February 2026

The worldwide rapid genomic diagnostics market is experiencing significant expansion, with projections indicating a revenue increase reaching several hundred million dollars by the end of the forecast period, spanning 2025 to 2034. This growth is driven by emerging trends and strong demand across key sectors.
The significant growth of the quick genomic diagnostics industry has led to a rise in consumer interest, the development of precision medical approaches, and a decrease in sequencing costs. Additionally, the increasing need for rapid genetic testing is being driven by the need for better management of chronic illnesses, effective treatment planning, and early sickness diagnosis. Growing integration with digital health infrastructure, an emphasis on data security and protection, and alliances and collaborations between biotechnology companies, healthcare providers, research organizations, and academic institutions are further drivers driving the industry.
The rapid genomic diagnostics market comprises tools, technologies, and services used to quickly identify genetic variations and mutations for clinical decision-making, particularly in acute, life-threatening, or time-sensitive conditions. These diagnostics typically deliver results within 24–72 hours and are vital in areas like neonatal intensive care (NICU), rare disease diagnosis, oncology, infectious diseases, and pharmacogenomics. Advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS), rapid whole genome sequencing (rWGS), AI-driven analytics, and regulatory support are accelerating the market’s growth
Genetic diagnoses might be made rapidly with the use of an AI-based diagnostic agent and a genome interpretation system linked to genomic data. In other domains, including clinical genomics, a specific type of AI algorithm known as deep learning is used to understand large and complex genetic information. AI-powered genetic testing speeds up genome analysis, increases the accuracy of diagnoses, and supports preventative healthcare.
How is Demand for Precision Medicine Driving the Market?
In precision medicine, rapid genomic diagnostics offers numerous and noteworthy benefits. By enhancing disease prevention and prediction, streamlining treatment plans, and promoting health equity, genomic testing is revolutionizing the delivery of healthcare. As people become more informed and active in their medical journeys, genomic testing empowers them to take control of their health. By embracing the information provided by genetic testing, individuals can work with healthcare providers to create personalized strategies that enhance health and prolong life.
Data Privacy Concerns
Due to the rapid growth of genetic databases, concerns about data privacy and ethical use have grown. Leaks in genomic data can lead to identity theft, genetic discrimination, and inappropriate use of personal health information. Governments should enact strict regulations protecting data, and diagnostics service providers should follow strict guidelines and protections.
Rise of Multi-Omics
Diagnostic performance will be improved by developments in bioinformatic analysis and the integration of multi-omic approaches, as it becomes more and more clear that clinical testing and discovery research must be tightly integrated to optimize diagnostic benefits for current and future patients. A powerful diagnostic and predictive tool, multi-omics helps make sense of a complex, multifaceted disease like cancer. Using multiomics in conjunction with AI and ML is a highly successful way to diagnose and make predictions.
By test type, rapid whole genome sequencing (rWGS) segment dominated the rapid genomic diagnostics market in 2024. Whole genome sequencing enables faster and more precise molecular diagnosis, which results in the development of safer, more effective medications for better patient outcomes. Compared to other molecular diagnostic methods, whole genome sequencing has been shown to be the most thorough and effective approach to understanding the genetic mechanisms underlying disease. As a result, whole genome sequencing has emerged as a crucial instrument for studying illness, opening the door for the genomic medical revolution that is transforming epidemiology.
By test type, the targeted gene panels segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth rate during the forecast period. Gene panel sequencing is frequently used in clinical diagnostics to identify the genetic cause of rare disorders. It is rapid and cost-effective. As gene panels are increasingly employed as first-line testing for many genetic disorders, such criteria are necessary to maintain a high degree of quality, standardize testing among diagnostic laboratories, and reduce patient time to diagnosis.
By application, the rare & undiagnosed genetic disorders segment held the largest revenue of the market in 2024. Approximately 300–400 million individuals globally and 30 million Americans suffer from uncommon diseases, which can lead to early mortality, chronic illness, and disability. In recent years, exome sequencing, gene panels, and microarrays have all been employed to help identify the genetic cause of these rare and inexplicable diseases. Thanks to these technologies, a sizable portion of unidentified patients (25–35%) have been able to acquire a diagnosis, often with beneficial outcomes.
By application, the oncology segment is expected to grow at the highest rate during the predicted timeframe. A significant change in demand for individualized tumor diagnoses in everyday settings has been brought about by the growth of the cancer genomics sector. New concepts for early tumor diagnosis and prognosis have been made possible by the development of liquid biopsy. With liquid biopsies, changes in the genome and transcriptome may be precisely identified, offering a more thorough description of the diverse tumor profile.
By technology, the next-generation sequencing (NGS) segment led the rapid genomic diagnostics market in 2024. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has a wide range of diagnostic applications, from identifying novel microbiological organisms that cause epidemics to identifying diverse mutations that underlie complex genetic diseases. The three main NGS methods used for diagnosis are NGS panels, WES, and WGS. The appropriate course of action depends on the nature of the illness and the available funds.
By technology, the long-read sequencing segment is estimated to be the fastest-growing during the upcoming period. LRS promises to significantly outperform short-read sequencing in four key areas: accurate long-range haplotype phasing, ability to detect base modifications natively from the sequencing data, improved resolution of highly repetitive or non-unique regions, and better detection of structural variation. LRS may resolve molecular diagnoses when short-read sequencing cannot identify the cause, as demonstrated by several successful applications.
By sample type, the buccal swab segment was dominant in the rapid genomic diagnostics market in 2024. A non-invasive, nearly painless method of obtaining DNA is using buccal swabs. Given that buccal swab samples may be preserved and kept for extended periods of time, transporting DNA to laboratories for processing is simple. Suitable for individuals of all ages, from babies to the elderly, buccal swabs offer a versatile option for family genetic testing and research initiatives.
By sample type, the tissue biopsies segment is estimated to be the fastest growing during the predicted timeframe. The gold standard for cancer diagnosis for a long time has been tissue biopsies, which provide a comprehensive understanding of the cellular composition of the tumor. Clinicians can use this technique to identify the type of cancer, its level of aggressiveness, and how well it would respond to therapy. Personalized medicine techniques in oncology research are greatly aided by the procedure, which is invasive yet offers priceless insights into the genetic and molecular features of the tumor, directing therapeutic options.
By end-user, the hospitals & NICUs segment held the dominant revenue share of the rapid genomic diagnostics market in 2024. Hospitals and NICUs are responsible for providing healthcare services from diagnosis to treatment to post-treatment services. A large patient pool relies on private and public hospitals and NICUs for disease diagnosis and treatment; therefore, these service providers need high-end diagnostic laboratories. They also rely on third-party diagnostic labs that specialize in diagnostic services, include rapid genome diagnostics.
By end-user, the direct-to-consumer (DTC) companies segment is expected to grow rapidly during 2025-2034. DTC lab testing is revolutionizing the healthcare sector by enabling individuals to obtain a range of medical tests without a physician's prescription. Through wellness and genetic predisposition testing, direct-to-consumer (DTC) companies are revolutionizing the way individuals interact with their health. They offer more accessibility and convenience. The growing interest in one's genetic composition and health has led to a demand for easy-to-use test options.
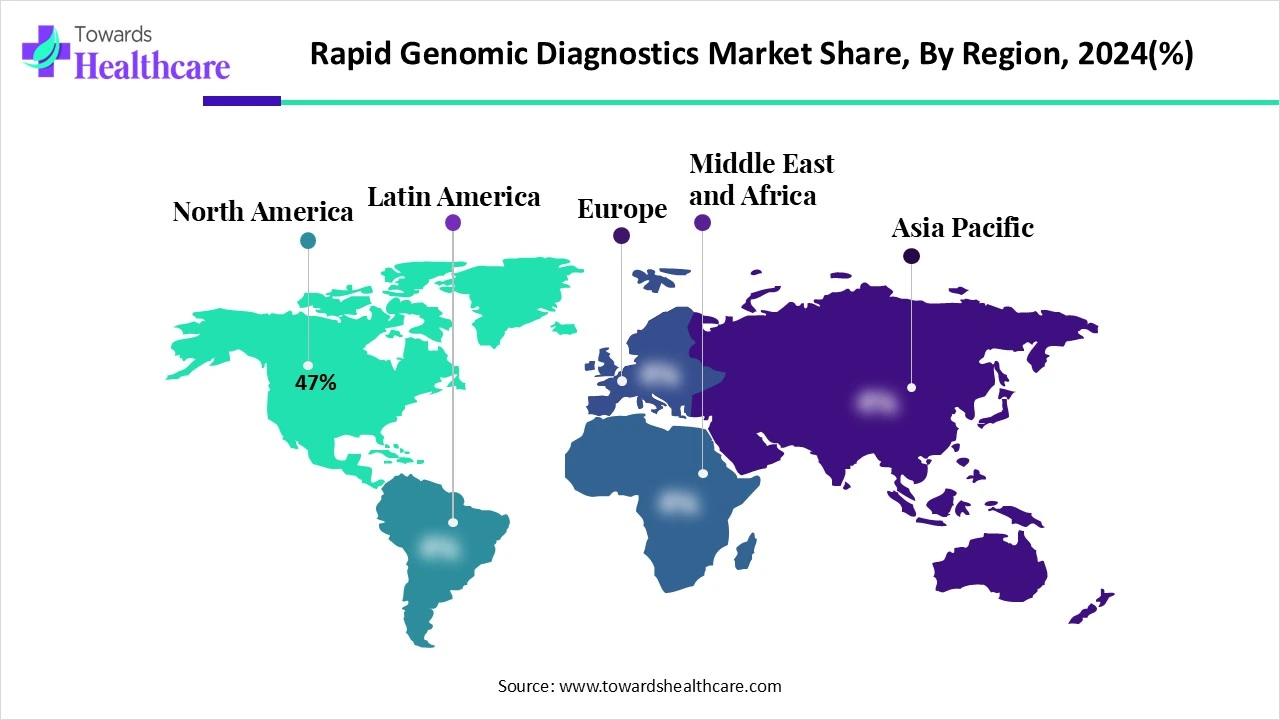
North America dominated the rapid genomic diagnostics market share by 47% in 2024. The primary drivers of the rising demand for diagnostic services are the rise in the prevalence of chronic illnesses and the advancement of diagnostic technologies. Furthermore, the growing prevalence of infectious diseases, including influenza, HIV, and TB, is expected to raise demand for effective detection and treatment alternatives. This demand is further supported by established healthcare infrastructure and government funding for regional research, which is anticipated to propel market development.
The U.S. is leading in the market due to the rising cases of cancer, which require genome testing for faster and accurate diagnosis. In the U.S., there will probably be 618,120 cancer-related deaths and 2,041,910 new cancer cases in 2025. The infrastructure required to gather, examine, and distribute national cancer statistics is one of DC's most significant responsibilities. CDC provides training, quality standard guidelines, computer-based processing solutions, funding, operational and technical support, and applications to facilitate the collection of event data.
The country will have the opportunity to observe major breakthroughs in rare disease research, screening, diagnosis, and treatment accessibility by June 2025, when all provinces and territories have embraced Canada’s National Strategy for Drugs for Rare Diseases. The signing of these agreements is seen by many working in the biotech and pharmaceutical sectors as proof of Canada's commitment to embracing innovation in the treatment of rare diseases.
Asia Pacific is estimated to host the fastest-growing rapid genomic diagnostics market during the forecast period. Genetic testing is becoming increasingly popular for early risk assessment and mitigation because of the burden of genetic diseases like sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, and cystic fibrosis in infants, as well as the prevalence of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases caused by environmental, behavioral, genetic, and physiological factors. The enormous populations of China and India, which together will comprise the majority of the world's population by 2024, are useful for gathering genetic information from diverse patient populations. The market for genetic testing is projected to grow along with healthcare facilities and investment.
China, the most populous country in the world, is still dealing with a lot of new problems when it comes to controlling infectious diseases among the general populace. In 2023, there were 25,525 reported deaths and 3.5078 million documented cases of Class A and B infectious diseases in China, excluding new coronavirus infections.
Over 7,000 rare illnesses have been found, affecting 5% of the global population. Patients in India face high healthcare expenditures, limited therapies, and delayed diagnosis. With over 450 rare diseases recognized, India is home to one-third of all rare disease cases worldwide. Cooperation between commercial pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, and government agencies is essential. The goal of programs like the Rare Disease Registry of the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and collaborations with international research institutes is to improve rare illness research.
Europe is expected to grow significantly in the rapid genomic diagnostics market during the forecast period. Advanced testing alternatives are now more widely available due to strong volumes in infectious diagnostics and increased R&D spending. Germany and the UK are incorporating state-of-the-art genetic technologies into clinical practice thanks to government backing for genomic research and robust healthcare systems. Additionally, strategic moves by key companies, such as mergers and acquisitions, are expected to drive the region's expansion.
In Germany, four million people suffer from a rare disease. Concerns over the future of treatment for patients with uncommon illnesses have been raised by a number of position papers on the situation of these patients in the German healthcare system that have been released in the run-up to the general election. More than 30 uncommon disease clinics have been established by German university hospitals in recent years.
Over 3.5 million people in the UK are afflicted with a rare disease. Many people who suffer from rare diseases struggle to obtain the care they need. The UK Rare Diseases Framework and England's action plans aimed to achieve this.

In April 2024, according to Christine Stanley, Chief Director of Clinical Genomics at Variantyx, it is evident that the current transition from panel and exome-based testing to whole genome testing is advantageous to payers, providers, and patients alike. With tens of thousands of genomes sequenced to date, Variantyx is a leader in clinically-accredited, genome-based testing and is well-positioned to lead the genomic diagnostics field through the continued development of new genome analysis technologies, offering a growing segment of the population notable improvements in patient outcomes. (Source - Businesswire)
By Test Type
By Application
By Technology
By Sample Type
By End User
By Region
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
January 2026
