February 2026

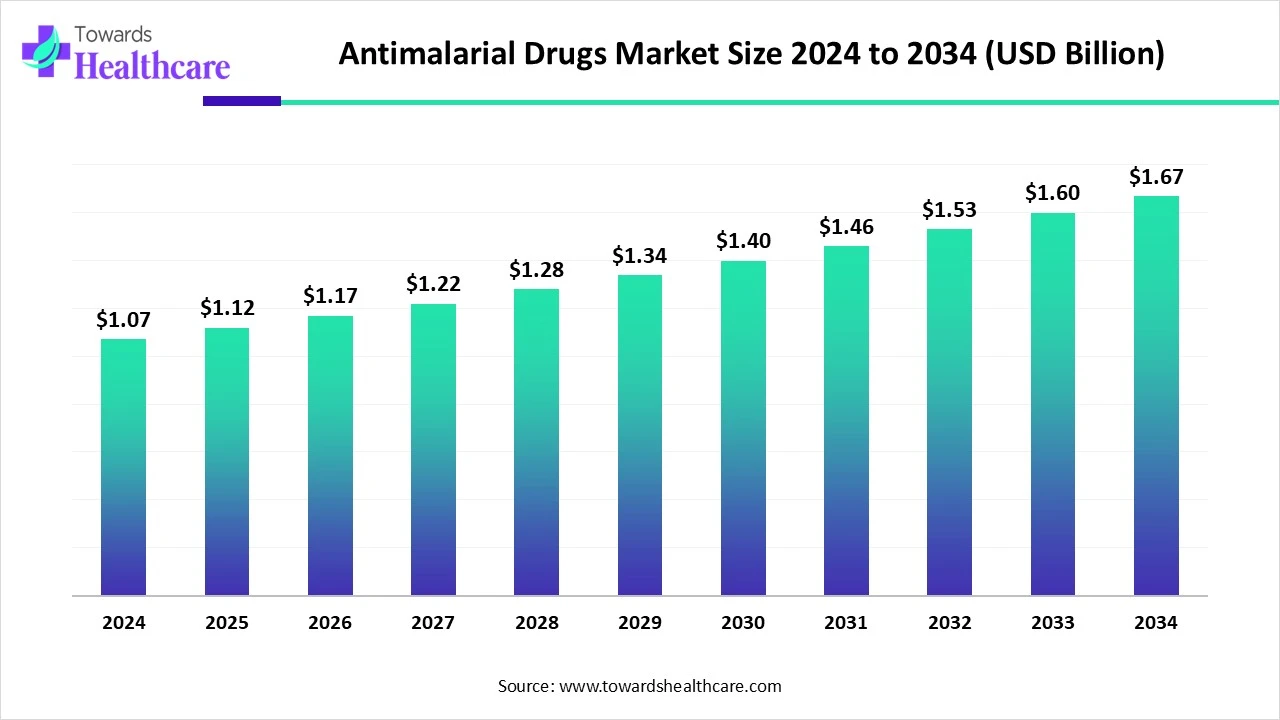
The global antimalarial drugs market size is calculated at US$ 1.07 in 2024, grew to US$ 1.12 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach around US$ 1.67 billion by 2034. The market is expanding at a CAGR of 4.57% between 2025 and 2034.
From 2020-2025, Africa, mainly South Africa and Nigeria, has been experiencing a growth in malaria cases and deaths, which are highly fueling demand for preventive measures and advanced treatment approaches. Whereas, around the globe, different steps in malaria prevention are going on, such as WHO-powered eradication programs, rising resistance to conventional therapies, and R&D in next-generation combination therapies and vaccines. The global antimalarial drugs market will have immense future opportunities in the development of combination therapies, like artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs). This further helps in exploring and improving the efficiency and efficiency and resistance profile of ACTs.
| Table | Scope |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.12 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 1.67 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 - 2034) | 4.57% |
| Leading Region | Africa 55% |
| Market Segmentation | By Drug Class, By Mode of Action, By Route of Administration, By Application, By Distribution Channel, By Region |
| Top Key Players | Novartis AG, Sanofi, Cipla Ltd., Ipca Laboratories Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Lupin Limited, Zydus Lifesciences, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals, Ajanta Pharma Ltd., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Mylan/Viatris, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Amneal Pharmaceuticals, Strides Pharma Science Ltd., Hetero Drugs Ltd., Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Alkem Laboratories Ltd. |
The antimalarial drugs market focuses on pharmaceutical treatments designed to prevent and cure malaria, a parasitic infection caused by Plasmodium species and transmitted through Anopheles mosquitoes. These drugs target different life stages of the parasite (liver stage, blood stage, and gametocytes) to either prevent infection (chemoprophylaxis) or cure the disease. Global demand is shaped by high malaria burden in Africa and parts of the Asia-Pacific, WHO-led eradication programs, growing resistance to traditional therapies, and R&D in next-generation combination therapies and vaccines.
In the prospective view, AI has a huge application and importance in the emerging markets, such as its widespread adoption can transform antimalarial drug development. In this process, AI-powered tools support expanding the detection and improvements in the potential drug molecule. Recently, by employing deep learning tools, DeepMalaria, a deep learning model, has been established. This helps in the prediction of the anti-Plasmodium falciparum inhibitory properties of compounds using their SMILES (Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System).
For instance,
Evolving Awareness and Government Initiatives
Primarily, the global antimalarial drugs market is fueled by a rise in public awareness campaigns, which are highly involved in educating people regarding malaria prevention and its robust treatment. This leads to major demand for novel and effective antimalarial drugs. Another crucial driver contributing to the market development is the escalating government initiatives in controlling and eliminating malaria. This comprises heavy funding for research and development, distribution of drugs, and public awareness campaigns.
Limitations in Healthcare Systems
Around the world, the emergence of major challenges is impacting overall market growth. Inclusion of the shortage of the healthcare system, including a lack of well-developed healthcare infrastructure in different malaria-endemic areas. These areas further lag due to limitations in sufficient diagnostic and treatment facilities, along with a shortage of specialized medical professionals.
Developments in Combination Therapies
During 2025-2034, the global antimalarial drugs market will have numerous and prominent opportunities, especially in the development of combination therapies. Recently, the WHO has recommended 6 diverse artemisinin-derived combination therapies for treating P. falciparum malaria. This further acts as assistance for researchers to explore and boost the efficiency and resistance profile of ACTs. Along with this, the growing developments in antimalarial drugs for pregnant women and young children. This is also accelerating many strategies, such as chemoprophylaxis and intermittent preventive therapy.
The aminoquinolines segment registered dominance in the global market in 2024. As this drug class has a long history regarding its applications in continuous pharmacovigilance, it is widely recommended in the growing malaria cases. Additionally, aminoquinolines are comparatively affordable, which fuels their widespread accessibility in resource-limited areas. Whereas, chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine have been applied for decades to treat malaria, which have strong effectiveness in inhibiting the parasite's growth and replication.
On the other hand, the artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) segment is predicted to expand at a rapid CAGR during the forecast period. As this drug class is currently recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), it acts as the first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria. A major benefit of these drug combinations, enable various mechanisms of action, which resolve the development of resistance to artemisinin and its partner drugs. Popular examples of ACTs encompass artemether-lumefantrine, artesunate-amodiaquine, and artesunate-mefloquine.
In the global antimalarial drugs market, the blood schizonticides segment dominated with a major share in 2024. This kind of mode of action particularly targets the parasite's asexual blood stages, which are significant causes for the symptoms of malaria. Furthermore, they support stopping the disease progression, preventing the development of severe malaria, and minimizing the risk of transmission. Inclusion of artemisinin and its derivatives, quinoline-based drugs, and other drugs is highly involved in these mechanisms.
And, the gametocytocidal agents segment is estimated to grow rapidly in the projected period. The segment is mainly driven by its direct targeting and killing of gametocytes, which prevents them from being taken up by mosquitoes during a blood meal. This eradication of gametocytes is important in the minimization of malaria transmission and prevention of further spread of drug resistance. For robust malaria prevention, Primaquine is the only drug recently recommended by the WHO for gametocytocidal therapy.
By route of administration, the oral segment led the antimalarial drugs market in 2024. As this route of administration is convenient and easy for patient compliance is fueling its wider adoption in novel drug development. This mainly comprises numerous antimalarial drugs, especially artemether-lumefantrine (Coartem), atovaquone-proguanil (Malarone), quinine, and mefloquine. As well as in the comparison with other routes, this segment widely assists in reducing hospital visits, is highly and easily accessible in advanced pharmacies, and also impacts its overall progression.
The injectable segment is anticipated to expand rapidly during 2025-2034. The segment is propelled by a rise in the need for efficient treatment of severe malaria, mainly in regions with high malaria burden such as sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. However, Artemether is used intramuscularly, which is a crucial injectable antimalarial, often employed as a backup for severe cases or when the oral route has limitations. This route has many advantages over oral, like high bioavailability, less time required for essential results, and reduced adverse or side effects which usually occur in oral administration.
In 2024, the treatment segment dominated the market by capturing a major share. A prominent usage of these drugs is to treat and mitigate malaria, which is emerged due to Plasmodium parasites and transmitted through mosquito bites. Along with ACTs, artemisinin is also used intravenously or intramuscularly in the treatment of severe malaria, particularly in cerebral malaria. Other treatments, like Mefloquine and other drugs, are employed in the treatment of chloroquine-resistant malaria.
And, the prophylaxis segment is estimated to expand at the fastest CAGR in the upcoming era. This mainly focused on travelers and the military use. The emergence of different types of prophylaxis, including causal prophylaxis, which acts on the parasite in the liver, as it can further infect red blood cells. In this case, tafenoquine and primaquine are increasingly used. Another type is blood schizonticide prophylaxis, which targets the parasite within red blood cells; this further needs a longer duration of use after travel. Well-known prophylactic drugs such as Atovaquone-proguanil and doxycycline are assisting overall market growth.
By distribution channel, the hospital pharmacies segment accounted for the biggest share of the global antimalarial drugs market in 2024. A provision of specialized and tailored treatments within healthcare settings is mainly influencing the expansion of hospital pharmacies. Alongside, they support in ensuring the quality, efficacy, and safety of antimalarials through stringent quality control, inventory management, and alliance with medical teams. Moreover, hospital pharmacies are providing patient education and monitoring to expand treatment adherence.
Whereas the online pharmacies segment is predicted to grow rapidly during 2025-2034. Nowadays, developing digital health technologies and raising awareness about these technologies among the public is fueling the growth of these online pharmacies, mainly in urban areas. Additionally, they provide convenient ordering of drugs at home, which further makes it attractive to urban consumers who are looking for a feasible way to get antimalarial drugs. A wide range of transformations in e-commerce platforms is boosting the expansion of online pharmacies as a distribution channel for numerous products.
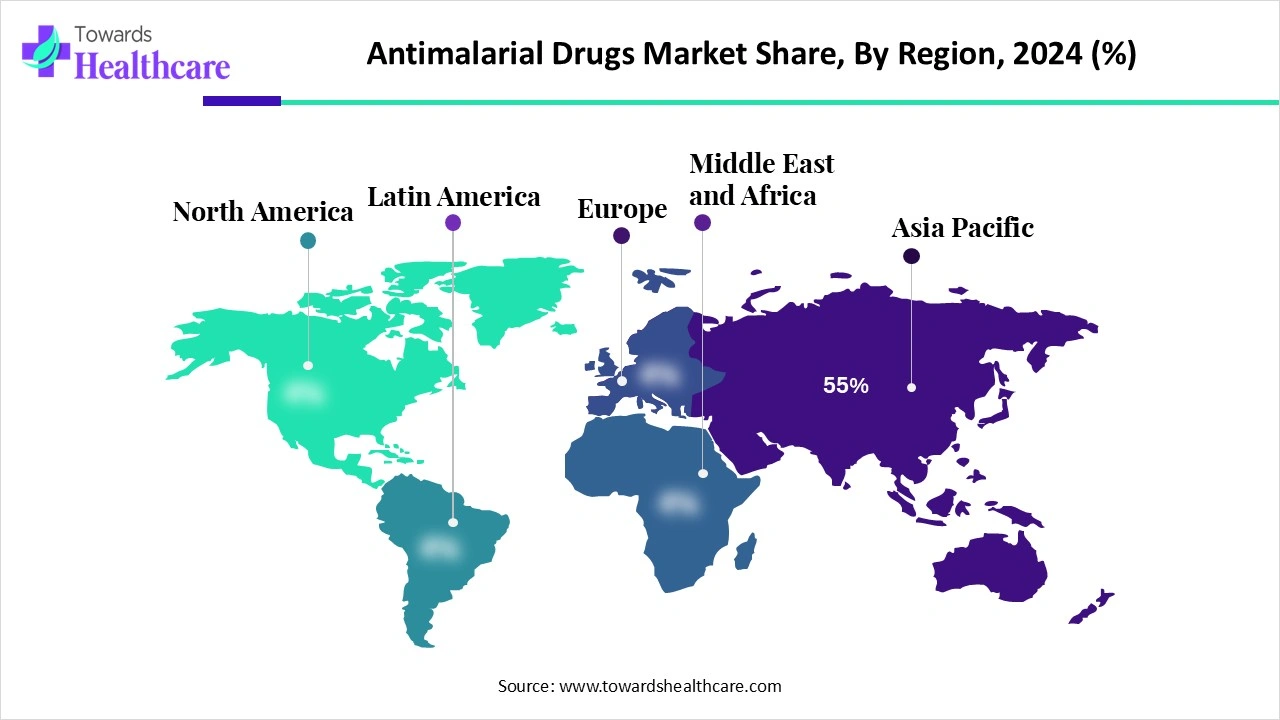
Africa was dominant in the global market share by 55% in 2024. Involvement of several factors, especially a rise in the burden of malaria with millions of cases and deaths annually, mainly in Sub-Saharan Africa, is fueling greater demand for novel and rigorous antimalarial treatment approaches. As well as, governments in this region are stepping into malaria control and eradication programs. Primarily involved organizations are the World Health Organization (WHO), Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV), the RBM Partnership to End Malaria, and the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC).
A huge expansion in the malaria cases and deaths in South Africa is mainly fueling demand for both generic and branded anti-malarial drugs, as generics often dominate due to their cost-effectiveness and availability. This region’s government and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are acting as a significant pillar in procurement and distribution, especially in resource-limited settings.
In this region, wider involvement of the Federal Ministry of Health in scaling up access to antimalarial treatments is acting as a vital driver in the market. As well as the presence of key players, including the private sector, primarily patent medicine vendors (PPMVs), and pharmacies, with a significant shift towards quality-assured Artemisinin-based Combination Therapies (ACTs), is propelling the overall market development.
During 2025-2034, the Asia Pacific is estimated to register the fastest expansion in the antimalarial drugs market. In India, China, and other areas of Southeast Asia, fostering innovations in new drug classes by wide-range investments in R&D. This trend also includes highlighting drug resistance and how to improve overall treatment effectiveness. As well as further putting efforts into the integration of surveillance and elimination strategies, which are going to be executed for optimizing malaria control and eradicating malaria.
In this sector, with the emergence of investment and participation of scientific research personnel discovery of new candidates, their further developments are being catered to. This also expands the study of drug resistance and optimizing treatment efficacy.
Key Players: Novartis AG, Cipla, Fosun Pharma, Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV), and Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi), etc.
This usually occurs through the developed supply chains, in which hospitals often receive drugs from respective regional stores and pharmacies acquire from different sources, such as wholesalers or direct suppliers.
Key Players: Max Healthcare, Hiranandani Hospital, IndiaMART, Unicure Remedies Pvt Ltd, and Skymax Life Science Pvt Ltd, etc.
Across the globe, different campaigns are making efforts to educate people regarding malaria symptoms, prevention, and medications. Alongside, through the programs they are distributing insecticide-treated bed nets, offering intermittent preventive treatment for pregnant women, or educating communities to reduce mosquito breeding.
Key Players: Seasonal Malaria Chemoprevention (SMC), Mass Drug Administration (MDA), PAHO, NIH, etc.

By Drug Class
By Mode of Action
By Route of Administration
By Application
By Distribution Channel
By Region
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
