January 2026

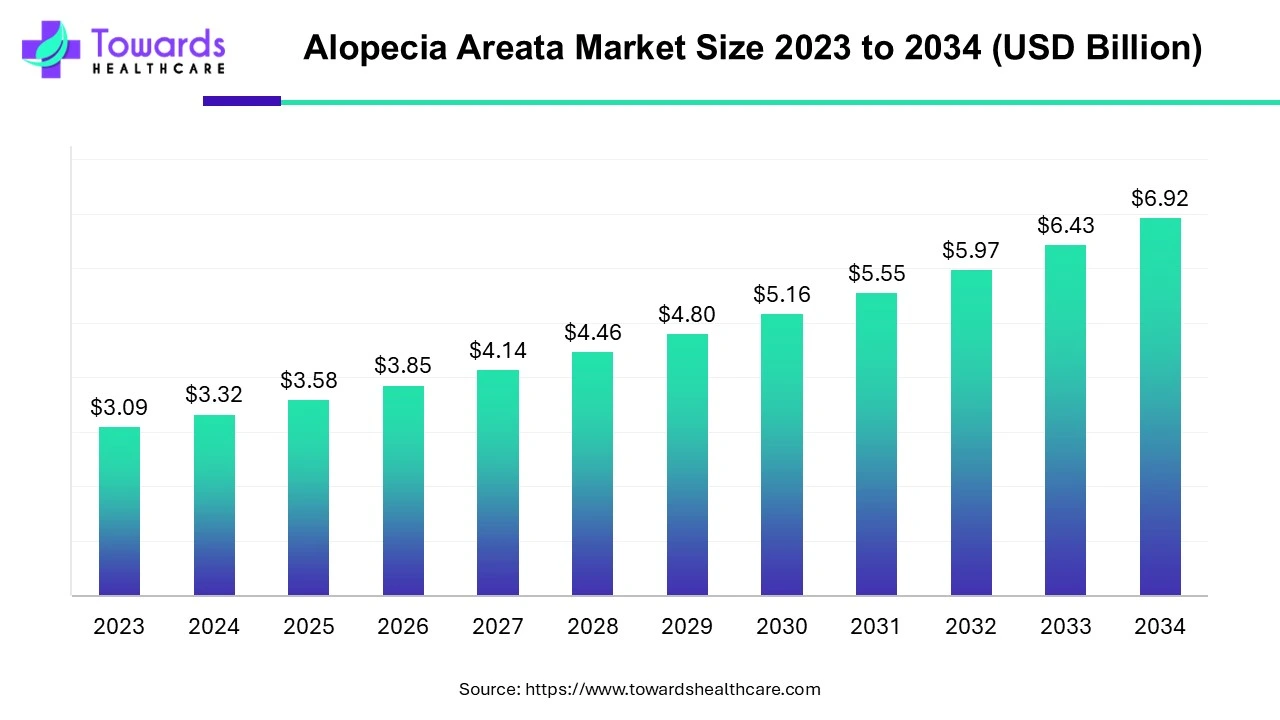
The global alopecia areata market size is calculated at USD 3.32 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth USD 6.92 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 7.6% from 2024 to 2034.
Around 2% of people globally will have alopecia areata at some time in their lives, and nowadays, more and more people are getting it. This increase in cases is why there's a more significant demand for treatments to help with alopecia areata.
Alopecia is a prevalent autoimmune condition characterized by patches of hair loss on the face, scalp, and other parts of the body. Hair loss results from the immune system attacking the hair follicles inadvertently in this situation. Any age, gender, or race can be affected, and its precise etiology is still unknown. The primary symptom of alopecia areata is hair loss in small, round patches on the scalp. In some cases, it can progress to total hair loss on the scalp (alopecia totalis) or even complete loss of body hair (alopecia universalis). The hair loss is usually temporary, and hair may grow back on its own, but it can also be recurrent or permanent for some individuals.
While alopecia areata itself isn't physically harmful, it can have significant emotional and psychological effects, causing distress, low self-esteem, and anxiety, especially if the hair loss is extensive. This is why treatment is important.
Various treatment options are available for alopecia areata, although none are guaranteed to be effective for everyone. These treatments stimulate hair regrowth, suppress the immune system, or reduce inflammation around the hair follicles. Common treatments include corticosteroid injections, topical corticosteroids, minoxidil (Rogaine), anthralin cream, and immunotherapy.
Additionally, medical treatments, counseling, and support groups can be beneficial for individuals coping with the emotional impact of alopecia areata. Individuals with alopecia areata need to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the best treatment plan for their specific situation.
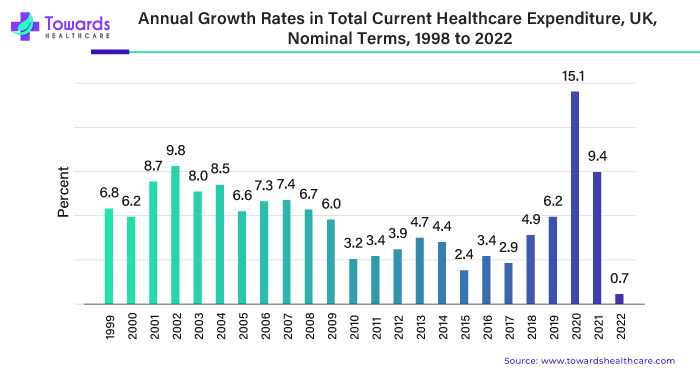
Furthermore, the government spent more on healthcare, as new information shows. This increase shows they're dedicated to improving healthcare services and buildings. They're being proactive in meeting people's changing healthcare needs. This money is crucial for making sure everyone can get good healthcare quickly. In a May 2023 article from the Office for National Statistics (ONS), healthcare spending in the UK for 2022 amounted to around USD 304.55 billion, marking a 0.7% rise compared to the preceding year.
Research into alopecia areata is ongoing, and new treatment options may become available. Some promising research areas include understanding the condition's underlying causes and developing targeted therapies to prevent hair loss and promote hair regrowth. While alopecia areata can be challenging to deal with, especially from a psychological standpoint, there are treatment options available to help manage the condition and support individuals in regaining their confidence and self-esteem.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Alopecia Areata market is poised to revolutionize the industry by enhancing diagnosis, treatment, and research. AI technologies, such as machine learning and deep learning, enable precise analysis of medical images and patient data, leading to more accurate and early detection of Alopecia Areata. This early detection facilitates timely intervention, potentially improving patient outcomes. Moreover, AI-driven predictive analytics can help identify patients at higher risk of developing the condition, allowing for proactive treatment strategies.
In research and drug development, AI accelerates the discovery of new therapeutic targets and optimizes clinical trial designs, thereby reducing costs and time to market for new treatments. Personalized medicine, powered by AI, offers tailored treatment plans based on individual genetic and lifestyle factors, improving efficacy and patient satisfaction. Additionally, AI-powered platforms enhance patient engagement by providing real-time monitoring and feedback, fostering adherence to treatment regimens.
As AI continues to evolve, its integration into the Alopecia Areata market promises significant advancements in patient care, research efficiency, and overall market growth, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Alopecia comes in various types, each with different characteristics and levels of severity. Alopecia Universalis (AU) involves the complete loss of hair on both the head and body, while Alopecia Totalis (AT) affects only the head. Another subtype, Alopecia Ophiasis (AO), is a rare form of alopecia areata that starts with hair loss from the back and sides of the head.
Patients with AU and AT generally have a lower likelihood of significant hair regrowth compared to those with standard Alopecia Areata (AA). AU and AT together account for about 7–30% of all alopecia areata cases. Most people with alopecia areata, approximately 60%, notice their first bald patch before turning 30. The lifetime risk of developing this condition is estimated to be between 1.7% and 2.1%, with about 20% of cases occurring in children.
Imagine waking up one day to find patches of your hair falling out, leaving bald spots on your scalp or other body parts. For many people, their hair is a big part of their identity, tied to their self-esteem and confidence. So, when they start losing it unexpectedly, it can be devastating.
For instance,
Alopecia areata doesn't just affect a person's physical appearance; it can also have profound effects on their mental health and emotional well-being. Many individuals with alopecia areata experience feelings of embarrassment, shame, and anxiety about their appearance, especially if the hair loss is noticeable or extensive. They may feel self-conscious in social situations, avoid going out in public, or even withdraw from social activities altogether.
The impact of alopecia areata can be particularly challenging for children and adolescents, who may face teasing, bullying, or social exclusion because of their hair loss. This can lead to low self-esteem, depression, and other psychological issues if not addressed promptly. There is a strong demand for effective treatments that can restore hair growth and improve self-esteem and quality of life for individuals with alopecia areata. People want solutions that not only address the physical symptoms of the condition but also help them feel confident and comfortable in their skin again.
Pharmaceutical companies and researchers are constantly striving to develop new therapies that stimulate hair regrowth and address the emotional and psychological aspects of alopecia areata. These therapies include psychological support, such as counseling and support groups, alongside medical treatments.
Advances in medical technology have vastly improved how we understand and treat alopecia areata, a condition that causes hair loss due to the body's immune system mistakenly attacking hair follicles. These advancements have opened up new possibilities for managing the condition effectively.
For instance,
One area of progress is in diagnostic tools. Doctors now have better methods for accurately diagnosing alopecia areata, including examining the pattern of hair loss and using tools like trichoscopy, which allows them to closely examine the scalp and hair follicles for signs of the condition. This means patients can receive a quicker and more accurate diagnosis, which is crucial for starting treatment promptly.
In terms of treatment, there are exciting developments in novel approaches such as biologics and stem cell therapy. Biologics are medications derived from living organisms that target specific molecules involved in the immune system's response, helping to regulate its activity. These drugs have shown promise in clinical trials for treating alopecia areata by reducing inflammation around hair follicles and promoting hair regrowth.
For instance,
Stem cell therapy involves using stem cells, which are special in the body and can develop into different types of cells, including those found in hair follicles. Researchers are investigating ways to harness the regenerative potential of stem cells to stimulate hair follicle growth and restore hair in individuals with alopecia areata.
These innovative treatment approaches could revolutionize how we manage alopecia areata. They offer hope to patients who may not have responded well to traditional treatments or are looking for more effective, long-lasting solutions. It's important to note that while these advancements hold great promise, they are still in the early stages of research and development. More studies are needed to understand their effectiveness, safety, and long-term outcomes fully. These treatments may only be suitable for some and may come with challenges and considerations.
Minoxidil is a popular and effective treatment for alopecia areata, showing prominent results in many cases. It's available in topical form and is applied directly to the scalp. Minoxidil works by stimulating hair follicles, increasing blood flow to the scalp, and prolonging the hair's growth phase. This promotes hair regrowth in areas affected by alopecia areata.
One reason minoxidil is widely used is that it's relatively easy to use and generally well-tolerated. It has different strengths and formulations, making it suitable for various individuals. Additionally, minoxidil doesn't require a prescription in many cases, making it accessible to many people.
Clinical studies have shown that minoxidil can effectively promote hair regrowth in individuals with alopecia areata, particularly in mild to moderate hair loss cases. Results may vary from person to person, and not everyone may respond to minoxidil treatment. To see the best results, it's also essential to use minoxidil consistently and as directed. This means applying it regularly to the affected areas of the scalp and continuing treatment even after hair regrowth occurs to maintain results.
Minoxidil is a valuable tool in the treatment of alopecia areata. It provides a safe and accessible option for promoting hair regrowth and improving the appearance and confidence of individuals affected by this condition. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any treatment regimen to ensure it's appropriate for your specific situation and to discuss any potential side effects or concerns.
By route of administration, the topical segment held a dominant presence in the alopecia areata market in 2023. The topical route is the most widely preferred route of administration to achieve targeted drug delivery and reduce systemic side effects and toxicity. Also, the absorption of drug molecules is rapid compared to the oral route. Some of the topical drugs used for alopecia areata include minoxidil, corticosteroids, anthralin, or topical immunotherapy.
By end-user, the dermatology clinic segment led the global alopecia areata market in 2023. The segment’s growth is attributed to the presence of key players, favorable infrastructure, and the availability of necessary specialized equipment and other treatment facilities. The growing number of dermatology clinics, due to increasing demand for hair loss treatment and other skin disorders, promotes the segment’s growth. In the U.S., there are around 5,328 dermatology clinics as of 2023.
One of the significant hurdles in the alopecia areata market is the variable treatment response among individuals. This means something other than what works for one person might work for another. Alopecia areata is a complex condition with diverse underlying causes and mechanisms, making it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all treatment. Finding the most effective treatment often involves a trial-and-error process, where individuals may need to try multiple treatment options before finding one that works for them.
The variable treatment response can be frustrating for both patients and healthcare professionals. It can lead to delays in finding effective treatment, increased healthcare costs, and emotional distress for patients who may feel discouraged by failed treatments. Additionally, the lack of predictability in treatment outcomes makes it challenging for pharmaceutical companies to develop new therapies and clinicians to make treatment recommendations.
To fix this challenge, there is a growing need for personalized medicine approaches that consider individual differences in genetics, immune function, and other factors that may influence treatment response. By better understanding the underlying mechanisms of alopecia areata and identifying biomarkers that predict treatment response, researchers hope to develop more targeted and effective treatments tailored to the needs of each individual.
In North America, the geographical landscape for the alopecia areata market is diverse and dynamic. The United States and Canada are the major players in this market, with a significant portion of the population affected by alopecia areata. In these countries, a well-established healthcare infrastructure, including hospitals, clinics, and research institutions, contributes to diagnosing and treating alopecia areata. A high level of awareness about alopecia areata among healthcare professionals and the general population characterizes the market in North America. This awareness drives demand for effective treatments and fosters innovation in developing new therapies. Major cities such as New York, Los Angeles, Toronto, and Chicago are hubs for medical research and innovation in dermatology and autoimmune disorders, including alopecia areata. These cities attract leading experts, clinicians, and researchers who collaborate to advance our understanding of the condition and develop new treatment options.
The prevalence of alopecia areata can vary significantly across countries in Asia Pacific. Some countries may have higher rates of alopecia areata due to genetic predispositions, environmental factors, or cultural practices. For example, countries with higher levels of stress or pollution may experience increased rates of alopecia areata. Access to healthcare services varies widely across the Asia Pacific region, with healthcare infrastructure, resources, and affordability disparities. In some countries, individuals may face challenges in accessing timely diagnosis and treatment for alopecia areata due to the limited availability of healthcare facilities or financial constraints.
The competitive landscape for alopecia areata refers to the different companies and treatments available for this condition. Just like other brands of cars compete in the automobile market, various pharmaceutical companies offer products to help people with alopecia areata. They might have different pills, creams, or other treatments. These companies compete to create the best and most effective options for people dealing with hair loss due to alopecia areata.
In July 2024, the FDA approved a third JAK inhibitor, deuruxolitinib, for the management of alopecia areata in adults 18 years and older. Leqselvi is a novel oral medication that is taken twice per day. Leqselvi was tested in two big placebo-controlled Phase 3 clinical trials of more than 1,200 patients with at minimum 50% scalp hair loss.
Investigators advanced a potential novel management therapy for alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss. The novel microneedle patch provides immune-regulating molecules that teach T cells not to attack hair follicles, supporting to regrowth of hair. This approach prevents systemic immune suppression and is modified for other autoimmune skin diseases, which drives the growth of the market.
Angela Hwang, Chief Commercial Officer, President, Global Biopharmaceuticals Business, Pfizer, commented on the US FDA approval of LITFULO that it is an important treatment advancement for alopecia areata that had no treatment options for adolescents and very limited options for adults. He added that both adolescents and adults will have an opportunity to achieve significant scalp hair regrowth.

By Treatment
By Route of Administration
By End User
By Geography
January 2026
December 2025
November 2025
November 2025