February 2026

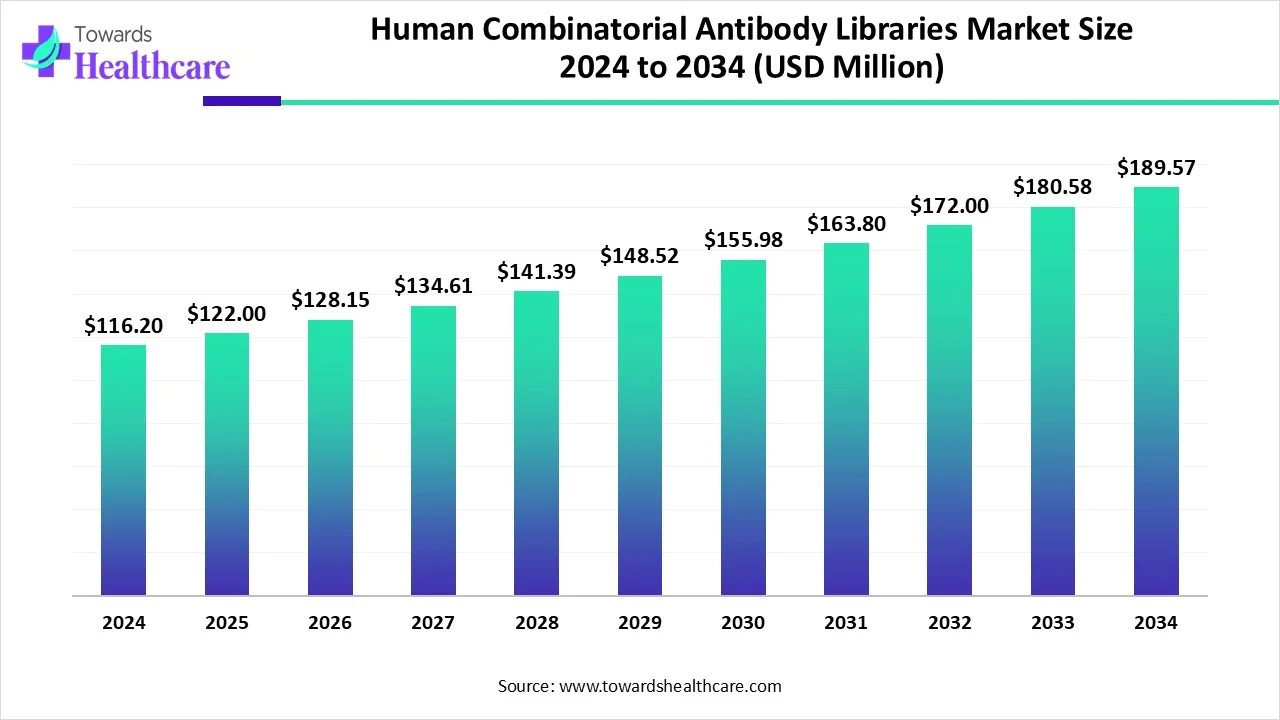
The global human combinatorial antibody libraries market size is calculated at US$ 116.2 in 2024, grew to US$ 122 million in 2025, and is projected to reach around US$ 189.57 million by 2034. The market is expanding at a CAGR of 5.04% between 2025 and 2034.
The human combinatorial antibody libraries market is rapidly expanding because of the growing demand for targeted therapies in therapeutics and diagnostics. North America is dominated in the market as pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies are growing funding for the development of monoclonal antibodies. Asia Pacific is fastest fastest-growing due to the strong R&D infrastructure and regulatory support, as well as the increasing trend of personalized medicine.
The human combinatorial antibody libraries market is rapidly growing because this technology signifies a significant tool for designing and discovering antibodies that bind targets with high specificity and affinity. The major advantage of this technology is the direct link that exists between the experimental phenotype and its encapsulated genotype, which permits the development of the designated binders in the enhanced molecules. By using this technique, antibody genes have been cloned from many species or expressed directly from large man-made ranges of antibody-encoding genes.
Advanced studies indicate that the technique allows for the in vitro evolution of antibodies to create molecules whose affinity for an antigen surpasses that of experimental. HuCAL antibody libraries are widely considered for their sequencing, numerous selection experiments, and expression behaviour against a broad range of antigens. Combinatorial antibodies play an important role in the design of vaccines and novel antiviral agents. These antibodies also offer an opportunity to determine receptor function in vivo and serve as templates for the design of various molecules.
AI integration in human combinatorial antibody libraries is driving the growth of the market as AI-driven and ML-powered technology are allowing rapid and engineering identification of improved-quality therapeutic antibody leads. The sector of antibody discovery is undergoing a transformative shift through the integration of advanced technology such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Powerful AI and ML computational procedures are intensely speeding up and refining antibody discovery and development workflows, helping to increase the probability and speed of finding high-quality therapeutic antibody drugs. By integrating advanced AI and ML computational strategies with wet-lab validation, high-quality antibody leads are optimized and identified faster. These methods are being used to quickly humanize leads, support discovery through precise design of variants, and increase focused screening libraries, lowering timelines, expenses, and risk for downstream manufacturing and developability challenges.
Increasing Mitochondrial Disease Cases
The growing significance of therapeutic mAbs is clear, as they now represent the main treatment option for many diseases. Therapeutic antibodies have become a fundamental part of modern medicine, offering targeted and effective therapies across various conditions. Their influence on fields such as oncology, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, personalized medicine, and rare diseases underscores their increasing role in healthcare. This expanding importance drives the need for rapid discovery platforms like combinatorial libraries, which in turn fuels the growth of the human combinatorial antibody libraries market.
Major Limitation of mtDNA
Challenges include recovering all antigen-specific antibodies, ensuring correct heavy and light chain pairing, and enabling high-throughput production. Moreover, immune libraries often require animal immunization or complex sourcing of human lymphocytes, which restricts the growth of the human combinational antibody libraries market.
Increasing Application of mtDNA in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Combinatorial antibody libraries enable detailed analysis of immune response outputs, helping us understand how the adaptive immune system manages infections when there isn't enough time to develop mature antibody responses. They have become essential tools for creating therapeutic antibodies, some of the most successful drugs. These libraries are made from mRNA or RNA obtained from B cells of either immunized or naïve donors. Since the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light (VL) chains, which encode the immunoglobulin repertoire, are well known, PCR can be used to facilitate their construction, opening up opportunities in the combinational antibody libraries market.
By applications, the oncology segment dominated in the human combinatorial antibody libraries market in 2024, as combinatorial antibody libraries have the significant strength to display the whole immunological record of a patient, enabling to identification and recovery of any antibody ever made, regardless of whether it is currently being produced. Combinatorial antibody libraries are broadly applied for the separation of therapeutic antibodies and reagents. Combinatorial antibody libraries from cancer patients yield ligand-mimetic Arg-Gly-Asp-containing immunoglobulins that hinder breast cancer metastasis.
The neurosciences segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period, 2025 to 2035, as antibodies are applied in neurosciences to research disease markers, cellular differentiation, and neuronal markers linked with the nervous system. Antibody libraries are significant resources to derive antibodies to be used for a broad range of applications, from functional and structural studies to intracellular protein interference studies to emerging novel diagnostics and therapeutics. Neural antibodies particularly recognize and label molecules on nerve cells, aiding in separating and recognizing different nerve cells and finding their roles.
By end-users, the pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment is dominant in the human combinatorial antibody libraries market in 2024, as antibody library technologies are used to produce diverse collections of antibodies for research, diagnostics, and medicinal purposes. This methodology allows the detection and screening of antibodies with designed properties, such as high affinity and specificity for a designed molecule. There are various types of antibody library technologies, including yeast display, phage display, mammalian cell display, and ribosome display.
The diagnostic labs segment is expected to fastest-growing over the forecast period 2025 to 2035 as combinatorial antibodies have become a significant component of many diagnostic assays. The capability of antibodies to bind a practically infinite number of target proteins with high specificity always meant they were destined to be used as therapeutics. Antibody libraries are applied to discover antibodies for diagnostic tests, including point-of-care devices and immunoassays.
North America is dominant in the human combinatorial antibody libraries market with the largest revenue share, as North America has a favourable regulatory environment for the healthcare system, which goals to avoid medical risk, enhance patient results, and preserve trust in the medical care system. Healthcare regulations and standards serve to safeguard the rights and interests of patients, with confidentiality and privacy, which speeds up the clinical transition of antibody-based drugs. Also strong presence of healthcare companies such as Labcorp, Charles River, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. This key player provides various services like antibody library screening, preclinical evaluation, and construction, which contribute to the growth of the market.
For Instance,
In the U.S., growing demand for targeted therapies due to increasing cases of cancer, rare diseases, and other chronic diseases. The targeted therapies have transformed the treatment of cancer and other diseases, providing enhanced efficacy with lower side effects as compared with traditional chemotherapy and treatment, increasing demand for human combinatorial antibody libraries for the development of targeted therapies.
In Canada, growing healthcare spending and government support of the healthcare sector drive the development of combinatorial antibody libraries. For Instance, in October 2022, Entos received a $15.5 million grant from the Government of Alberta’s Vaccine Manufacturing Program to support the province’s innovation and technology strategy. Of that $15.5 million grant, $7.6 million will be used toward this project. Also, increasing collaboration between public and private research institutes drives the growth of the market.
The Asia Pacific region is projected to experience the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period, because the socioeconomic conditions, growing technological advancements, and the regulatory landscape will eventually transform medical care delivery in APAC, which will improve optimization, screening, and design of antibodies. Governments are presenting a robust desire to speed up healthcare R&D. For Instance, the Healthy China 2030 initiative plans to meet the requirements of an aging population, which causes growth of the market.
China’s research and innovation capabilities in biotechnology are increasing domestic demand in chemicals, healthcare, energy, agriculture, and other fields. China’s R&D expenditure is growing, directed toward advanced technologies like mRNA vaccines, cell and gene therapies, and artificial intelligence (AI) in drug discovery. In 2023, 58% of novel drugs developed by Chinese companies were biologics, which drives demand for human combinatorial antibody libraries.
India is speedily becoming a global hub for biosimilars and biologics, leveraging expertise in making affordable and high-quality therapies and treatments for the regulated sector. India provides strong opportunities for public-private partnerships, supported by institutions such as DBT-BRIC institutes for fostering collaborative R&D for the expansion of advanced biotech solutions, which drives the growth of the market.
Europe is expected to grow significantly in the human combinatorial antibody libraries market during the forecast period, as government bodies in Europe are actively encouraging the biotech sector through streamlined frameworks such as the EU Biotech Act. These trends position Europe as a global leader in biotech innovation and investment. Europe shows an excellent growth opportunity for small biotechs looking to commercialize their novel, patented pharmaceuticals.
For Instance,
The application of antibody-based pharmaceuticals is growing in Germany, driven by progress in research, development, and the increasing demand for targeted therapies, specifically in cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders. Presence of major biotech key players in Germany drives the growth of the market such as YUMAB, a worldwide provider of fully human monoclonal antibody development and discovery, has relocated its headquarters to Germany’s hotspot of infectious research and is advancing novel opportunities for the expedited adavancement of prophylactic and therapeutic antibodies and vaccines to fight against infectious diseases, which increases the demand of human combinatorial antibody libraries.

In April 2025, Hesham Abdullah, Senior Vice President, Global Head Oncology, R&D, GSK, states, “approval of Blenrep combinations in the UK is a transformative milestone for patients with multiple myeloma, a cancer marked by remission and relapse. As the only BCMA-targeted ADC therapy, Blenrep has the potential, supported by robust phase III data, to extend survival and remission versus standard of care and redefine treatment at or after first relapse.” (Source GSK)
By Application
By End User
By Region
February 2026
February 2026
January 2026
December 2025
