canadian hospital to offer in-house liquid biopsy testing for cancer care.
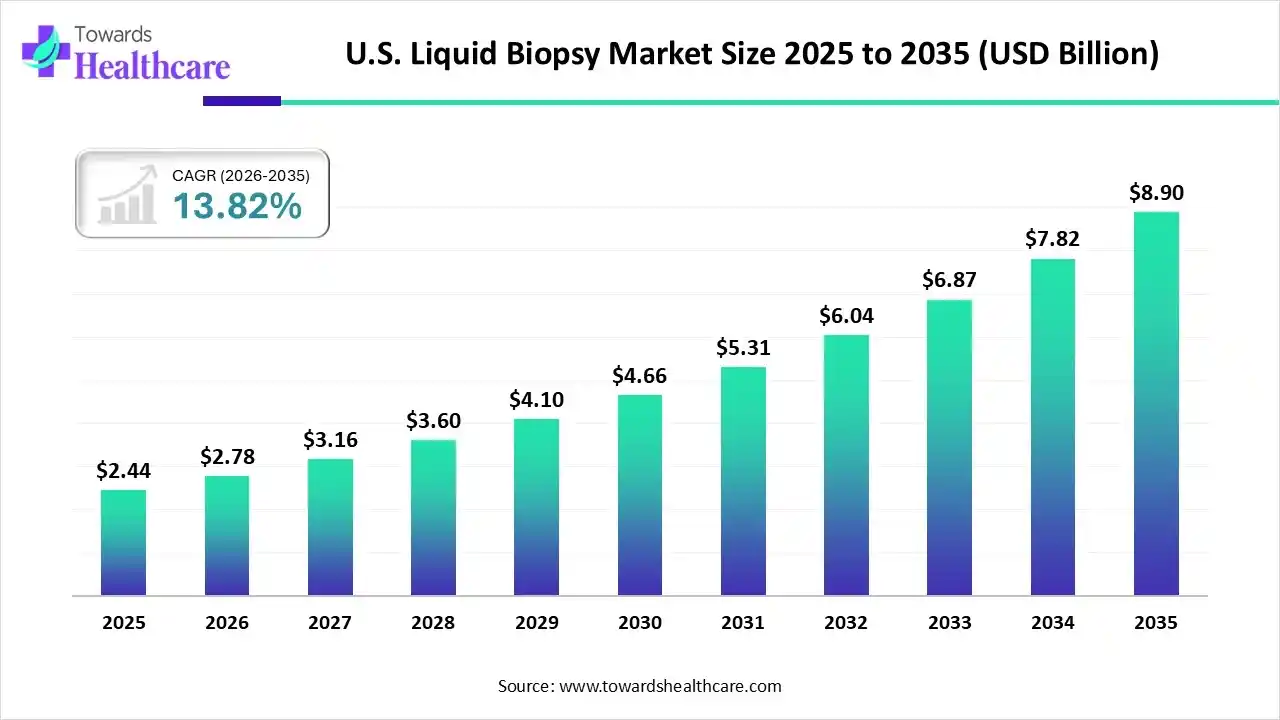
U.S. Liquid Biopsy Market Growth
The U.S. liquid biopsy market size stood at US$ 2.44 billion in 2025, grew to US$ 2.78 billion in 2026, and is forecast to reach US$ 8.90 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 13.82% from 2026 to 2035.
Asia-Pacific is projected to host the fastest-growing market in the coming years. The growing research and development activities and burgeoning healthcare sector drive the market. Countries like China, Japan, and India are at the forefront of developing and using liquid biopsy tests to detect cancer and other related disorders. The rapid advancements in genomics and proteomics also contribute to the market. The increasing investments, collaborations, and mergers & acquisitions fuel the Asia-Pacific market. The growing awareness about early detection and screening of cancer increases the demand for liquid biopsy testing. Several government agencies and research institutions organize conferences, workshops, and symposiums to increase awareness and train people regarding liquid biopsy testing.
Japan Market Trends
As of 2024, two liquid biopsy tests are approved in Japan. One is FoundationOne Liquid by Foundation Medicine, and the other is Guardant360 by Guardant Health, Inc. According to the SCRUM-Japan GOZILA Project by the National Cancer Center, 24% of participants received personalized targeted therapy based on their liquid biopsy results.
Europe is estimated to be the fastest-growing during the forecast period. People in that area were more aware of the two conditions cancer and illnesses that may be screened for during pregnancy, which is why the share was so high. In addition, a lot of competitors in the industry are focusing on obtaining capital in order to develop a liquid biopsy platform utilizing modern technology. Regional development will be further reinforced throughout the predicted period by the European government's expanding strategic actions to increase cancer screening and other pathology testing.
Researchers and clinical trials are being actively funded by the German government to enhance liquid biopsy cancer diagnosis. For example, the SURVIVE trial, which examined the possible survival advantage of liquid biopsy-guided follow-up care in patients with intermediate and high-risk early breast cancer, was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
Latin America is considered to be a significantly growing area, due to the burgeoning healthcare sector and increasing cancer cases in the region. Latin America is emerging as a favorable location for advanced diagnosis and treatment with the rapidly expanding medical tourism sector. Government organizations support the use and development of liquid biopsy tests through initiatives and funding. Numerous foreign companies have established their manufacturing infrastructure in the region to address niche markets and serve a larger patient population.
Brazil Market Trends
In 2023, approximately 704,000 new cancer cases were reported in Brazil. The Brazilian government has established the Statute for Persons with Cancer that guarantees the right to early diagnosis, free, equitable, universal treatment, and clear information regarding the disease. Multinational companies, such as PacBio, Illumina, and Eppendorf, offer their proprietary products in Brazil.
Dr. Dimitris Vavoulis, a co-ed researcher at Oxford’s Wellcome Center for Human Genetics, commented on the development of liquid biopsy tests for detecting multiple cancers that many cancers, such as pancreatic and ovarian, are difficult to detect, leading to less effective treatment. The current screening methods are limited to a few cancers and are often invasive. He said that their method is still early in development, but he envisioned that it could give patients and doctors a faster and more convenient tool to stay ahead of the disease.
Explore and Learn how top players are redefining the Liquid Biopsy Market: https://www.towardshealthcare.com/companies/liquid-biopsy-companies
By Sample Type
By Biomarker
By Technology
By Application
By Clinical Application
By Product
By End-Use
By Region
January 2026
December 2025
December 2025
October 2025