February 2026

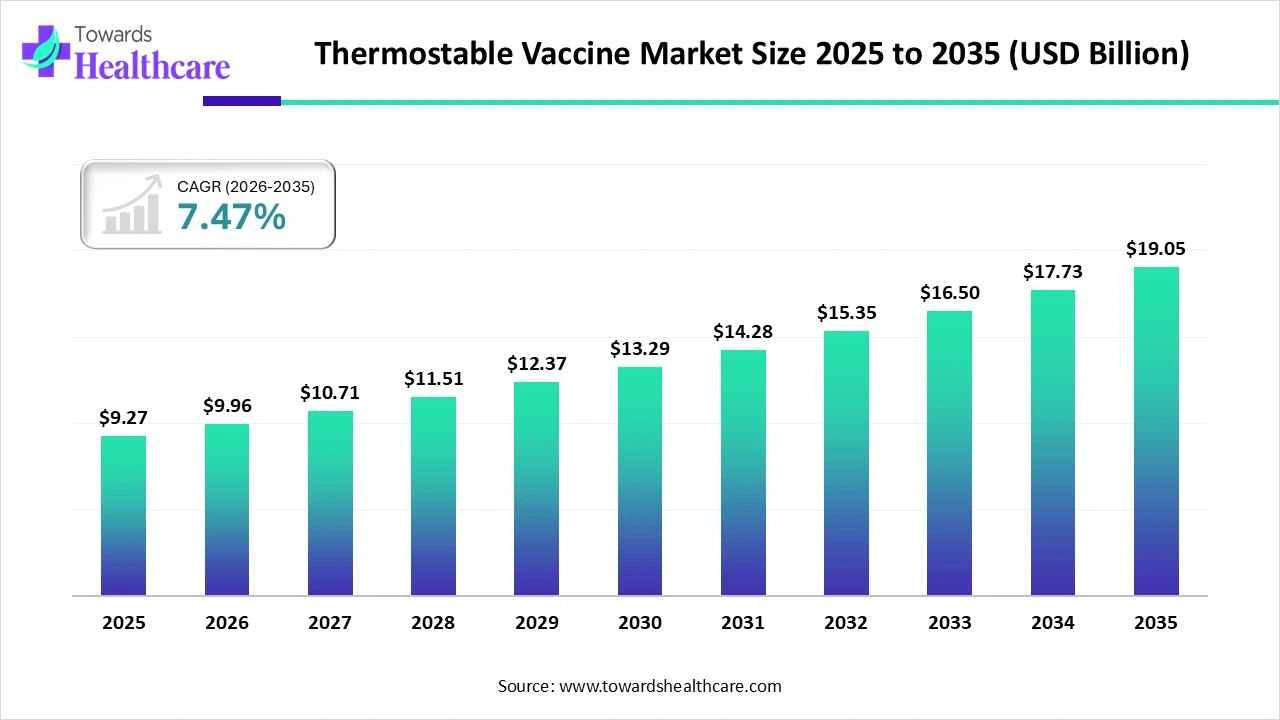
The thermostable vaccine market size stood at US$ 9.27 billion in 2025, grew to US$ 9.96 billion in 2026, and is forecast to reach US$ 19.05 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 7.47% from 2026 to 2035.
The World Health Organization estimates that immunization prevents 3.5-5 million deaths annually from diseases such as diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, influenza, and measles, but cold storage issues damage vaccines. Thermostable vaccines can be stored at room temperature for extended periods, eliminating the need for cold chain logistics. This reduces storage and transportation costs, making mass immunization projects more affordable.
A thermostable vaccine is a type of vaccine that can maintain its effectiveness even when exposed to fluctuations in temperature. Unlike traditional vaccines that require strict refrigeration to preserve their potency, thermostable vaccines can remain viable even if not cold. This is particularly advantageous in regions with limited access to reliable refrigeration facilities, such as remote areas or during emergencies.
The importance of thermostable vaccines lies in their ability to overcome logistical challenges associated with vaccine storage and transportation. Maintaining a cold chain for vaccine distribution can be difficult in many parts of the world, especially in developing countries or areas with limited infrastructure. Thermostable vaccines solve this problem by eliminating the need for continuous refrigeration, thus expanding access to immunization programs and ensuring that more people, especially those in underserved communities, can receive vital vaccinations.
Tuberculosis (TB) spreads when sick people breathe the bacteria into the air. In 2021, TB caused 1.6 million deaths and affected 10.6 million people. The World Health Organization says almost two billion people worldwide have TB bacteria inside them. Thermostable vaccines can help manage TB.
Recent Update
These vaccines act as superheroes because they enable vaccination efforts to reach even the most remote or resource-constrained areas, where traditional vaccines might not be feasible due to refrigeration requirements. By extending the reach of vaccination programs, thermostable vaccines play a crucial role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases and reducing illness and death in vulnerable populations.
Scientists are developing thermostable vaccine formulations for various diseases, including measles, polio, influenza, and COVID-19. Their ongoing research aims to optimize vaccine stability under varying environmental conditions, ensuring vaccines remain effective and accessible across different regions and circumstances.
FDA-approved vaccines that are completely thermostable, meaning they don't require refrigeration. However, several vaccines have increased thermal stability compared to traditional vaccines, which means they can withstand higher temperatures longer without losing potency.
No FDA-approved vaccines that are completely thermostable, meaning they don't require refrigeration. However, several vaccines have improved thermal stability compared to traditional vaccines, which means they can withstand higher temperatures for extended periods without losing potency.
Thermostable vaccines represent a significant advancement in vaccine technology, offering a practical solution to the challenges of cold chain logistics and helping to improve global vaccination coverage. By ensuring that vaccines remain potent even in challenging conditions, thermostable vaccines contribute to the global effort to protect populations from preventable diseases and promote public health worldwide.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on thermostable vaccines. It showed how hard it can be to distribute vaccines, especially in places without refrigeration. Thermostable vaccines help because they don't need cold temperatures to stay good, making them easier to ship worldwide, especially to places with fewer resources.
For instance,
Additionally, when COVID-19 hit, everyone needed vaccines fast. That made it clear how important it is for vaccines to stay effective even in different temperatures. So, scientists focused on making thermostable COVID-19 vaccines that could be shipped easily and used in places without good refrigeration.
Furthermore, the pandemic showed that not everyone has equal access to vaccines. Poorer countries often struggle to get vaccines because they can't keep them cold enough. Thermostable vaccines can help fix this by offering easier access to vaccines for everyone, no matter where they live.
Because of COVID-19, there's been more interest in different kinds of vaccines. Thermostable vaccines are becoming popular because they're more flexible and can be used in other situations, which was important during the pandemic. COVID-19 taught us that we need to be ready for future health emergencies. Investing in thermostable vaccines can help us prepare better for the next pandemic or crisis, ensuring vaccines stay effective even when things get tough.
The COVID-19 pandemic showed us how critical thermostable vaccines are for solving global health problems, ensuring everyone can access vaccines, and being ready for future emergencies. That's why we expect more people to use thermostable vaccines in the future, leading to more innovation and growth in this area.
| Key Elements | Scope |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 9.96 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 19.05 Billion |
| CAGR (2026 - 2035) | 7.47% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Market Segmentation | By Vaccine Type, By Application, By Development Stage, By Geography |
| Top Key Players | Serum Institute of India, Sanofi, GSK, Hilleman Laboratories, Soligenix |
The improved accessibility of thermostable vaccines is a significant advancement in immunization. Traditional vaccines often require strict refrigeration throughout storage and transportation to maintain effectiveness. Thermostable vaccines can remain stable and retain their potency even when exposed to fluctuating temperatures, eliminating the need for continuous refrigeration.
This characteristic is particularly beneficial in regions with limited access to reliable refrigeration infrastructure, such as remote or rural areas and developing countries. Maintaining a cold chain for vaccine storage and transportation in these areas can be challenging due to factors like inadequate refrigeration facilities, unreliable electricity supply, and long distances between healthcare facilities.
By removing the strict requirement for cold storage, thermostable vaccines overcome logistical barriers and expand access to immunization programs in these underserved regions. Health workers can transport and distribute these vaccines more easily, reaching communities that were previously difficult to access. This means that people living in remote or resource-limited areas can receive vital vaccinations without the constraints imposed by cold chain requirements.
The increased accessibility of thermostable vaccines has several important implications for public health. It enables more individuals, especially those in vulnerable populations, to receive timely vaccinations, which is essential for preventing infectious diseases and reducing morbidity and mortality rates. Additionally, expanded vaccine coverage contributes to herd immunity, protecting entire communities from outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases.
Furthermore, the improved accessibility of thermostable vaccines supports global health equity initiatives by ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status, have access to life-saving vaccines. This aligns with the goals of organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF to achieve universal immunization coverage and promote health for all.
For instance,
Moreover, the improved accessibility of thermostable vaccines represents a significant step forward in public health efforts to increase vaccine coverage and reduce health disparities worldwide. By overcoming the challenges associated with cold chain logistics, thermostable vaccines empower healthcare providers to reach underserved populations, ultimately contributing to healthier communities and improved global health outcomes.
Ensuring thermostable vaccines' safety, effectiveness, and stability is crucial to protect people from diseases. Before these vaccines can be used, they must undergo a thorough approval process by regulatory agencies. This process can be lengthy and expensive for vaccine developers.
Regulatory agencies have strict standards that vaccines must meet to ensure they are safe for people to use. These standards include testing the vaccine in clinical trials to ensure it works well and doesn't cause harmful side effects. Additionally, the stability of the vaccine needs to be demonstrated, meaning it remains effective even when exposed to different temperatures over time.
The approval process involves submitting extensive data and evidence from laboratory studies and clinical trials to regulatory authorities. This data helps regulators evaluate the vaccine's safety, efficacy, and stability. The review process can take several months to years, depending on the complexity of the vaccine and the amount of data provided.
The lengthy approval process can delay the availability of thermostable vaccines in the market. This delay means that people may have to wait longer to access vaccines that could protect them from diseases. Furthermore, the high costs of conducting clinical trials and preparing regulatory submissions can be a barrier for smaller vaccine developers or organizations with limited resources.
Despite these challenges, obtaining regulatory approval is essential to ensure that thermostable vaccines meet the necessary standards for safety and effectiveness. It's a crucial step in protecting public health and ensuring that vaccines provide the expected benefits without causing harm.
Moreover, while the approval process for thermostable vaccines may be challenging, it's necessary to ensure the quality and reliability of these vaccines before they are made available to the public. Collaboration between vaccine developers, regulatory agencies, and other stakeholders is essential to streamline the approval process and facilitate timely access to safe and effective thermostable vaccines.
North America holds a significant share of the global thermostable vaccine market, driven by a robust healthcare infrastructure, intense research and development capabilities, and high vaccine development and production investment. The region is governed by stringent regulatory standards set by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Health Canada. Compliance with these regulations is essential for gaining approval and market access for thermostable vaccines. North America is a hub for technological innovation in vaccine development, with leading pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and biotechnology firms actively advancing thermostable vaccine technologies. The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of pandemic preparedness and vaccine development in North America. The region has witnessed accelerated efforts to advance thermostable vaccine candidates for COVID-19 and other infectious diseases, driving investment in vaccine research, manufacturing capacity, and distribution infrastructure.
The Asia-Pacific region presents a diverse geographical landscape for the thermostable vaccine market, influenced by population density, economic development, healthcare infrastructure, and climate variations. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea have well-established healthcare systems and significant vaccine research and development investments. These countries also have large populations, contributing to a substantial market size for thermostable vaccines. This region includes Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, and the Philippines. Southeast Asia has a mix of developing and emerging economies with varying degrees of healthcare infrastructure. Some countries face challenges related to vaccine distribution in remote and rural areas due to geographical barriers and inadequate cold chain infrastructure. Thermostable vaccines could address these challenges and improve accessibility in such regions.
Europe is considered to be a significantly growing area, owing to a robust healthcare infrastructure and growing research and development activities. Favorable government policies and increasing investments drive the market. The rising collaborations and mergers & acquisitions govern market growth. Several government and private organizations conduct seminars, workshops, and conferences to create awareness about thermostable vaccines. The rising prevalence of infectious and other disorders necessitates researchers to develop novel thermostable vaccines.
UK Market Trends
In April 2025, Stablepharma, a UK-based company, announced the initiation of the world’s first clinical trial to assess Stablepharma tetanus-diphtheria vaccine (SPVX02), a thermostable vaccine, at the University Hospital Southampton. The trial is supported by a UK-backed program.
The thermostable vaccine market has been an area of growing interest and innovation, particularly in addressing vaccine storage, distribution, and administration challenges, especially in regions with limited access to reliable cold chain infrastructure. Numerous other biotech companies and academic institutions worldwide are researching and developing thermostable vaccine technologies. Some focus on novel approaches such as virus-like particles (VLPs), stabilized proteins, and alternative delivery methods to improve vaccine stability.
By Vaccine Type
By Application
By Development Stage
By Geography
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026