November 2025

The global age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market size touched US$ 10.57 billion in 2024, with expectations of climbing to US$ 11.69 billion in 2025 and hitting US$ 29.04 billion by 2034, driven by a CAGR of 10.66% over the forecast period.
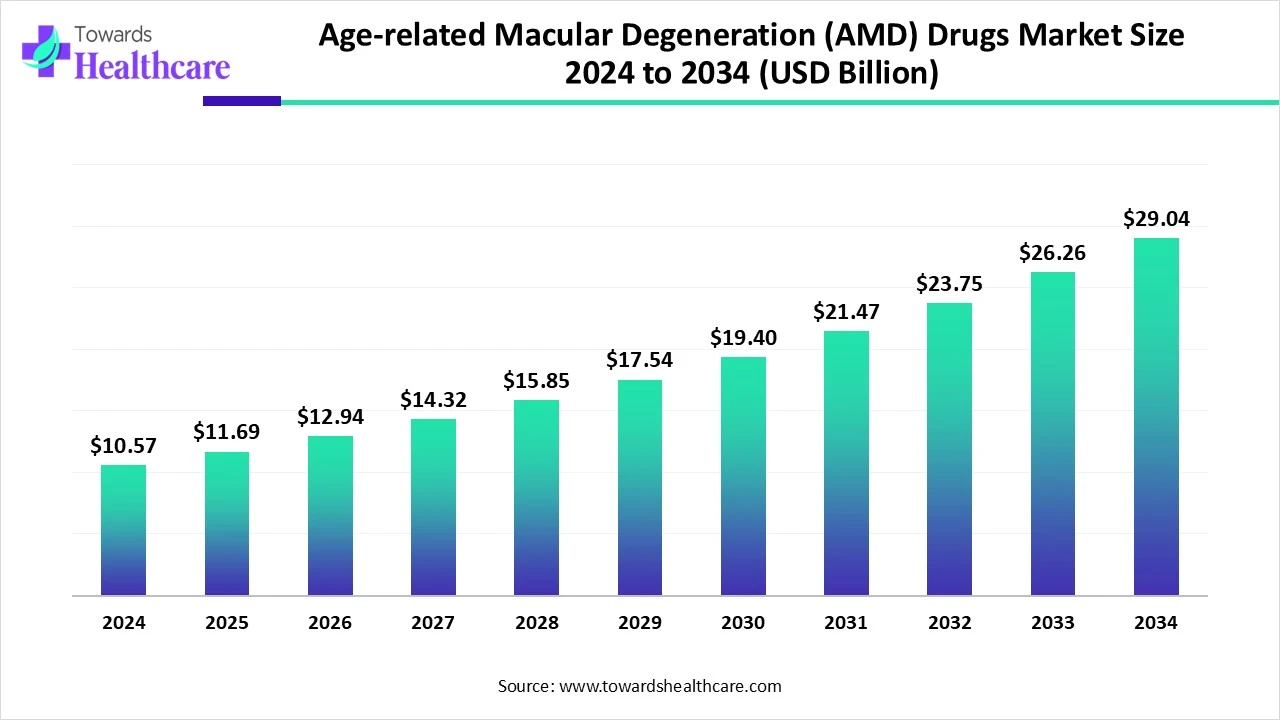
The age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the rising prevalence of AMD among the rapidly aging global population. AMD is a leading cause of vision impairment in older adults, creating strong demand for effective treatments, particularly for wet AMD. Advances in therapies such as anti-VEGF injections, long-acting biologics, and gene therapies are transforming treatment approaches by improving patient outcomes and reducing treatment frequency. Growing awareness, early diagnosis through advanced imaging technologies, and increasing healthcare expenditure are further supporting market expansion. Additionally, strong R&D investments, strategic partnerships, and new product approvals are fueling innovation.
| Table | Scope |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 11.69 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 29.04 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 - 2034) | 10.66% |
| Leading Region | North America 41% |
| Market Segmentation | By Disease Type, By Drug Class, By Route of Administration, By End User, By Region |
| Top Key Players | Roche/Genentech, Regeneron, Novartis, Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Iveric Bio / Astellas (Izervay), Bayer, Allergan/AbbVie, Adverum Biotechnologies, Gyroscope Therapeutics, Kodiak Sciences, Ocular Therapeutix, Opthea, PanOptica, Graybug Vision, Regenxbio, Bausch + Lomb, Clearside Biomedical, Biogen, MeiraGTx, Lineage Cell Therapeutics |
The age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market focuses on pharmaceuticals developed to treat AMD, a leading cause of vision loss in people aged 50 and older. AMD occurs due to damage in the macula, the central part of the retina, which affects sharp and central vision. Current drug therapies primarily target the wet (neovascular) form of AMD, using anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) inhibitors to slow disease progression and improve vision outcomes. Increasing prevalence of AMD due to aging populations, ongoing R&D in gene therapy and regenerative medicine, and growing awareness of early treatment are driving market expansion.
An age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drug refers to a type of medication developed to treat or manage vision loss caused by AMD, an eye disease that damages the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. These drugs do not cure AMD but help slow its progression, preserve vision, and, in some cases, improve eyesight. The most common AMD drugs are anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) therapies, such as ranibizumab (Lucentis), aflibercept (Eylea), and brolucizumab (Beovu), which work by blocking abnormal blood vessel growth and leakage in the retina. Other emerging drugs include complement inhibitors, gene therapies, and regenerative treatments aimed at addressing both wet and dry forms of AMD.
Collaborations between biotech firms, pharma companies, and research institutions accelerate the development and commercialization of next-generation AMD treatments, expanding global market opportunities.
For instance,
Government initiatives and funding are emerging as key trends and growth drivers in the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market, as public health systems increasingly recognize the disease’s rising burden among aging populations. National health agencies and governments are allocating more funds for ophthalmology research, accelerating clinical trials for novel therapies, including anti-VEGF biologics, gene therapies, and regenerative approaches. U.S. agencies like the National Eye Institute (NEI) provide significant grants for AMD drug development and early detection technologies. Similarly, European and Asian governments are expanding reimbursement policies to improve patient access to advanced AMD treatments. These initiatives not only encourage pharmaceutical innovation but also reduce patient cost barriers, thereby boosting adoption rates.
For instance,
For instance,
Governments and private insurers are increasing healthcare spending, improving access to advanced ophthalmic treatments. Reimbursement policies in developed markets (e.g., the U.S., Europe) are making expensive biologics more affordable for patients.
AI integration is transforming the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market by enhancing diagnosis, treatment, and drug development. AI-powered retinal imaging combined with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) enables early and highly accurate detection of AMD, allowing timely treatment and expanding the pool of patients eligible for therapies. By analyzing genetic and clinical data, AI helps create personalized treatment plans, optimizing the frequency and dosage of anti-VEGF injections and improving patient outcomes. In drug development, AI accelerates discovery by identifying therapeutic targets, predicting efficacy, and streamlining clinical trial design, which reduces costs and timelines. Additionally, AI-enabled monitoring tools, such as home-based retinal scanners and apps, improve patient compliance and reduce hospital visits. Collectively, these advancements drive innovation, adoption, and accessibility of AMD drugs.
Rising Prevalence of Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
With the global population aging rapidly, the incidence of AMD, particularly wet AMD, is increasing. Since AMD is most common in individuals over 60, the expanding elderly demographic is a primary demand driver for effective therapies. For instance, in January 2025, according to the data published by the American Macular Degeneration Foundation, approximately 20 million Americans over 40 have been diagnosed with macular degeneration of some kind. A late-stage, vision-threatening form of age-related macular degeneration affects 1.49 million Americans. This represents roughly 22% of the 7 million Americans who are blind or have vision loss.
Limited Access to Healthcare and Treatment Burden & Compliance Issues
The key players operating in the market are facing issues due to limited access to healthcare and regulatory compliance issues, which are estimated to limit the growth of the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market over the forecast period. In developing regions, the lack of advanced ophthalmic facilities, skilled specialists, and diagnostic technologies hinders the timely detection and treatment of AMD. Current therapies often require frequent intravitreal injections, which are invasive, uncomfortable, and discourage patient adherence.
Advancements in Treatment Options & Increased Awareness, and Early Diagnosis
The introduction of anti-VEGF therapies (e.g., ranibizumab, aflibercept, brolucizumab) has revolutionized treatment, offering improved vision outcomes. New drug delivery methods, such as sustained-release implants and gene therapies, are enhancing patient compliance and extending treatment duration. Furthermore, improvements in ophthalmic imaging technologies (like OCT—Optical Coherence Tomography) and awareness campaigns help detect AMD earlier, increasing the number of patients eligible for treatment and reducing late-stage blindness.
The wet AMD segment dominates the Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Drugs market due to its higher risk of causing severe and rapid vision loss compared to the dry form. Although less common, wet AMD accounts for the majority of blindness cases among AMD patients, driving demand for effective treatment. The availability of advanced therapies, particularly anti-VEGF drugs like Eylea, Lucentis, and Vabysmo, has significantly improved disease management and patient outcomes. Continuous R&D, including gene therapies and long-acting formulations, further strengthens this segment. Additionally, strong reimbursement support and healthcare prioritization ensure wider access, making wet AMD the leading treatment area.
The dry AMD segment (geographic atrophy) is estimated to emerge as the fastest-growing segment in the Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Drugs market due to the recent introduction of approved therapies and rising research investments. Historically, treatment options for GA were limited to supportive care, but the approval of novel drugs such as Syfovre (pegcetacoplan) and Izervay (avacincaptad pegol) has transformed disease management, offering patients targeted therapies for the first time. Increasing clinical trials exploring complement pathway inhibitors and gene therapies are further fueling growth. The rising prevalence of GA among aging populations, combined with improved diagnostic capabilities, is accelerating demand, positioning dry AMD as the fastest-growing market segment.
The anti-VEGF agents segment dominates the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market because these therapies have become the gold standard for treating wet AMD, the leading cause of severe vision loss. Drugs like Eylea, Lucentis, and Vabysmo have demonstrated high efficacy in reducing abnormal blood vessel growth and preserving vision, making them widely adopted. Their proven safety profiles, frequent regulatory approvals, and inclusion in reimbursement programs have boosted accessibility across major healthcare systems. Additionally, pharmaceutical companies are investing in extended-dosing formulations and biosimilars to improve patient compliance, further reinforcing the dominance of anti-VEGF agents in the market.
The complement inhibitors segment is anticipated to be the fastest-growing segment in the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market, driven by the recent approval of breakthrough therapies for geographic atrophy (GA), an advanced form of dry AMD with limited treatment options until recently. Drugs like Syfovre (pegcetacoplan) and Izervay (avacincaptad pegol), targeting the complement pathway, have created significant momentum by offering patients the first effective therapies to slow disease progression. Growing R&D investments in complement biology, expanding clinical trials, and strong demand from the large GA patient population are fueling rapid uptake. With rising global approvals and supportive reimbursement frameworks, this segment is expected to expand quickly.
The intravitreal injections segment dominates the route of administration in the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market due to its proven effectiveness in delivering drugs directly into the eye, ensuring high concentrations at the site of action. This method is the standard for administering anti-VEGF therapies like Eylea, Lucentis, and Vabysmo, which have significantly improved patient outcomes in wet AMD. Despite being invasive, intravitreal injections provide rapid therapeutic benefits and better control of disease progression compared to systemic delivery. Continuous innovations, including sustained-release formulations and extended dosing intervals, further strengthen its dominance by enhancing patient compliance and reducing treatment burden.
The oral segment is estimated to be the fastest-growing route of administration in the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market, driven by the growing demand for less invasive and more convenient treatment alternatives to intravitreal injections. Oral therapies are gaining attention due to their potential to improve patient compliance, reduce treatment-related discomfort, and lower the risk of injection-associated complications such as infections. Advances in drug delivery technologies and ongoing clinical trials for oral formulations targeting complement pathways and oxidative stress are further accelerating interest. As promising candidates progress through regulatory pipelines, the oral route is expected to transform AMD management, supporting its rapid growth.
The hospital pharmacies segment holds the largest share in the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market because most advanced AMD treatments, particularly anti-VEGF injections and complement inhibitors, require administration in clinical or hospital settings under specialist supervision. Hospitals serve as primary centers for ophthalmology care, ensuring safe handling, storage, and administration of high-cost biologics and injectables. Additionally, hospital pharmacies benefit from direct collaborations with drug manufacturers and reimbursement systems, making them reliable access points for patients. The need for continuous monitoring, follow-up treatments, and specialized infrastructure further strengthens hospital pharmacies as the leading distribution channel for AMD therapies.
The online pharmacies segment is estimated to be the fastest-growing segment in the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market due to the increasing adoption of digital healthcare platforms and rising patient preference for convenient, home-based access to medicines. Online channels offer patients, especially the elderly with mobility challenges, easier ordering and doorstep delivery of prescribed drugs, reducing dependency on frequent hospital or retail visits. Expanding e-pharmacy regulations, secure digital prescription uploads, and discounts on high-cost AMD drugs further drive growth. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated digital adoption, and continued telemedicine integration is expected to strengthen the role of online pharmacies in AMD treatment access.
The specialty eye clinics segment is the dominant segment in the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market because these clinics provide focused expertise and advanced diagnostic tools required for precise AMD management. Patients with AMD often require regular monitoring, imaging, and intravitreal injections, which are best delivered in specialized ophthalmology centers equipped with skilled retinal specialists. Specialty clinics also serve as hubs for clinical trials, early adoption of novel therapies, and personalized treatment approaches. Their ability to offer comprehensive care—from diagnosis to advanced drug administration makes them the primary choice for AMD patients, establishing their dominance in this market segment.
The homecare segment is the fastest-growing end-user segment in the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market due to the increasing demand for patient convenience, reduced hospital visits, and personalized care. With advancements in oral therapies and sustained-release drug delivery systems under development, AMD patients are gradually shifting toward treatments that can be managed at home. Additionally, the aging population often faces mobility challenges, making home-based care a practical option. The rise of teleophthalmology, remote monitoring, and home delivery of prescribed drugs through online pharmacies further supports this trend, driving rapid growth of the home care segment in AMD management.
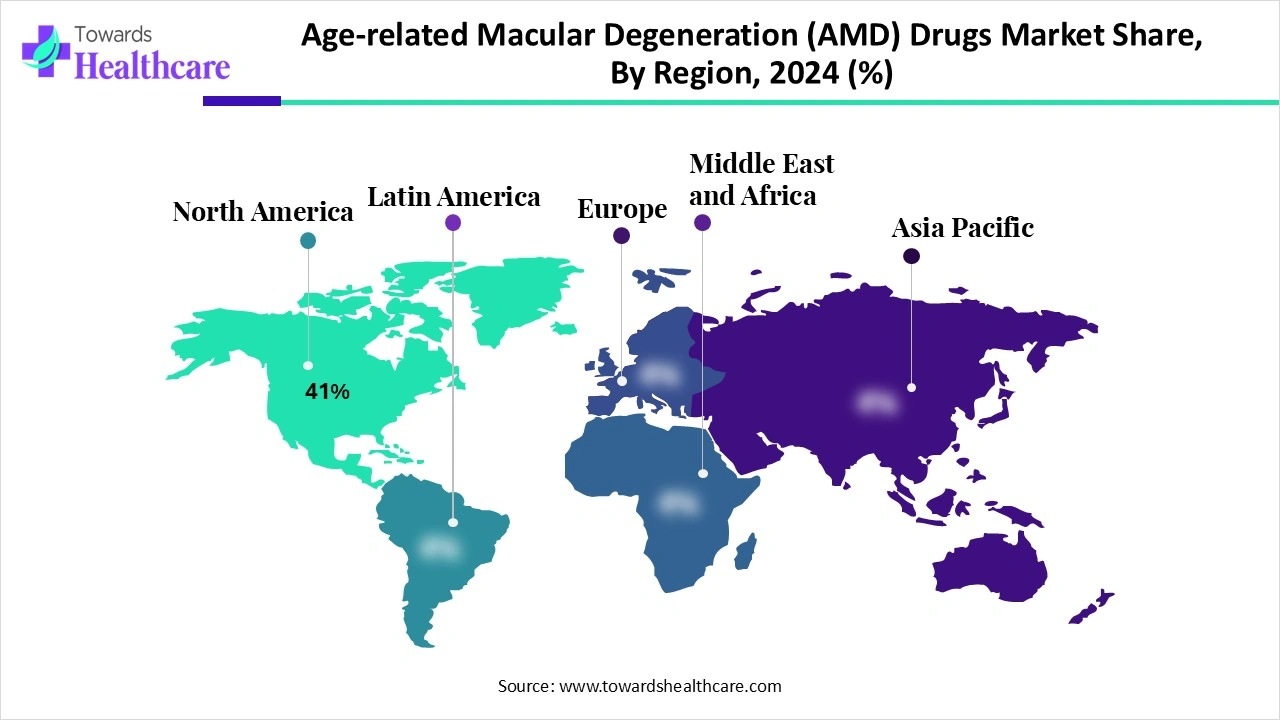
North America dominates the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market share by 41% due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high awareness levels, and significant patient pool, particularly within the aging population, where AMD prevalence is rising rapidly. The region benefits from strong research and development activity, with leading pharmaceutical companies such as Regeneron, Roche, and Novartis actively developing innovative therapies, including long-acting anti-VEGF drugs and gene therapies. Favorable reimbursement policies and widespread adoption of advanced diagnostic tools like OCT further support early detection and treatment uptake.
In February 2025, Astellas’ IZERVAY (avacincaptad pegol) received FDA approval to extend dosing duration beyond its previous 12-month limit, offering increased treatment flexibility for patients with geographic atrophy (GA), an advanced form of dry AMD.
The U.S. is the largest and most dynamic Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Drugs market, driven by a large aging population, widespread access to advanced diagnostics (OCT, fundus photography), and dense retina specialist networks. Strong reimbursement (Medicare/private payers) and favorable coding facilitate uptake of costly biologics and long-acting therapies. The U.S. leads in R&D and clinical trials, hosting major pharma (Regeneron, Roche/Genentech, Novartis, Apellis) and rapid regulatory activity — for example, recent 2025 label expansions and fast-track designations. Adoption is high for anti-VEGF agents, and emerging long-acting implants, sustained-release formulations, gene therapies, and complement inhibitors are expanding treatment options.
Canada has excellent clinical capacity and strong specialist care in major provinces, but market uptake is slower and more centralized by provincial formularies and HTA processes. Health Canada regulatory approvals and provincial reimbursement/coverage decisions determine real-world access; costly novel AMD drugs often face rigorous HTA review and negotiated pricing. Clinician interest mirrors U.S. practice, but public plan listing delays and budget constraints can slow adoption. Urban centers provide advanced diagnostic services, while rural/remote access disparities remain a concern. Manufacturers frequently align reimbursement strategies and patient support programs to navigate provincial systems.
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market for age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs, driven by multiple interlinked factors. A rapidly aging population in countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India is significantly increasing the prevalence of AMD, creating strong demand for effective therapies. Rising awareness and improved screening programs are facilitating earlier detection, particularly in urban areas. Governments are expanding healthcare spending, while private healthcare providers are investing in advanced ophthalmology infrastructure and imaging technologies. Moreover, growing clinical trial activity and local manufacturing partnerships are improving access to innovative therapies. Favorable regulatory reforms, coupled with rising disposable incomes and expanding insurance coverage, are further accelerating the adoption of advanced AMD treatments across the region.
China represents one of the largest and fastest-growing AMD drug markets due to its massive aging population and rising prevalence of retinal diseases. Increasing government investment in healthcare infrastructure, wider use of advanced imaging like OCT, and the expansion of urban hospitals drive early detection and treatment. However, affordability remains a key barrier, with widespread use of lower-cost alternatives such as off-label bevacizumab. Recent regulatory reforms by the NMPA are accelerating approvals of innovative drugs, while domestic biopharma companies are entering the AMD space through biosimilars and novel molecules, making China a highly competitive market.
Japan has one of the highest elderly populations globally, making AMD a critical healthcare concern. The country boasts advanced ophthalmic infrastructure and strong adoption of cutting-edge therapies, such as anti-VEGF biologics and sustained-release delivery systems. The Japanese regulatory authority (PMDA) has been proactive in approving innovative AMD drugs, ensuring quick market access. Reimbursement through the national health insurance system supports patient uptake despite high costs. Additionally, Japanese pharma companies, including Santen Pharmaceutical, are actively engaged in R&D for AMD therapies, further solidifying Japan’s leadership in the Asia-Pacific age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market.
India’s AMD market is growing rapidly due to increasing awareness of eye health and the rising prevalence of AMD among its aging population. Access to treatment is improving as private hospitals and specialty eye centers expand across urban areas. However, affordability remains a major challenge, leading to heavy reliance on off-label and cost-effective options like bevacizumab. The government’s push toward strengthening healthcare infrastructure, coupled with increasing penetration of health insurance, is expected to enhance accessibility to advanced AMD therapies.
For instance,
South Korea’s Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Drugs market is expanding steadily, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong government healthcare policies, and rapid adoption of innovative therapies. The Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) ensures timely regulatory approvals for novel biologics. The country also benefits from high awareness levels, widespread insurance coverage, and significant clinical trial participation. Pharmaceutical companies, both domestic and global, are actively collaborating to introduce advanced therapies, including biosimilars and long-acting delivery systems. South Korea’s emphasis on healthcare digitization and teleophthalmology further improves access to AMD screening and treatment.
Europe is witnessing notable growth in the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) drugs market, driven by its rapidly aging population and the rising prevalence of vision-related disorders. Increased government funding for ophthalmic research, coupled with supportive reimbursement policies across countries like Germany, the UK, and France, is improving access to advanced AMD therapies. The region is also experiencing strong adoption of innovative treatments, such as anti-VEGF drugs and gene therapies, with several European pharmaceutical companies investing in R&D collaborations. Additionally, awareness campaigns and improved diagnostic infrastructure are enabling earlier detection, further fueling the demand for AMD drugs across the region.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) medication research and development (R&D) is a multi-phase process that includes preclinical research, clinical trials, and regulatory approval. Before requesting FDA approval, important steps include determining possible drug targets, synthesizing or discovering candidate molecules, conducting preclinical testing in vitro and in vivo, and moving forward through Phase I, II, and III clinical trials to evaluate safety and efficacy.
Organizations: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Bayer AG, Astellas Pharma, F. Hoffmann-La Rocheetc.
Preclinical research and post-market surveillance are two of the many steps involved in clinical trials and regulatory approvals for medications used to treat AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration). Clinical trials (phases 1–3), preclinical research, regulatory review (e.g., by the FDA), and post-market are important phases of observation. In recent years, anti-VEGF and anti-complement medications have been approved for the neovascular and geographic atrophy forms of AMD, respectively.
Organizations: regulatory bodies like the FDA (US) and CDSCO (India), CROs (Contract Research Organizations), ethics committees, etc.
Formulation Development
Activities: Converting APIs into stable, safe, and effective formulations (e.g., intravitreal injections, long-acting implants, sustained-release systems).
Organizations Involved: Pharmaceutical Companies: Roche (Susvimo implant), Novartis (Beovu), Regeneron (Eylea HD).
Drug Delivery Innovators: Clearside Biomedical (suprachoroidal injection technology), EyePoint Pharmaceuticals (sustained-release implants).
Final Dose Preparation & Packaging
Activities: Sterile fill-finish operations, vialing, pre-filled syringes, or ocular implant device assembly; compliance with FDA/EMA regulations.
Organizations Involved: Specialized CDMOs: Baxter BioPharma Solutions, Vetter Pharma.
In-house facilities: Bayer, Roche, and Regeneron maintain sterile fill-finish sites.
Distribution & Supply Chain
Activities: Cold chain logistics for biologics, warehousing, and delivery to hospitals and specialty eye clinics.
Organizations Involved: Wholesalers/Distributors: McKesson, AmerisourceBergen, Cardinal Health.
Specialty Distributors: Besse Medical, ASD Healthcare.
Patient Advocacy Groups: BrightFocus Foundation, American Macular Degeneration Foundation (AMDF).
In July 2025, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced the fast track designation to SAR446597, a one-time intravitreal gene therapy for the treatment of Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)-related geographic atrophy (GA). Facilitating the development and accelerating the review of medications to treat serious conditions and address unmet medical needs is the goal of the fast track designation process. The FDA developed this procedure, which addresses a wide range of serious illnesses, to help get important new medications to patients sooner.
In May 2025, A clinical-stage business called Cognition Therapeutics, Inc. is creating medications that treat neurodegenerative diseases. Today released the topline findings from the zervimesine Phase 2 COG2201 'MAGNIFY' trial (CT1812) in adults suffering from dry age-related macular degeneration (dry AMD)-related geographic atrophy (GA). The results show participants receiving zervimesine experienced an average GA lesion growth rate of 28.6% slower, and at 18 months, their lesions were 28.2% smaller in contrast to a placebo. NCT05893537, the MAGNIFY study, was completed after about 100 of the 246 participants were enrolled.
By Disease Type
By Drug Class
By Route of Administration
By Distribution Channel
By End User
By Region
November 2025
