December 2025

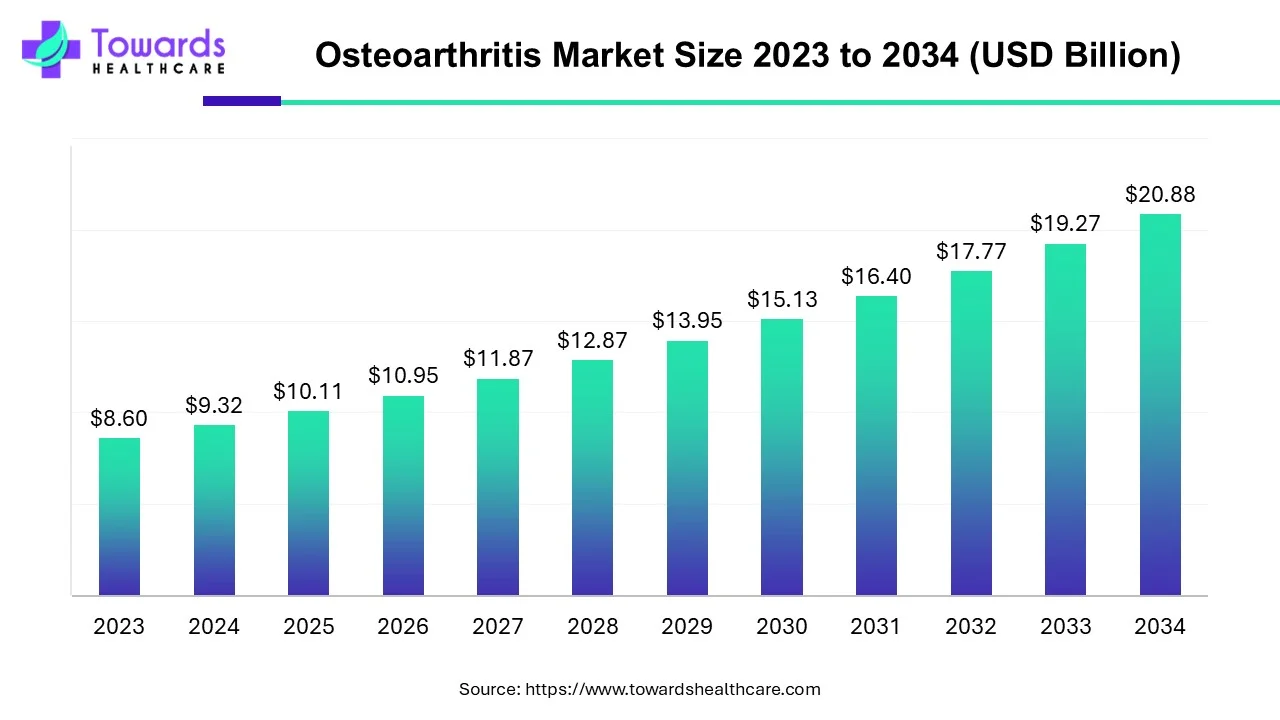
The osteoarthritis market size is anticipated to grow from USD 10.11 billion in 2025 to USD 20.88 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, osteoarthritis constituted 2.5% of the total health issues experienced by individuals in 2023, and it accounted for 20% of the overall burden attributed to musculoskeletal conditions.
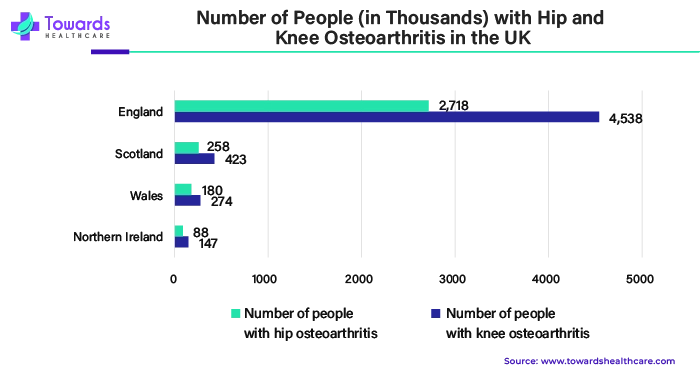
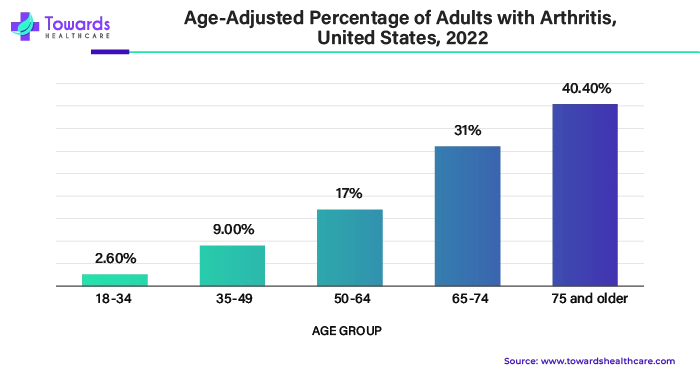
Osteoarthritis affects around 3.3 to 3.6% of people around the world. It's a significant cause of disability for about 43 million individuals, ranking it as the 11th most disabling condition globally. In the United States, around 80% of people over 65 show signs of osteoarthritis on X-rays, but only 60% of them feel symptoms. This is because changes in the X-ray images don't always mean the joint pain someone feels is directly caused by osteoarthritis.
A common joint ailment known as osteoarthritis develops when the layer of cartilage that protects the bony ends of your bones wears down over time. In the hands, hips, and knees among other afflicted joints, this may result in pain, stiffness, and decreased flexibility.
Proper treatment of osteoarthritis is crucial because it helps manage symptoms, improve joint function, and enhance overall quality of life. While it may not be curable, appropriate care can slow down the progression of the disease and alleviate discomfort. Treatment options include lifestyles modification like exercise and weight management, medications to manage pain and inflammation, and in some cases, surgical interventions. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing further joint damage and maintaining an active lifestyles.
Ignoring osteoarthritis can result in increased pain, reduced mobility, and potential disability. By managing the condition appropriately, individuals can lead more comfortable lives, staying active and enjoying daily activities without the limitations imposed by joint pain and stiffness. Regular medical check-ups adherence to prescribed treatments, and a healthy lifestyle are essential for managing osteoarthritis effectively.
As people get older, their joints can wear down, leading to a common condition called osteoarthritis. This is more likely to happen as we age. The increasing number of people dealing with obesity is significant factor. Carrying extra weight puts extra stress on joints, making them more prone to osteoarthritis.
For instance,
Imagine joints as cushions over time, they can become worn out. So, an aging population and rising obesity rates contribute to the growth of osteoarthritis cases. This condition mainly affects the knees, hips, and hands, causing pain and stiffness. As our population gets older and more people gets to struggle with excess weight, the demand for solutions to manage and treat osteoarthritis rises. Medical advancement and increased awareness are crucial in addressing this growing health concern. Research and innovation therapies aim to provide better options for those affected by osteoarthritis, enhancing the quality of life for many individuals.
Technological advancement plays a crucial role in shaping the market of osteoarthritis. These innovations primarily focus on developing more effective and patient-friendly therapies. One notable trend involves the rise of regenerative medicines, where stem cell therapy and tissue engineering offer promising avenues for repairing damaged joint tissues. These approaches aim to address the root cause of osteoarthritis, providing long-lasting relief.
For instance,
Minimally invasive procedures have gained popularity due to their reduced impact on patients. Arthroscopy, a common minimally invasive technique, involves small incisions and specialized tools to visualize and treat joint problems. Patients experience quicker recovery times and less postoperative discomfort compared to traditional open surgeries. The demand for such procedures is fueled by the growing preference for outpatient treatments and shorter hospital stays.
In Drug development, biologics have emerged as a breakthrough. These medications, derived from living organisms, target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process associated with osteoarthritis. This precision enhances treatment effectiveness while minimizing side effects. Advanced imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans, aid in early and accurate diagnosis, allowing healthcare professionals to intervene at the onset of symptoms. This proactive approach aligns 3D printing has revolutionized the production of customized implants. This technology enables the creation of patient-specific joint replacement, improving the overall fit and functionality. Customized implants contribute to better outcomes, especially in complex cases.
For instance,
Telemedicine now allows patients to easily connect with healthcare professionals to monitor and manage osteoarthritis. This virtual method boosts patient involvement, enables timely treatment, and eases pressure on healthcare systems.
Hyaluronic acid is a substance found naturally in our bodies, particularly in our joints and eyes. It acts like a lubricant and shock absorber, helping joints move smoothly and comfortably. In osteoarthritis, the cartilage that cushions our joints wears away, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. Hyaluronic acid injections are being used as a treatment for osteoarthritis to help ease these symptoms. When injected into the joint, hyaluronic acid acts as a lubricant, reducing friction and pain during movement. It also helps to improve the quality of the joint fluid, providing better cushioning and support.
Studies have shown that hyaluronic acid injections can help reduce pain and improve joint function in people with osteoarthritis, particularly in the knee.
The treatment is usually administered as a series of injections given over several weeks, and the effects can last for several months. Hyaluronic acid injections are generally considered safe, with minimal side effects such as temporary pain or swelling at the injection site.
Not everyone with osteoarthritis may benefit from hyaluronic acid injections, and it may not be suitable for those with certain medical conditions or allergies. It's essential to discuss with your healthcare provider if hyaluronic acid injections are right for you and to understand the potential benefits and risks.
For instance,
Hyaluronic acid offers a promising treatment option for osteoarthritis, providing relief from pain and improving joint function, thus helping people with osteoarthritis live more comfortably and actively.
Creating personalized therapy for osteoarthritis faces challenges because each patient's condition is unique. Traditional treatments often use a "one-size-fits-all" approach, but osteoarthritis can vary greatly from person to person. To make personalized treatments, scientists must thoroughly study and understand factors like genetic differences and the specific characteristics of each person's affected joints. Developing personalized therapies requires a lot of research and development. Scientists have to look closely at each patient's details, such as genetic markers and the specific conditions of their affected joints.
This in-depth understanding is needed for customizing treatments that address the specific nuances of osteoarthritis in an individual. The complexity of customization poses a significant challenge. Unlike mass-produced medications, personalized therapies require a more intricate approach. This complexity not only extends the time required for research but also increases the overall cost of developing these customized treatments.
Additionally, regulatory approval for personalized therapies adds another layer of complexity. Health authorities need robust evidence of safety and efficacy, which can be challenging to establish when dealing with individualized treatment. The aging population compounds these challenges osteoarthritis is more prevalent in older individuals, and as the global population ages, the demand for effective, personalized treatment is on the rise. This creates a sense of urgency for researchers and pharmaceutical companies to overcome the hurdles and develop innovative solutions.
The osteoarthritis market in North America includes factors like prevalence rates, treatment options, and healthcare infrastructure. In the United States, osteoarthritis is a big concern, especially among older people.
For instance,
There are many treatments available, from medications to surgery, and a lot of research is being done to find new therapies. Canada has similar trends, with more people getting osteoarthritis and efforts to improve access to care. There's a focus on finding better treatments and making sure people can get the care they need.
Osteoarthritis poses a significant health challenge in the Asia Pacific region due to reasons such as aging populations, increasing obesity rates, and improved awareness. Healthcare systems and treatment availability differ among countries, with some having better access to advanced therapies while others face barriers like cost and availability. Cultural and dietary practices also play a role in influencing osteoarthritis prevalence and management across the region.
For instance,
The osteoarthritis market involves companies making medicines, devices, and therapies for treating osteoarthritis. They compete by offering different products, prices, and marketing strategies. Factors like product effectiveness, safety, regulatory approvals, and brand reputation affect competition. Pharmaceutical companies make drugs like pain relievers and anti-inflammatories. Medical device makers create implants and braces for joint treatment. Biotech firms focus on innovative therapies like drugs that slow down osteoarthritis or help tissue regrowth. Healthcare providers also play a role by offering treatments like physical therapy and joint injections. The market is always changing due to research, new technology, and companies teaming up or buying each other. They aim to meet the needs of osteoarthritis patients and stay ahead of competitors.

By Type
By Diagnosis
By Treatment
By Geography
December 2025
November 2025
November 2025
November 2025