February 2026

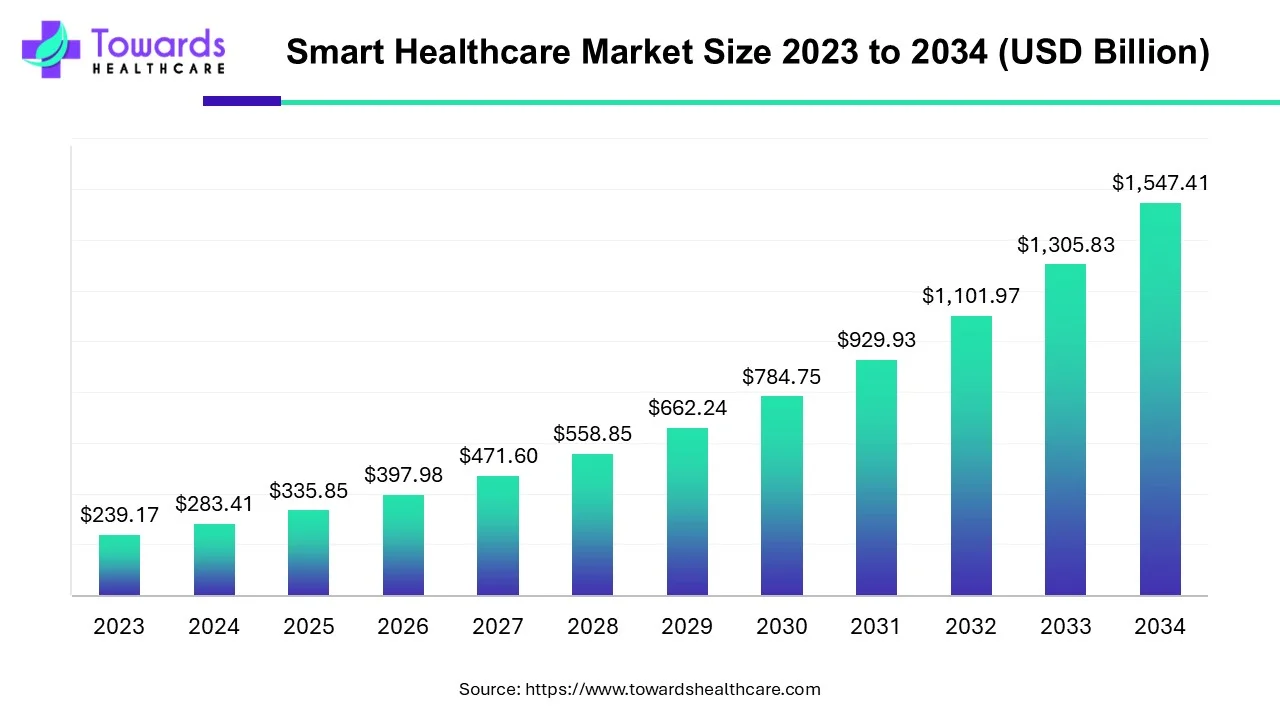
The global smart healthcare market size was calculated at USD 335.85 billion in 2025, to reach USD 397.98 billion in 2026 is expected to be worth USD 1833.7 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 18.5% from 2026 to 2035, as a result of the rising popularity of telemedicine. The smart healthcare market is rising due to the growing demand for better healthcare services, home-based services, and telehealth.
| Key Elements | Scope |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 335.85 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 1833.7 Billion |
| CAGR (2026 - 2035) | 18.5% |
| Leading Region | Europe |
| Market Segmentation | By Product Type, By Region |
| Top Key Players | Allscripts, Logi-Tag Systems, Cerner Corporation, SAMSUNG, Cisco Systems, GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANY, Siemens Healthcare Private Limited, IBM Corporation, BD, AirStrip, Terumo Corporation, eClinicalWorksResideo Technologies, Inc., STANLEY Healthcare, Medtronic |
The smart healthcare market refers to using advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics, to enhance the quality and efficiency of healthcare services. Smart healthcare solutions include telemedicine, electronic health records (EHR), remote patient monitoring, and healthcare information exchange (HIE).
The market is driven by increasing demand for healthcare services, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, the growing adoption of digital health solutions, and the need to reduce healthcare costs. Smart healthcare solutions can improve patient outcomes, enhance the patient experience, and increase operational efficiency in healthcare organizations.
Telemedicine, which allows healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat patients remotely, is expected to dominate the smart healthcare market during the forecast period. The adoption of telemedicine is driven by factors such as the shortage of healthcare professionals in certain regions, the need for remote monitoring of patients with chronic diseases, and the growing demand for virtual consultations.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been found to disrupt the healthcare sector, driving the latest innovations. AI transforms the practice of medicine and the delivery of healthcare. Integrating AI in medical devices and tools improves the efficiency of disease diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. The advent of telemedicine provides advanced patient care, especially in remote areas. AI-based technology aids in faster disease detection by accelerating the process of collecting samples and accurate analysis. AI and machine learning (ML) aid in more accurate disease diagnosis by identifying suitable biomarkers involved in the disease. AI also helps healthcare professionals evaluate medical imaging data. Additionally, AI-enabled robotics assist surgeons in performing surgeries.
Remote Monitoring and Automated Healthcare Systems: 66% of asthma deaths could have been prevented with smart technology monitoring like connected inhalers. Smartwatches and fitness trackers have become commonplace, monitoring vital health metrics such as heart rate, blood oxygen levels, and irregular heartbeats. This technology extends healthcare beyond clinics, allowing continuous monitoring which can potentially prevent health complications.
Telehealth and Remote Care: Telehealth services have gained popularity with patients expressing high satisfaction rates (up to 78%). Many physicians (68%) are also eager to expand telehealth offerings, enabling remote consultations and medical advice.
AI in Healthcare: Artificial Intelligence (AI) adoption is growing among healthcare providers, offering potential annual savings of up to $360 billion. AI-powered models assist in diagnostics, treatment planning, and operational optimizations, marking a significant evolution in healthcare delivery.
Connected Emergency Response Solutions: Integration of smart technology in emergency care improves response times significantly. Real-time data sharing between ambulances, healthcare providers, and emergency departments enhances coordination, crucial in critical situations.
Smart Hospital Management: Implementing smart systems in hospitals enhances operational efficiency and patient care. These systems streamline access to information such as bed availability, equipment status, and supply levels, optimizing hospital workflows and improving overall patient experience.
What Made the mHealth Segment Dominate the Smart Healthcare Market in 2025?
By product type, the mHealth segment is anticipated to grow with the highest CAGR in the market during the studied years. mHealth includes the use of mobile phones and other wireless technology in medical care. It is widely used to educate customers about preventive healthcare services, disease surveillance, treatment support, epidemic outbreak tracking, and chronic disease management. The rising adoption of smartphones and advancements in 5G technology potentiate the segment’s growth. The increasing awareness of mHealth, especially in low- and middle-income countries, promotes the segment’s growth. Favorable government support also increases awareness about mHealth in their respective nations.
Telemedicine: Virtual Healthcare Bridging the Gap in Medical Services
Telemedicine, also known as telehealth, uses technology to provide remote medical care and consultation to patients. It allows healthcare providers to diagnose, treat, and monitor patients from a distance using various tools such as video conferencing, remote monitoring devices, and mobile health apps. Telemedicine has been rapidly gaining popularity in recent years. Its importance has been further highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic, as it enables patients to receive medical care without physically visiting a healthcare facility.
The telemedicine market is expected to grow significantly over the coming years, driven by several factors, including the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the rising demand for healthcare services, and the need for cost-effective healthcare solutions. Europe and Asia Pacific are at the forefront of this trend, with several countries investing in telemedicine infrastructure and adopting policies to promote telemedicine adoption.
The increasing use of mobile health apps and remote monitoring devices also drives the telemedicine market. These tools enable patients to monitor their health conditions and communicate with healthcare providers remotely, improving patient engagement and outcomes. It has emerged as a promising solution to address the challenges of healthcare access and efficiency, particularly in remote and underserved areas. The rise of telemedicine has been facilitated by technological advancements, changing patient preferences, and the need to reduce healthcare costs.
Telemedicine offers several benefits, making it an attractive option for patients and healthcare providers. First and foremost, it improves access to healthcare services, particularly in rural or remote areas with a shortage of healthcare providers. Telemedicine also reduces the need for travel, which can be costly and time-consuming, and allows patients to receive care in their homes. Furthermore, telemedicine can improve healthcare efficiency by reducing wait times, improving patient flow, and enabling healthcare providers to see more patients in less time.
Smart healthcare, which refers to integrating technology and healthcare services, is rapidly gaining popularity worldwide. Europe and Asia Pacific are at the forefront of this trend, with both regions experiencing significant growth in the smart healthcare market. Europe is one of the leading regions in the smart healthcare market, accounting for a substantial global market share. The region's growth is driven by the increasing aging population, rising healthcare costs, and the growing demand for digital healthcare solutions. In addition, supportive government initiatives, such as the Digital Single Market strategy, are expected to accelerate the growth of the smart healthcare market in Europe. This strategy aims to create a single demand for digital products and services across the European Union, facilitating the adoption of innovative healthcare solutions across the region.
UK Smart Healthcare Market Trends
The growing digital health solutions are driving smart health in the UK. At the same time, the growing government support is accelerating their adoption rates. Additionally, the companies are developing various remote monitoring technologies, which are attracting patients and promoting their advancements.
Furthermore, the quick adoption of the latest medical technologies in the mainstream is also a vital feature of the European healthcare industry. Favorable reimbursements in the EU further enable the swift uptake of advanced therapeutics and medical technologies in the European market. North America closely follows the lead of Europe; high healthcare expenditure, better reimbursements, and greater awareness are the key drivers of the North American market.
The Asia Pacific region is also seeing a significant increase in the adoption of smart healthcare solutions. The region's growth is driven by the growing demand for healthcare services, increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases. Additionally, technological advancements such as 5G networks, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing are expected to further accelerate the adoption of smart healthcare solutions in the Asia Pacific. According to the Times of India, the Indian wearable market grew by 47% YoY in 2022, led by smartwatches. Furthermore, the rapid growth of the Asia Pacific market is attributed to the improving healthcare infrastructure and growing healthcare infrastructure in the developing economies. Due to its massive population base, the region consistently seeks new technologies to serve the large patient volumes, where smart healthcare solutions become an appropriate fit. China dominates the area due to the country's rapid progress and transitional evolution of healthcare infrastructure.
India Smart Healthcare Market Trends
Due to the presence of a large population, the risk of chronic diseases is increasing, driving the demand for smart healthcare in India. The expanding healthcare sector is also increasing the adoption of various digital health solutions, which are being supported by government initiatives.
North America is expected to grow significantly in the smart healthcare market during the forecast period, due to the presence of a robust healthcare system. This is increasing the use of various AI-based health solutions, where the companies are also developing various wearable and remote monitoring solutions, which is promoting the market growth.
U.S. Smart Healthcare Market Trends
The U.S. consists of an advanced healthcare IT infrastructure, which is increasing the use of various digital health platforms. At the same time, the growing healthcare investments and growing diseases are also increasing their use, which in turn, is encouraging new innovations.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is rapidly emerging as a game-changer in healthcare, allowing patients to receive continuous monitoring and care outside of traditional healthcare settings. The combination of RPM with smart healthcare technologies such as wearables and mobile apps is revolutionizing patient care and creating new opportunities for healthcare providers.
RPM involves using connected devices to track and transmit patient data, such as vital signs, medication adherence, and symptoms, to healthcare providers in real-time. This allows for early intervention and personalized care, reducing hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes. With the aging population and rising incidence of chronic diseases, RPM is becoming increasingly important for managing the health of patients with complex and ongoing medical needs.
The integration of RPM with smart healthcare technologies is enhancing the patient experience and improving healthcare delivery. Wearables such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and biosensors can monitor activity levels, heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, providing valuable data to healthcare providers for proactive care management. Mobile apps can also help patients track and manage their health data, communicate with their providers, and receive real-time alerts and reminders. In addition, rising product launches related to digital health devices thrive the growth of RPM.
The use of RPM and smart healthcare technologies are also creating new business opportunities for healthcare providers, from remote patient monitoring services to the development of innovative healthtech solutions. The global RPM market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by factors such as increasing demand for telehealth services, rising healthcare costs, and advances in connected devices and healthcare technology.
The convergence of self-care, wellness, and smart healthcare is transforming the healthcare landscape, with a growing emphasis on prevention and proactive management of health. Smart healthcare technologies are increasingly being integrated with self-care and wellness devices, such as wearables and mobile apps, to provide patients with more control over their health and well-being. In addition, self-care is becoming increasingly important in the healthcare industry, and it is driving growth in the smart healthcare market. Self-care involves individuals taking responsibility for their health and well-being, which can be achieved through the use of digital tools and technologies.
Smart healthcare technology has made it easier for patients to monitor and manage their health from the comfort of their homes. Remote patient monitoring devices, for instance, allow patients to track their vital signs, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and blood glucose levels, and share this information with their healthcare providers in real time. This enables healthcare providers to monitor their patient's health remotely and intervene if necessary, leading to more timely and effective care.
Furthermore, the growth of the smart healthcare market is being fueled by several factors, including a growing emphasis on preventive care and wellness. Rather than simply treating illnesses, healthcare providers are now focusing on preventing them, and smart healthcare solutions are proving to be an essential tool in this regard. With the help of digital tools that monitor their health and well-being, individuals can take a proactive approach to managing their health, preventing illness, and improving their overall quality of life.
The convergence of self-care, wellness, and smart healthcare is also creating new opportunities for healthcare providers and payers. By leveraging smart healthcare technologies, providers can deliver more personalized and proactive care, leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs. Payers can also use smart healthcare technology to incentivize patients to adopt healthy behaviors and prevent the onset of chronic diseases, ultimately reducing healthcare costs in the long term.
As with any sector that deals with sensitive information, data security and privacy are major concerns in the smart healthcare market. With the increasing use of connected medical devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare, there is a growing risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks.
Patient data is susceptible and valuable, making it a prime target for cybercriminals. Healthcare organizations must ensure that they have robust security measures in place to protect against data breaches and unauthorized access to patient information. This includes implementing strong access controls, using encryption and other security technologies to protect data both at rest and in transit, and regularly testing and auditing security systems to identify and address vulnerabilities. Privacy concerns are also a significant issue in the smart healthcare market, and patients are understandably concerned about how their data is being used and who has access to it. As healthcare providers and patients alike become more reliant on digital technologies, protecting sensitive patient data becomes increasingly important. Here are some ways to overcome data privacy and security concerns in the smart healthcare market:
Thus, protecting patient data in the smart healthcare market requires a proactive, comprehensive approach to data privacy and security. Healthcare providers can ensure that patients' sensitive information is kept safe and secure by implementing advanced security measures, adhering to compliance standards, and continuously monitoring for potential threats.
App-based personal emergency response systems (PERS) are emerging as a new trend in the healthcare market. These systems allow individuals to access emergency services at the touch of a button on their smartphones or other connected devices, providing peace of mind for seniors, people with disabilities, and others who may need immediate assistance in case of a medical emergency.
Additionally, app-based PERS often offer additional features beyond just emergency response, such as medication reminders, activity tracking, and fall detection. However, a potential downside of app-based PERS is that they rely on a smartphone and a reliable internet or cellular connection, which may only sometimes be available in emergencies. This could potentially limit their effectiveness in certain situations, particularly for elderly individuals who may not be as comfortable using a smartphone or may not have one at all. Another potential issue is privacy and security concerns related to transmitting personal health information through the Internet.
Furthermore, app-based PERS can be more affordable than traditional PERS devices, with lower upfront costs and no or low monthly monitoring fees. This makes them a more accessible option for individuals who may not have the financial means to invest in traditional PERS devices but still want to ensure their safety and security.
In addition to personal emergency response, app-based PERS can also provide other connected care services. For example, some systems may include medication reminders, fall detection, and other features that can help users manage their health and well-being. These additional services can further enhance the value of app-based PERS, making them a more comprehensive solution for individuals looking to stay healthy and independent.
Thus, the emergence of app-based PERS represents an exciting development in the healthcare market, offering a convenient, affordable, and effective way for individuals to access emergency services and connected care solutions. As technology continues to evolve, we will likely see even more innovative solutions in the years ahead, helping to revolutionize how we approach healthcare and personal safety.
| Companies | Headquarters | Smart Healthcare Products |
| Apple Inc. | California, U.S. | Apple Health App |
| Samsung Electronics | Suwon, South Korea | Galaxy Watch 7 and Galaxy Ring |
| GE HealthCare | Illinois, U.S. | Portrait Mobile |
| Philips Healthcare | Amsterdam, Netherlands | HealthSuite and Lumify |
| Medtronic | Dublin, Ireland | MiniMed 780G system |
| Google (Fitbit) | California, U.S. | Fitbit Premium and Google Health AI |
| Dexocom | California, U.S. | Dexocom G7 |
| Siemens Healthineers | Erlangen, Germany | Syngo.via |
| Abbott Laboratories | Illinois, U.S. | freeStyle Libre 3 |
| Honeywell Life Sciences | North Carolina, U.S. | LifeStream |
Girish Krishnamurthy, CEO & MD, Tata MD, commented that the future of healthcare is more collaborative and is not just about AI. The future should include how humans choose AI to use it, enhancing humanity and making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and compassionate for all.
By Product Type
By Region
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026