December 2025

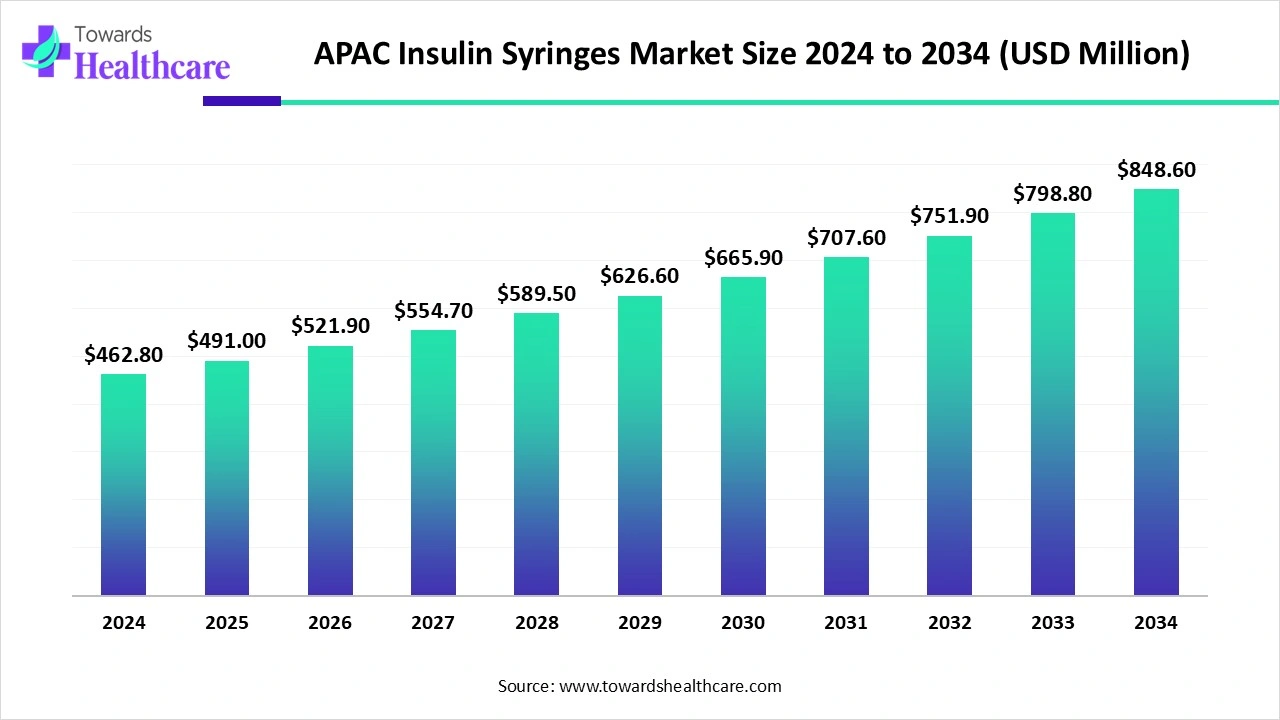
The APAC insulin syringes market size is calculated at US$ 462.8 million in 2024, grew to US$ 491 million in 2025, and is projected to reach around US$ 848.6 million by 2034. The market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 6.1% between 2025 and 2034.
The APAC insulin syringes market is experiencing growth due to the rising global incidence of diabetes, their affordability relative to other delivery methods, improvements in syringe design that enhance patient comfort and adherence, an expanding elderly population, and supportive government programs aimed at improving diabetes care.
| Metric | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 491 Million |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 848.6 Million |
| CAGR (2025 - 2034) | 6.1% |
| Market Segmentation | By Syringe Size (Capacity), By Needle Gauge, By Needle Length, By Usability, By End User, By Diabetes Type |
| Top Key Players | Becton and Dickinson, Terumo Corporation, Nipro Corporation, HMD Healthcare Ltd, Cardinal Health Inc., Roche Diagnostics (Accu-Chek), Abbott Laboratories (Freestyle), Terumo Corporation, Nipro Corporation, Medtronic Plc, Dr. Morepen (Morepen Laboratories Ltd.), Hindustan Syringes & Medical Devices Ltd. (HMD), Poly Medicure Ltd., Ypsomed India Pvt. Ltd., ARKRAY Healthcare Pvt. Ltd. |
The APAC insulin syringes market refers to the regional healthcare segment involved in the production, distribution, and use of insulin syringes, medical devices specifically designed for the subcutaneous injection of insulin by people with diabetes.
This market includes various countries across the Asia-Pacific region, such as India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, and others, where the demand for insulin delivery devices is driven by the rising prevalence of diabetes, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and growing awareness of diabetes management.
Type 2 diabetes is increasing rapidly in countries such as India, China, Indonesia, and Vietnam due to urbanization, aging populations, and changing diets.
Insulin syringes remain the most affordable insulin delivery option, especially in low- and middle-income households.
Syringe manufacturers are developing ultra-thin needles, low-friction plungers, and low dead-space designs to improve injection comfort and reduce medication waste.
The elderly population in APAC is expanding rapidly, particularly in Japan, South Korea, and Thailand.
AI-powered tools are being adopted in public health systems and telemedicine platforms across APAC too. Some hospitals in India and China are piloting AI-driven retinal screening for diabetic retinopathy, identifying undiagnosed diabetics who may require insulin. Though more common in pen/pump devices, insights from such AI platforms may still result in patients being prescribed insulin in syringe-compatible form, especially in cost-sensitive or rural settings. In densely populated countries like Indonesia and the Philippines, AI-led logistics platforms are improving cold chain management and inventory restocking.
Increasing Diabetes Prevalence and Aging Population
Across the Asia-Pacific region, there has been a significant increase in type 2 diabetes cases, primarily due to rapid urbanization, lifestyle changes (like reduced physical activity and unhealthy diets), and population aging. Countries such as India and China are seeing particularly high growth in their diabetic populations.
As diabetes management often requires regular insulin injections, especially in low-resource settings, insulin syringes remain a primary tool for many patients. Syringes are affordable, simple to use, and don't require the same level of infrastructure or training as more advanced devices.
Patient Preference Shifting to Pens and Other Devices
One of the major restraints in the market is the gradual shift in patient preference toward insulin pens, pumps, and other modern delivery systems. These alternatives are often seen as more user-friendly, discreet, and less painful, making them especially popular among younger or tech-savvy populations.
Even in lower and middle-income countries, government programs and NGOs are beginning to distribute pens or promote other alternatives. As awareness of these newer delivery systems grows, syringe usage may decline, especially in urban areas with access to better healthcare.
Expanding Rural Healthcare Access and Education
A key opportunity lies in the penetration of insulin syringes into rural and semi-urban regions, where advanced insulin delivery technologies are either unavailable or unaffordable. Many patients in these areas rely on insulin syringes due to their low cost, ease of storage, and no reliance on electricity or digital literacy. With growing investments in primary healthcare infrastructure and government-led diabetes awareness campaigns, manufacturers and health systems have an opportunity to educate patients and improve access to safe injection practices.
The 1.0mL segment dominated the APAC insulin syringes market due to its wide use for patients requiring higher insulin doses or multiple daily injections, particularly those with Type 2 diabetes. This size offers flexibility to accommodate varying insulin regimens, making it suitable for both hospital and home care use. Its ability to deliver accurate doses while minimizing the frequency of injections further drives its dominance.
Additionally, the increasing prevalence of obesity and insulin resistance in the region makes larger-dose syringes essential for effective therapy. Hospitals and diabetes clinics also prefer 1.0mL syringes because they support multiple units of insulin in a single shot, improving patient compliance and reducing wastage.
The 0.3mL segment is growing rapidly in the market due to its growing popularity among young patients and those with lower insulin needs. Because they are easier to handle and offer a more accurate dosage, smaller syringes lower the chance of overdosing. Demand for this market has increased due to the rise in early-stage diabetes detection and the focus on precise microdosing for children and thin adults.
Furthermore, 0.3mL syringes are becoming more popular among new users due to the trend toward patient-friendly, less frightening injection options and rising awareness of the advantages of precise dosing for small quantities.
The 31G-33G segment dominated the APAC insulin syringes market because they offer a balance of patient comfort and effective insulin delivery, making them the standard choice for most users. These ultra-fine needles significantly reduce pain during injections, which improves therapy adherence. Their compatibility with commonly used syringe sizes and their availability across brands make them the preferred option. Furthermore, manufacturers continuously innovate within this gauge range, offering enhanced lubrication and bevel technology for smoother penetration, ensuring continued dominance in the region.
>33G segment is growing fastest due to the growing need for incredibly thin needles that reduce pain and anxiety associated with injections. First-time insulin users and pediatric patients for whom pain management is a top priority are especially fond of these finer needles. The use of these needles has increased as medical professionals place a greater emphasis on patient comfort. Their quick market expansion is also fueled by manufacturing technological advancements that make ultra-thin needles stronger, more accurate, and safer
6-8 mm needle length dominates the APAC insulin syringe market as it is considered the standard length for effective subcutaneous insulin delivery in adults. This range provides a good balance between safety and efficiency, reducing the risk of intramuscular injections while ensuring proper absorption. Most hospitals and clinics prefer this length due to its proven reliability across diverse patient profiles. Additionally, widespread clinical recommendations for this size and compatibility with multiple insulin concentrations make it the most trusted option for healthcare professionals.
<6mm needle length is growing rapidly because patients are looking for injection options that are less frightening and more comfortable. Shorter needles are better for children, lean adults, and self-administration because they are less painful and less likely to result in an incorrect injection. Demand is being fueled by growing knowledge of how well shorter needles deliver insulin to subcutaneous tissue. Additionally, producers are aggressively pushing shorter needle syringes as a safer substitute, fostering regional adoption.
Disposable insulin syringes dominated the market because they offer high safety standards by minimizing contamination and infection risks. Their single-use design is widely recommended in clinical settings and by healthcare authorities, ensuring patient safety and compliance with hygiene protocols. Affordable pricing and easy availability further strengthened their dominance in APAC markets. Moreover, government regulations emphasizing single-use products in hospitals and diabetic care programs have accelerated adoption, making disposable the preferred choice across all end-user categories.
The disposable syringes segment is expected to sustain the growth during the forecast period as they keep taking the place of reusable options in home care and hospital settings. Single-use solutions are becoming more popular among patients and healthcare professionals due to the growing awareness of infection control and support from guidelines.
Additionally, bulk availability and large-scale manufacturing help lower costs, which sustains this segment's growth over the forecast period. Government tenders and bulk procurement for public health initiatives further solidify the trend, guaranteeing a high demand for disposable syringes in the years to come.
Hospitals remain the dominant end-user segment because they handle a high volume of diabetic patients requiring insulin therapy and precise dosing. The presence of trained medical professionals ensures correct usage, making hospitals the preferred point of insulin administration. Strong procurement networks and strict adherence to safety protocols further drive this segment’s leadership. Hospitals also benefit from bulk purchase agreements and centralized distribution systems, enabling cost efficiency while maintaining high-quality standards for insulin delivery.
Homecare settings are growing rapidly because more people are choosing to administer their insulin and because simple-to-use insulin syringes are becoming more widely available. This tendency is being aided by elements like growing diabetes awareness, the use of telemedicine, and reasonably priced syringe kits. To save money and reduce their reliance on in-person visits, patients are increasingly choosing to manage their diabetes at home. The demand for home-use syringes is also rising as a result of patients being empowered to safely manage insulin therapy at home through digital education resources and self-care initiatives.
U-100 insulin concentration dominated because it is the most widely prescribed and standardized formulation globally, making it compatible with the majority of insulin syringes. Its ease of dosing and established clinical guidelines ensure widespread use in both hospital and home settings. The strong presence of U-100 in APAC markets reinforces its continued dominance. Moreover, pharmaceutical companies continue to prioritize U-100 production due to its universal acceptance and cost efficiency, ensuring sustained demand in the region.
The U-500 segment is growing rapidly due to patients who require high doses or have severe insulin resistance increasingly using concentrated formulations. By allowing for fewer daily injections, these syringes enhance patient convenience and compliance. The increasing number of diabetes cases linked to obesity in APAC further supports the segment's growth. Additionally, the U-500 is becoming more and more popular in specialty diabetic care as a result of medical professionals recommending concentrated insulin to make therapy easier for patients who require large doses.
Type 2 diabetes dominated the APAC insulin syringes market due to its accounting for the largest share of diabetic patients in APAC, driven by lifestyle factors such as poor diet and sedentary habits. These patients often require higher doses of insulin, making syringes the preferred choice for cost-effective delivery. The growing aging populations in the region further strengthen this segment's position. Additionally, government-led screening programs and early detection initiatives are expanding the treated patient base, ensuring steady demand for insulin syringes among Tyre 2 diabetic patients.
Type 1 diabetes is growing fastest because of the rising rates of diagnosis in APAC youth and young adults. The need for syringes, particularly those made for accurate microdosing, is sustained because these patients need lifelong insulin therapy. Growth in this category is accelerated by early detection programs and growing awareness campaigns. Additionally, more Type 1 diabetes patients are using insulin syringes due to improvements in pediatric care and school-based diabetes programs.

India is one of the strong shareholders in APAC insulin syringes market due to the high number of diabetics and growing knowledge of insulin therapy. Access to insulin delivery devices in rural and semi urban areas is greatly aided by the government. National Programmed for Prevention and Control of Cancer Diabetes Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS).
With reasonably priced syringes designed for patients in a tight budget regional producers like Terumo India HMD and Wockhardt have increased their market share. This trend toward increasing patient comfort and injection accuracy is reflected in the November 2023 launch of Terumo Indias cutting edge insulin syringes. Despite the increasing use of insulin pens syringes are still essential in India because of their low cost and extensive use in public healthcare facilities.
China is another key marketplace for insulin syringes driven by a high prevalence of diabetes lifestyle changes and fast urbanization. With initiatives like Made in China 2025 the government promotes domestic manufacturing which has increase the presence of domestic companies like Sino care and Lyphomed China. Despite insulin pens growing popularity due to their convenience, syringes are still frequently used in hospitals and low-income populations. Access to affordable syringe options is guaranteed by rising investments in manufacturing technology and distribution networks. Although more people are adopting sophisticated devices in cities, demand for syringes is still high in rural areas due to price sensitivity.
On 14 November 2023, Termo India introduced a sterile insulin syringe that includes a 3 level super sharp needle, high grade silicon lubrication and plunger retention technology to prevent dose spillage. It comes in U-40 and U100 variants with multiple needle gauge and length options to cater to patient comfort and ensure accurate dosing. (Source - Terumo)
By Syringe Size (Capacity)
By Needle Gauge
By Needle Length
By Usability
By End User
By Diabetes Type
December 2025
November 2025
January 2026
October 2025