February 2026

The global humanized mouse and rat model market size is calculated at US$ 278.16 million in 2025, grew to US$ 300.83 million in 2026, and is projected to reach around US$ 608.92 million by 2035. The market is expanding at a CAGR of 8.15% between 2026 and 2035.
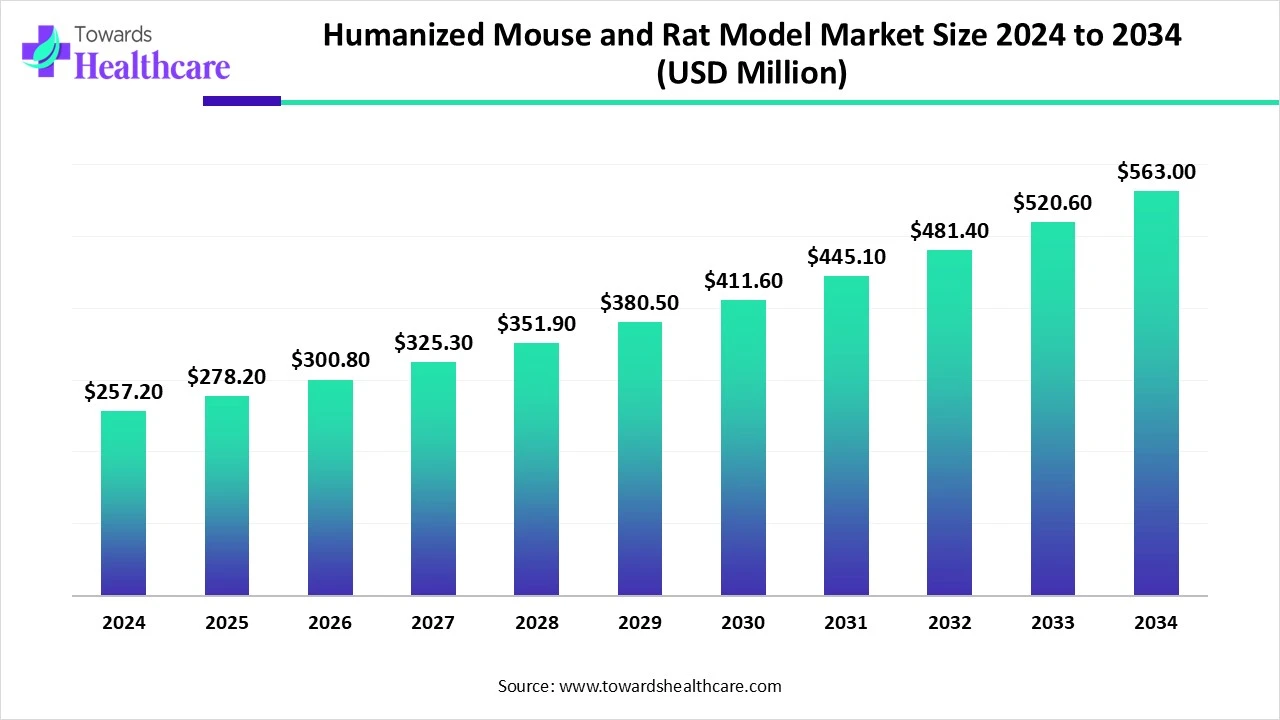
The humanized mouse and rat model market is witnessing significant growth in 2025, driven by the growing demand in immuno-oncology, infectious disease research, and drug discovery for highly predictive preclinical models. Compared to traditional animal models, these models, which are designed to carry human gene tissues or immune systems, offer greater translational relevance.
Widespread adoption in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries is being driven by technological developments in gene editing tools like CRISPR, as well as growing use in personalized medicine and immunotherapy development. Expanding applications in vaccine testing and rare disease modeling, as well as growing investments from drug developers and contract research organizations (CROs), all support the market's upward trend. The market is still strong because of continuous innovation and strategic industry partnerships, even in the face of obstacles like high costs and moral dilemmas.
| Table | Scope |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 300.83 Million |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 608.92 Million |
| CAGR (2026 - 2035) | 8.15% |
| Leading Region | North America share 48% |
| Market Segmentation | By Model Type, By Application, By Species, By End User, By Region |
| Top Key Players | Taconic Biosciences.Inc, The Jackson Laboratory, Charles River Laboratories, Hera BioLabs, Envigo, GenOway, Harbour BioMed, Crown Bioscience, Vitalstar Biotechnology, Bicytogen Pharmaceuticals, Yecuries Corporation, Champions Oncology, Abnova Corporation,Oncodesign Services, ImmunoPrecise Antibodies, Tacrogen Biotech, Ingenious Targeting Laboratory, Biomedical Research Models, TransGenic Inc., SAGE Labs |
The humanized mouse and rat model market focuses on the development and commercialization of rodent models that carry functional human genes, cells, tissues, or immune systems. These models are essential for preclinical evaluation of immunotherapies, infectious diseases (like HIV and COVID-19), oncology drugs, gene therapies, and transplantation research. Humanized rodents bridge the gap between in vitro testing and human clinical trials, offering a more predictive model of human biological response. The growing demand in precision medicine, biologic drug development, and immuno-oncology is fueling this market.
In the market, artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming a potent enabler that improves everything from data interpretation to model development. By anticipating the best gene-editing techniques and modeling biological outcomes prior to lab work starting, AI-driven platforms are being used to create genetically modified models more effectively. Shorter development periods, less trial-and-error work, and lower R&D expenses result from this.
AI is transforming data collection, analysis, and interpretation in preclinical research. Machine learning tools increase throughput and decrease human error by automating the monitoring of tumor growth, immunological responses, and physiological changes in live animals. More accurate clinical outcome predictions are made possible by this technology's ability to extract significant patterns from complicated datasets such as gene expression profiles or treatment responses. Researchers can more accurately model human disease mechanisms and drug interactions by combining AI with humanized models. This will ultimately increase the success rate of clinical translation and quicken the pace of personalized medicine.
Rising Demand for Personalized Medicine
Scientists need animal models that closely resemble human physiological and immunological responses as personalized medicine gains traction. By expressing human genes in cells or tissues, humanized mice and rats aid in bridging the gap between laboratory and human results. Research on rare diseases, autoimmune diseases, and oncology is seeing an increase in demand as customized treatments become more common.
Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
The degree of biological integration between humans and animals is a delicate ethical issue that is brought up by humanized animal models, particularly when those models contain human tissues or immune systems. Research involving these models must be conducted under stringent animal welfare regulations in a number of nations, which also demand thorough documentation, ethical approvals, and supervision. Some organizations may be discouraged from investing in humanized models due to the potential for project timeline delays and administrative complexity caused by these regulations. In some areas, funding and policy decisions may also be influenced by public opposition to genetic modification and animal testing.
Rising Demand in Oncology and Immunotherapy Research
As cancer immunotherapies gain popularity around the world, there is an increasing demand for models that accurately mimic human immune responses. A crucial platform for testing CAR-T cells, checkpoint inhibitors, and antibody therapies is provided by humanized mice, especially those with reconstituted human immune systems. Such models will become more and more in demand as cancer pipelines spread throughout the world. Preclinical validation of these models will become more and more important for biotech companies investing in customized cancer treatments.
The humanized immune system (HIS) models segment dominated the humanized mouse and rat model market owing to their essential for research on autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and immuno-oncology because of their capacity to closely resemble the human immune response. These models support more precise preclinical drug development by allowing researchers to examine the relationship between human immune cells and disease mechanisms in vivo. Pharmaceutical companies' increasing use of this technology for checkpoint inhibitor research and vaccine development solidifies their market-leading position.
The humanized liver models segment is the fastest-growing because of their growing use in the study of infectious diseases like hepatitis B and C drug drug-induced hepatotoxicity, and liver metabolism specific to humans. These models for assessing drug safety and pharmacokinetics are becoming more and more popular due to the growing need for precision drug testing, and personalized medicine improvements in xenotransplantation methods are also increasing the repeatability and dependability of liver humanization, which is increasing the rate of adoption.
The oncology segment dominated the humanized mouse and rat model market in 2024, driven by the need for precise preclinical tumor models, the increased incidence of cancer, and the worldwide focus on cancer research. Humanized mice are essential for testing new immunotherapies and targeted treatments because they allow the study of tumor growth, metastasis, and immune evasion in a setting similar to that of humans. For preclinical efficacy studies, pharmaceutical and biotech companies mainly rely on these models, which strengthens their market dominance.
The infectious diseases segment is expected to be the fastest-growing during the forecast period, fueled by growing risks from emerging infections, viral outbreaks, and antibiotic resistance. Humanized mouse and rat models are becoming indispensable for assessing vaccines and antiviral treatments as well as for comprehending pathogen-host interactions. Investments in these areas have increased due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the resurgence of illnesses like TB and the Zika virus, which have pushed for quick adoption in both academic and commercial research settings.
The mice segment was the dominant species in the humanized mouse and rat model market due to their genetic similarity to humans, cost-effectiveness, shorter breeding cycles, and well-established protocols for genetic manipulations. They are the go-to option for both academic and commercial research because of their adaptability in simulation a wide range of human diseases and the availability of multiple well-established HIS and liver humanization techniques. The dependability of humanized mouse models in drug development pipelines is further increased by a wealth of literature and validation data.
The rats segment is projected segment is expected to be the fastest growing during the forecast period, owing to their size, which makes advanced imaging studies, repeated blood sampling, and surgical procedures easier. Recent developments in technology have increased the effectiveness of rat humanization, increasing their suitability for intricate research in neurodegenerative diseases, toxicology, and pharmacology. They are becoming more and more relevant in translational studies due to their physiological resemblance to humans, particularly in cardiovascular and metabolic research.
The pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies segment dominated the humanized mouse and rat model market in 2024 as they made significant investments in 0reclinical drug discovery validation and regulatory submissions using humanized mouse and rat models. To lower the risk of late-stage failures, these businesses use humanized models to close the translational gap between in vitro research and clinical trials. The need for advanced HIS and liver models has increased due to the rise in biologics, cell therapies, and immunotherapies.
The contract research organizations (CROs) segment is estimated to be the fastest-growing end-user segment, fueled by growing preclinical research outsourcing trends. Small and mid-sized biotech companies without internal facilities find CROs appealing because they provide specialized, scalable, and affordable humanized model services. Key elements driving this growth are the development of international CRO networks and their capacity to provide quick turnaround on intricate humanized model studies.
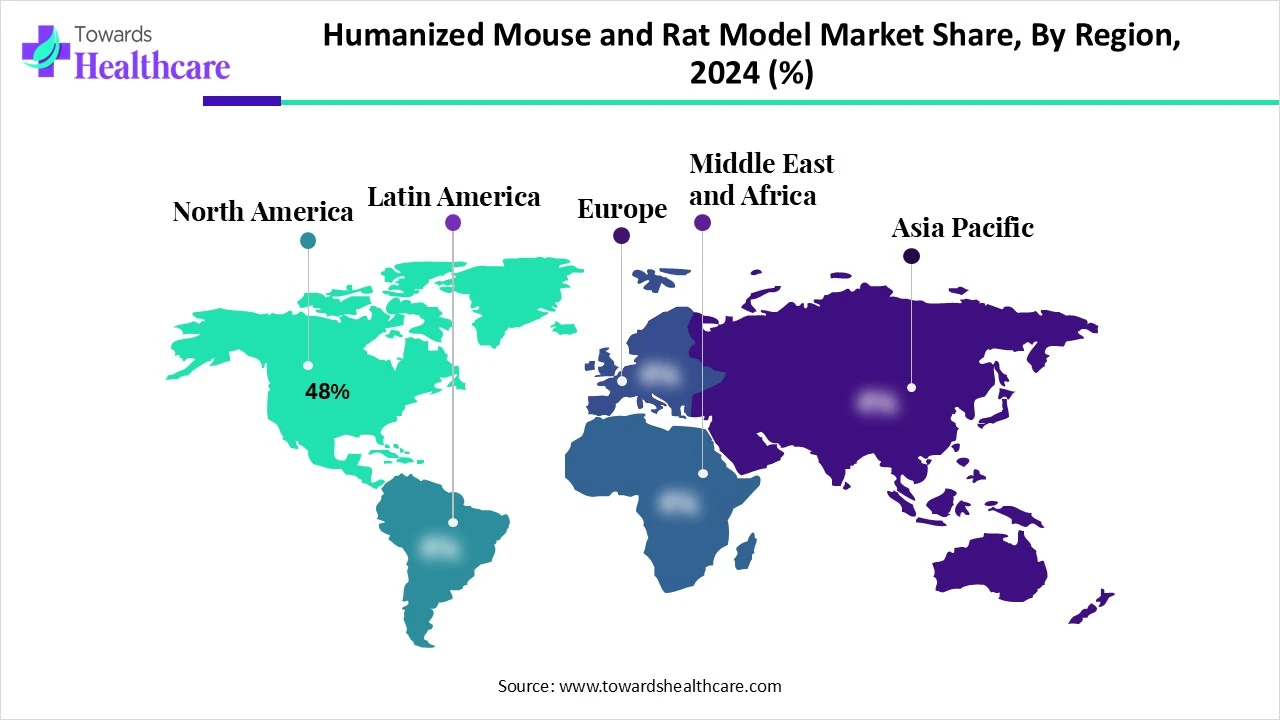
North America dominates the humanized mouse and rat model market share by 48% in 2024, because of the presence of top pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and CRO companies, its strong funding from the public and private sectors, and its strong biomedical research infrastructure. The areas have led the way in implementing humanized models for research in immunology, infectious disease, and oncology, thanks to advantageous regulatory frameworks and a large number of highly qualified researchers.
The U.S. market is witnessing steady growth, fueled by the nation's robust biomedical research infrastructure, substantial government and private investment funding, and the existence of top academic biotechnology and pharmaceutical institutions. Since regulatory agencies have acknowledged the predictive accuracy of humanized models in investigational new drug (IND) submissions, their use in preclinical drug development is growing in oncology, immunology, and infectious disease research. The significance of genetic engineering technologies in the country's drug discovery and development pipeline is being cemented by developments like CRISPR, which are increasing model precision and broadening their uses in co-clinical trials and personalized medicine.
The Canada market is growing steadily, supported by expanding biomedical research programs, increasing investment in preclinical studies, and strong collaboration between academic institutions and the life sciences industry. Advancements in genetic engineering and rising demand for precision medicine are further boosting the adoption of these models in drug discovery and therapeutic development.
Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing region during the forecast period, driven by growing biopharmaceutical industries, increased investments in life science research, and encouraging government programs. Access to advanced humanized model technologies is becoming easier due to the rapid advancements in genetic engineering and laboratory animal facilities. Further driving market expansion are CRO expansions in the areas and growing partnerships with foreign research institutes.
China's market is expanding rapidly, driven by the expansion of the domestic biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, increased R&D investment, and robust government support for biomedical innovation. The growing application of these models in research on infectious diseases, immunology, and oncology is strengthening their contribution to precision medicine and speeding up drug development.
The India market is growing with momentum, driven by expanding clinical research endeavors, encouraging regulatory changes, and an increase in partnerships between biopharma companies and academic research facilities. The integration of cutting-edge genetic engineering technologies and a growing emphasis on affordable preclinical solutions are propelling the broader use of these models in therapeutic research.
By Model Type
By Application
By Species
By End User
By Region
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
