March 2026

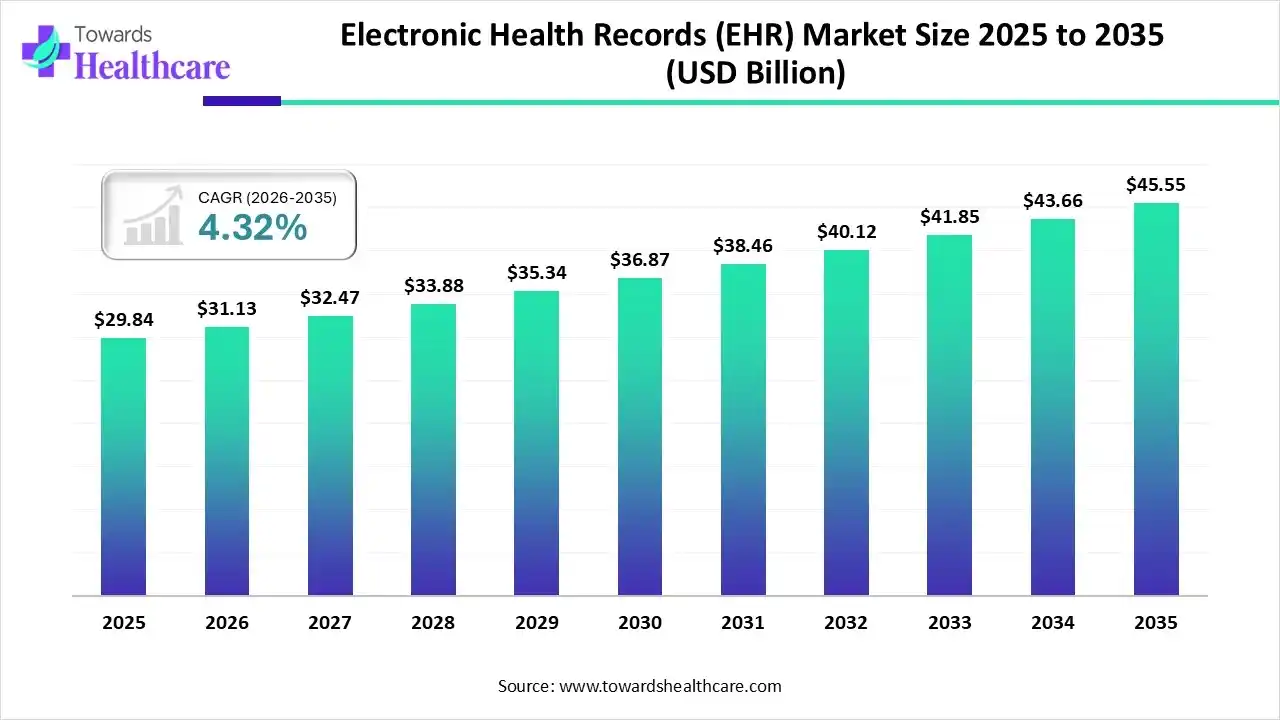
The global electronic health records market size is calculated at USD 29.84 billion in 2025 and is expected to be worth USD 45.55 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 4.32% from 2026 to 2035.
| Key Elements | Scope |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 31.13 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 45.55 Billion |
| CAGR (2026 - 2035) | 4.32% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Market Segmentation | By Type, By Product, By Business Models, By End-User, By Region |
| Top Key Players | Epic Systems Corporation, Allscripts Healthcare Solutions, Inc., McKesson Corporation, GE Healthcare, NextGen Healthcare, Inc., Athenahealth, OpenEMR, Siemens Healthineers AG, eClinicalWorks, Medical Information Technology, Inc. |
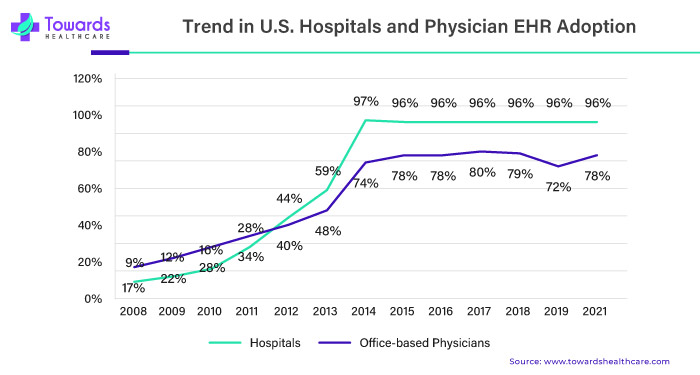
According to Healthit.gov, in the transformative landscape of healthcare, a remarkable surge in Electronic Health Records (EHR) adoption has been witnessed, with an impressive 78% adoption rate among office-based physicians and an even 96% among non-federal acute care hospitals as of 2021.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) are comprehensive digital repositories of an individual's health information. These records go beyond just a medical history; they encompass a patient's entire healthcare journey. Within Electronic Health Records (EHR), you'll find details about diagnoses, treatments, medications, immunizations, allergies, and even demographic information. One key advantage is accessibility. EHR allows authorized healthcare professionals to access your information securely, promoting seamless collaboration among healthcare providers. This accessibility enhances the continuity of care, ensuring your doctors have up-to-date and accurate information to make informed decisions.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) also facilitate data sharing between various healthcare settings, like hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies. This interoperability reduces redundancies, minimizes errors, and streamlines processes. For instance, if you visit a specialist, they can quickly review your medical history and coordinate treatments more effectively. Additionally, Electronic Health Records (EHR) contribute to improved patient engagement. Some systems enable patients to access their health records, fostering a better understanding of their conditions and encouraging active participation in their healthcare journey. Data security is a paramount concern in Electronic Health Records (EHR). Robust encryption and authentication measures are in place to safeguard sensitive health information. This ensures that only authorized individuals have access to the data, maintaining patient privacy and complying with regulatory standards.
Furthermore, Electronic Health Records (EHR) revolutionize healthcare by digitizing and centralizing health information, fostering collaboration among healthcare providers, enhancing patient engagement, and prioritizing data security to provide efficient, personalized, and high-quality care. The global increase in the adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHR) is a response to these systems' transformative impact on healthcare delivery, efficiency, patient outcomes, and compliance with evolving regulatory standards. As technology advances, the adoption of electronic health records is likely to expand further.
2009: 46% – In 2009, less than half of the public reported that their healthcare providers were using computer-based medical records. At this stage, many providers still relied on traditional paper records or were in the early phases of transitioning to digital systems.
2016: 80% – By 2016, there was a substantial increase to 80%. This shift reflects a growing trend towards the digitization of health records, likely driven by advancements in technology, government incentives, and a push for improved efficiency and accuracy in healthcare management.
2019: 88% – By 2019, the percentage had risen further to 88%. This indicates that computer-based medical records had become quite common, with the majority of healthcare providers now using these systems. This increase could be attributed to continued improvements in technology, greater adoption of electronic health record (EHR) systems, and possibly regulations or policies encouraging the use of digital records.
According to Healthit.gov
In 2021, Electronic Health Records (EHR) enhance patient information accuracy and accessibility at the point of care, offer insights into healthcare costs and outcomes, and support quality care. In Germany, the Patient Data Protection Act requires electronic patient records. While EHR implementation is widespread, a survey in Norway revealed concerns among physicians, such as system interruptions and perceived complexity. Despite the essential role of EHRs, ongoing evaluation is crucial for continuous improvement in healthcare effectiveness and efficiency.
For Instance,
The introduction of Electronic Health Records (EHR) stands as a revolutionary force within the healthcare industry, fundamentally transforming the management and utilization of patient information globally. This digital paradigm shift has propelled the healthcare market across various crucial dimensions. Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems replace traditional paper records and expedite information retrieval, providing healthcare professionals instantaneous patient data access. This facilitates quicker decision-making and timely interventions and enhances overall productivity by enabling healthcare providers to attend to more patients.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) also foster seamless communication among diverse healthcare entities, ensuring that hospitals, clinics and laboratories are interconnected, thereby promoting a well-coordinated approach to patient care. The comprehensive view of a patient's medical history, medications, allergies and test results offered by electronic records contributes to a holistic perspective, empowering healthcare professionals to make more informed decisions, ultimately reducing errors and elevating the overall quality of care. Furthermore, Electronic Health Records (EHR) address issues associated with illegible handwriting and transcription errors in paper records.
Moreover, incorporating advanced analytics within these systems provides decision support, assisting healthcare professionals in identifying trends, anticipating issues and making evidence-based decisions. Beyond healthcare providers, patients themselves are empowered by Electronic Health Records (EHR), allowing them access to their health information and fostering a collaborative relationship with healthcare providers. Adopting Electronic Health Records (EHR) aligns with evolving global healthcare regulations and standards, ensuring data security and privacy and positioning healthcare organizations to meet industry requirements.
While the initial implementation of Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems necessitates an investment, the long-term benefits, including reduced paperwork, fewer duplicate tests, and improved operational efficiency, contribute to substantial cost savings within the healthcare system. In summary, the widespread integration of Electronic Health Records represents a pivotal step towards creating a more interconnected, data-driven, and patient-centric healthcare ecosystem.
Advancements in technology are like superheroes for Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems, making them even more awesome! Let's break it down: First up, we have interoperability improvements. Imagine Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems as super communicators they can talk to other healthcare systems like pharmacies, labs and imaging centers. Everyone gets the same superhero view of patient info, making healthcare more connected and efficient.
Next on the tech list is cloud computing. Think of it as a magical cloud where patient data is stored securely. This cloud lets healthcare providers access info from anywhere with the internet, making things super convenient. Plus, it's like a superhero shield for data, ensuring it stays safe and protected. Now, let's talk about mobile health solutions (mHealth). Electronic Health Records (EHR) on mobile apps bring a new level of cool. Healthcare providers can update patient records on the go, and patients can dive into their health info through apps, becoming the heroes of their health journey. These mobile solutions also support telehealth, making remote consultations easier, especially during pandemics or for folks in faraway places. Enter data analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI). These tech superheroes help Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems understand patterns, predict health outcomes, and make intelligent decisions. It's like having a sidekick that takes care of routine tasks, freeing up healthcare providers to focus on what they do best taking care of patients.
User-friendly interfaces and design are like the friendly faces of Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems. Improved tech makes it super easy for healthcare pros to navigate and find info fast. In a fast-paced healthcare world, quick access to accurate information is vital, and these user-friendly designs make it happen. Last but not least, we have the integration with wearable devices. Electronic Health Records (EHR) team up with wearables like fitness trackers to gather real-time health data. It's like having a superhero sidekick that monitors your health 24/7, helping catch potential issues early. These tech upgrades aren't just cool gadgets for Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems they're the heroes that make healthcare more connected, efficient and patient-focused. It's like giving superpowers to the tools that help improve patient care and outcomes.
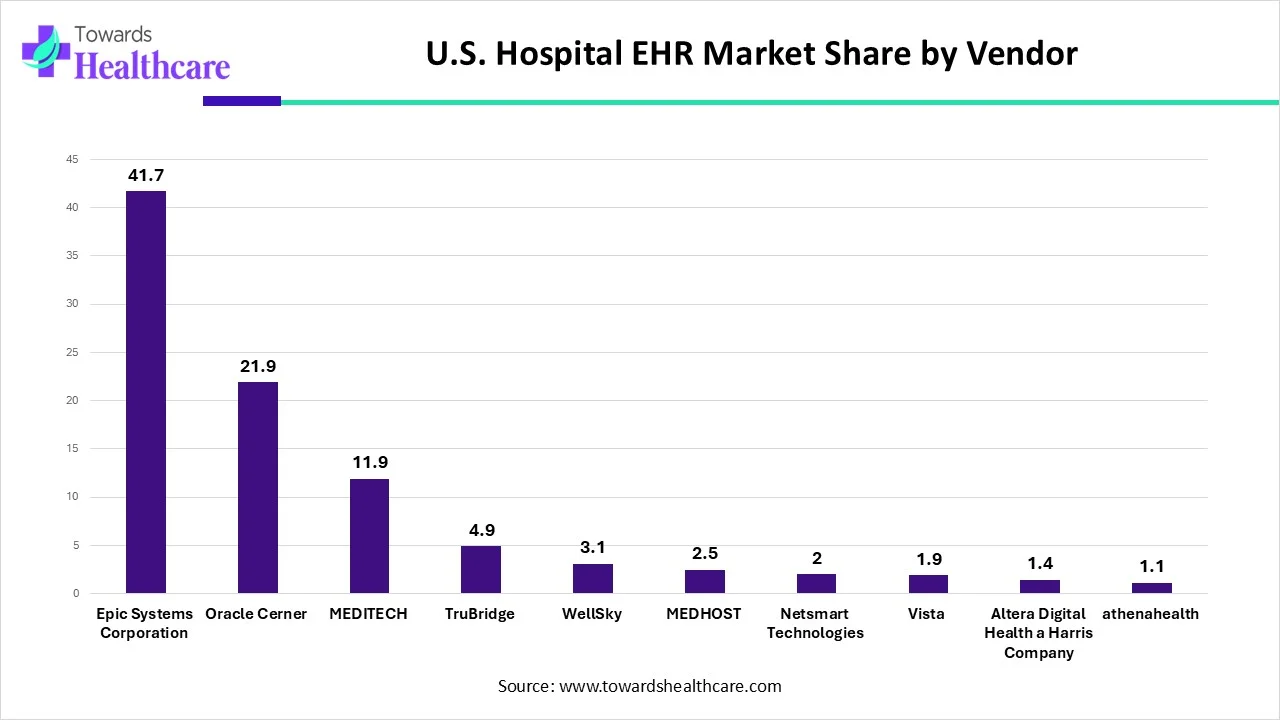
| Vendor | % of U.S. hospital EHR market share |
| Epic Systems Corporation | 41.7 |
| Oracle Cerner | 21.9 |
| MEDITECH | 11.9 |
| TruBridge | 4.9 |
| WellSky | 3.1 |
| MEDHOST | 2.5 |
| Netsmart Technologies | 2 |
| Vista | 1.9 |
| Altera Digital Health a Harris Company | 1.4 |
| athenahealth | 1.1 |
This data highlights how a small group of vendors dominates the U.S. hospital electronic health record (EHR) market. Epic Systems Corporation clearly leads the landscape, capturing 41.7% of the market and setting the standard for large health systems and academic hospitals. Oracle Cerner follows with a strong 21.9% share, reflecting its deep-rooted presence and continued adoption across diverse hospital networks.
MEDITECH secures the third position with an 11.9% share, driven by its long-standing relationships with community and mid-sized hospitals. TruBridge and WellSky play focused roles, holding 4.9% and 3.1% respectively, as they cater to specific hospital segments and care settings. MEDHOST and Netsmart Technologies further strengthen the competitive mix by supporting niche hospital and behavioral health requirements.
Smaller vendors such as Vista, Altera Digital Health (a Harris Company), and athenahealth collectively represent a modest share of the market. However, they continue to add value by offering flexible, specialized, and cost-effective EHR solutions. Overall, this distribution shows a highly concentrated market where leading platforms shape interoperability, data integration, and digital transformation across U.S. hospitals, while smaller players address targeted operational and clinical needs.
In low-income countries, adopting Electronic Health Records (EHR) encounters various challenges that hinder its growth. Financial constraints play a significant role, as limited budgets restrict the upfront investment required for implementing EHR systems. Furthermore, inadequate infrastructure, including poor internet connectivity and outdated hardware, poses substantial obstacles to a seamless adoption process. The need for a skilled workforce and resistance to change among healthcare professionals further impede the integration of Electronic Health Records (EHR), making the transition more challenging. Data security and privacy concerns also act as barriers, eroding trust in digital health management.
The impact on market growth in low-income countries is evident as these barriers collectively restrain the adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems, slowing down the overall pace of implementation. Financial limitations, infrastructure challenges, resistance to change, and workforce shortages contribute to reluctance to embrace electronic health records. Conversely, facilitators such as government support and international collaboration stimulate growth by addressing these challenges, potentially paving the way for a more widespread adoption of EHR systems. The successful navigation of these barriers and the effective implementation of facilitators will be crucial in determining the extent of EHR adoption in low-income countries and influencing the overall market growth in these regions.
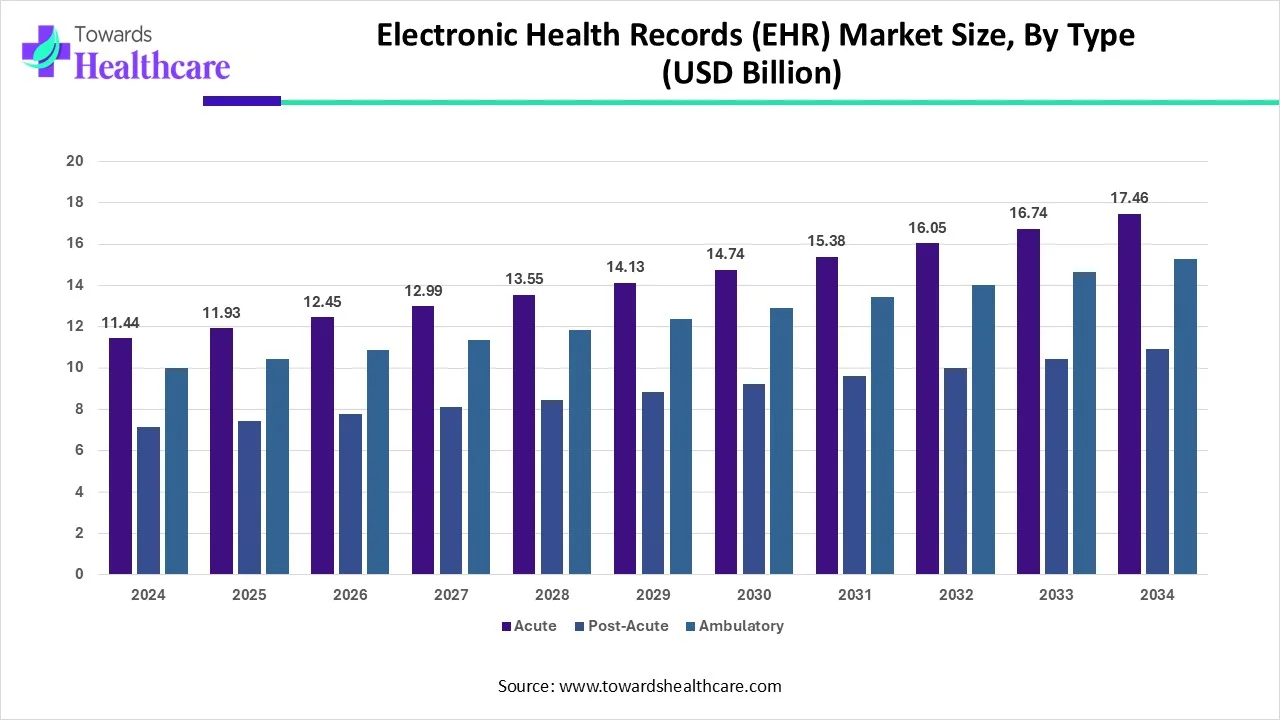
| Year | Acute | Post-Acute | Ambulatory |
| 2024 | 11.44 | 7.15 | 10.01 |
| 2025 | 11.93 | 7.46 | 10.44 |
| 2026 | 12.45 | 7.78 | 10.89 |
| 2027 | 12.99 | 8.12 | 11.36 |
| 2028 | 13.55 | 8.47 | 11.86 |
| 2029 | 14.13 | 8.83 | 12.37 |
| 2030 | 14.74 | 9.22 | 12.90 |
| 2031 | 15.38 | 9.61 | 13.46 |
| 2032 | 16.05 | 10.03 | 14.04 |
| 2033 | 16.74 | 10.46 | 14.65 |
| 2034 | 17.46 | 10.91 | 15.28 |
Acute Segment Dominated
By type, the acute segment held the largest share of the electronic health records (EHR) market in 2023. Acute care involves a level of healthcare wherein the patients receive treatment for a short period. Acute care involves emergency departments, intensive care, coronary care, cardiology, etc. The increasing number of patients in acute care settings due to rising acute disorders and demand for faster and more efficient patient care boosts the segment’s growth. In 2023, 70% of non-federal acute care hospitals in the US were engaged in all domains (send, find, receive, and integrate) of interoperable exchange.
Post-Acute Segment: Fastest Growing
By type, the post-acute segment is anticipated to grow with the highest CAGR in the market during the studied years. EHR allows healthcare professionals to get real-time data about patients after discharge from acute care settings. EHR improves communication, coordination, and decision-making. The demand for advanced treatment care, the rising geriatric population, and increasing home health services drive the segment’s growth.
Web Server-Based Segment Led
By product, the web server-based segment led the global market in 2023. The advent of cloud services and further technological advancements to store large amounts of data on external servers augment the segment’s growth. The recent developments in the internet and telecommunication sectors and the demand to access data anywhere and at any time also drive the segment’s growth. In addition, it does not require any specialized infrastructure to maintain data.
Client-Server-Based Segment: Fastest-Growing
By product, the client-server-based segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the market during the forecast period. Unlike web server-based, client-server-based is operated by the organization’s IT department on local servers. It enables customization and ease of use as it can be modified based on the hospital’s requirements. Additionally, it provides enhanced security and is cost-effective compared to web server-based, which makes it a preferable choice.
Hospitals Segment Dominated
By end-user, the hospitals segment registered its dominance over the global market in 2023. The segment’s growth is attributed to the increasing number of patients in hospitals, favorable infrastructure, and suitable capital investments. The need to streamline the complex healthcare process also drives the segment.
Ambulatory Services Segment: Significantly Growing
By end-user, the ambulatory services segment is predicted to witness significant growth in the market over the forecast period. EHR systems in ambulatory services increase the speed and efficiency of processing a patient’s medical appointment or emergency care situation. The increasing use and level of portability for patients promote the segment’s growth.
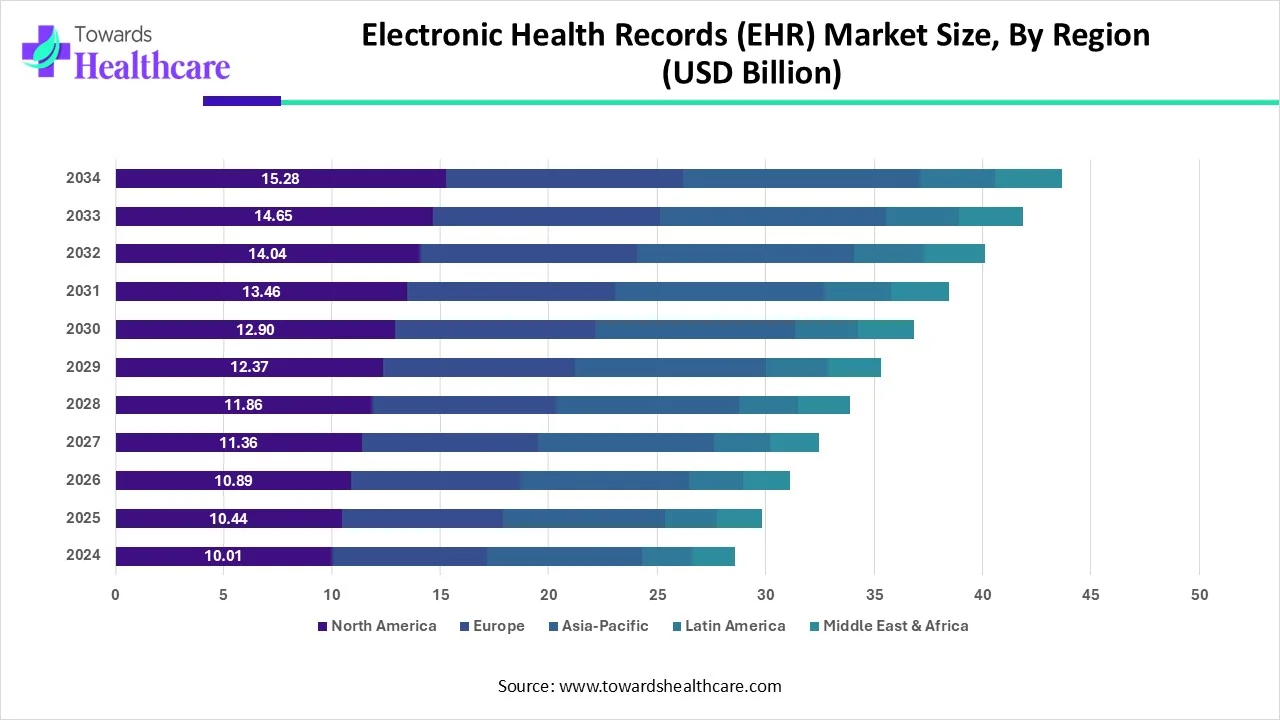
| Year | North America | Europe | Asia-Pacific | Latin America | Middle East & Africa |
| 2024 | 10.01 | 7.15 | 7.15 | 2.288 | 2.002 |
| 2025 | 10.44 | 7.46 | 7.46 | 2.39 | 2.09 |
| 2026 | 10.89 | 7.78 | 7.78 | 2.49 | 2.18 |
| 2027 | 11.36 | 8.12 | 8.12 | 2.60 | 2.27 |
| 2028 | 11.86 | 8.47 | 8.47 | 2.71 | 2.37 |
| 2029 | 12.37 | 8.83 | 8.83 | 2.83 | 2.47 |
| 2030 | 12.90 | 9.22 | 9.22 | 2.95 | 2.58 |
| 2031 | 13.46 | 9.61 | 9.61 | 3.08 | 2.69 |
| 2032 | 14.04 | 10.03 | 10.03 | 3.21 | 2.81 |
| 2033 | 14.65 | 10.46 | 10.46 | 3.35 | 2.93 |
| 2034 | 15.28 | 10.91 | 10.91 | 3.49 | 3.06 |
The geographical landscape for the Electronic Health Records (EHR) market in North America is dynamic and robust, reflecting a well-established and technologically advanced healthcare environment. The United States is a dominant force in the North American EHR market, with a robust healthcare system and widespread adoption of digital health technologies. The implementation of EHRs is driven by regulatory initiatives, such as the HITECH Act, which incentivizes healthcare providers to adopt electronic records.
The geographical landscape for Electronic Health Records (EHR) in Europe showcases a diverse and evolving environment characterized by various initiatives, regulations and technological advancements. The geographical landscape for EHR in Europe reflects a region actively working towards a more interconnected and patient-focused healthcare environment. While facing interoperability challenges, the collaborative efforts of EU member states, national strategies, and adherence to privacy regulations contribute to the growth and advancement of electronic health records in Europe.
The geographical landscape for Electronic Health Records (EHR) in the Asia Pacific region is characterized by well-established digital health ecosystems in some countries and emerging adoption in others. Government initiatives, collaboration between sectors, and efforts to address interoperability challenges are shaping the trajectory of EHR adoption in this diverse and dynamic region. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telehealth services in the Asia Pacific. EHR systems are adapting to support virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and the secure exchange of patient information to facilitate remote healthcare delivery.
Key players create a vibrant, competitive Electronic Health Records (EHR) market landscape. This dynamic neighborhood of EHR providers showcases a mix of pioneers, innovators, and community builders, each contributing uniquely to the competitive landscape.
Susan Albano, CEO of Prime Healthcare, in an interview, shared that implementing athenahealth, an electronic health record, provided numerous benefits to the organization. The organization embraces value-based care through provider engagement, having good contracts with the payers, and having access to data. She said that the usable, reliable, and available information will help the organization manage its patients.

By Type
By Product
By Business Models
By End-User
By Region
March 2026
March 2026
March 2026
February 2026
