March 2026

The baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market is rapidly advancing on a scale, with expectations of accumulating hundreds of millions in revenue between 2025 and 2034. Market forecasts suggest robust development fueled by increased investments, innovation, and rising demand across various industries.
A number of significant factors are driving the baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market, such as the growing incidence of chronic illnesses that call for sophisticated treatments, the growing use of cell-based assays in drug discovery, and the growing application of BHK-21 cells in the creation of viral vectors for gene therapy. This market's segments exhibit a heavy reliance on life science research, with the biopharmaceutical application sector expected to increase at the fastest rate. Reputable businesses like ATCC, Merck, and Creative Biolabs are significant players in this industry, propelling supply and innovation for premium BHK-21 cells and associated goods.
The baby hamster kidney (BHK) fibroblast cells market comprises suppliers, cell banks, distributors and contract developers that provide BHK cell lines (most commonly BHK-21 and its subclones), related frozen vials/working/ master cell banks, specialized culture media and services (e.g., cell bank characterization, cGMP cell bank development and custom cell line services) for use in virology, vaccine production, recombinant protein expression, transfection studies and basic research.
The baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market is driven by vaccine manufacturing, viral vector production, biopharma R&D, and diagnostic applications, where BHK cells' ease of culture, high transfectability, and established regulatory history make them a preferred substrate; the market therefore includes major international cell banks, reagent companies, distributors, and CDMOs that supply authenticated BHK lines, reagents, and associated services.
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and automated cell culture techniques can increase the repeatability of cell culture protocols, which will ultimately result in more in-depth research and medication development by lowering variability and improving results. Real-time culture condition modifications are made by AI systems that track cell behaviour. Because AI allows researchers to generate spheroids or organoids from many cell sources at once, guaranteeing uniformity and reproducibility, it is seen as a major game-changer in 3D cell culture. Furthermore, without the requirement for modularization or human interaction, researchers and scientists may use AI to design customised workflows and procedures that follow the natural flow of the cell culture process.
By product type, the adherent BHK cells segment held the major share of 40% of the baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market in 2024. Flasks, roller bottles, cell factories, and cell cubes are the most used methods for cultivating adherent cells. It has been demonstrated that microcarriers and fixed beds in bioreactors are suitable substitutes for cultivating adherent cells in a regulated and agitated environment.
By product type, the suspension-adapted BHK cells segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period. While FMD vaccines are commonly produced using suspension cultures of baby hamster kidney (BHK)-21 cells. Although suspension cells are essential to biomanufacturing, their expensive cost frequently prevents them from being widely available. This simple technique provides a quick and affordable way to produce BHK-adapted suspension cells that are perfect for large-scale bioreactor culture.
By cell line/strain, the BHK-21 (parent) segment captured a revenue of 50% of the baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market in 2024. The BHK-21 cell line has many benefits, such as a well-established origin and history, which make it a popular choice for producing viral vaccines. BHK-21 cells, a non-neuronal cell line, are utilised to make seeds for various vaccinations because they are receptive of viral infection. For many years, the BHK-21 cell line has been used to make animal rabies vaccinations, which have been shown to be both safe and effective.
By cell line/strain, the BHK-21 C13 segment is estimated to be the fastest-growing during 2025-2034. An uninfected golden hamster's kidney produces BHK-21 [13] fibroblasts. These cells can be utilised for regular rabies diagnosis, according to the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). Expression vectors with selectable and amplifiable marker DNAs have been utilised to alter this cell line.
By application, the vaccine production segment was dominant, accounting for 30% of the baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market revenue in 2024. A rabies vaccine is produced in China and the former USSR using primary baby hamster kidney cells, and it is extensively utilised in both countries. In Europe, Japan, and India, embryonated eggs are the main cell culture medium used to make at least three distinct rabies vaccines. Two other rabies producers, one in Europe and the other in India, also make two rabies vaccines using human diploid cells. Lastly, a continuous cell line is utilised to develop Vero cells, which are then employed in numerous nations in Asia, Europe, and Latin America to generate a variety of high-quality vaccines.
By application, the gene therapy/viral vector production segment is estimated to achieve the highest CAGR during the forecast period. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) and Semliki Forest virus (SFV) vectors are made using BHK (Baby Hamster Kidney) cells, which are also utilised in gene therapy. AAV may be produced using BHK-21 cells, and specific BHK cell lines have been developed to increase AAV yields. Other viral vectors, such as SFV replicon particles (VRPs), can also be produced using them; greater production titers are obtained using certain serum-free medium.
By end-user, the pharmaceutical & biopharmaceutical companies segment captured the major share of 45% of the baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market in 2024. The industry uses BHK-21 cells extensively to produce therapeutic proteins like Factor VIII and vaccines. These biologics would be used in the manufacturing processes of companies that develop and manufacture them, including large pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical organisations.
Among end-users, the CROs/CDMOs segment is anticipated to be the fastest-growing during 2025-2034. For early-stage research, trials, and development, pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical businesses employ CROs; for later-stage drug development, formulation, and commercial manufacture, they utilise CDMOs. Because they may offer services from preclinical testing to large-scale production, companies frequently collaborate with one or both of these organisations to get access to specialised knowledge, manage scale-up, save costs, and expedite the drug's time to release.
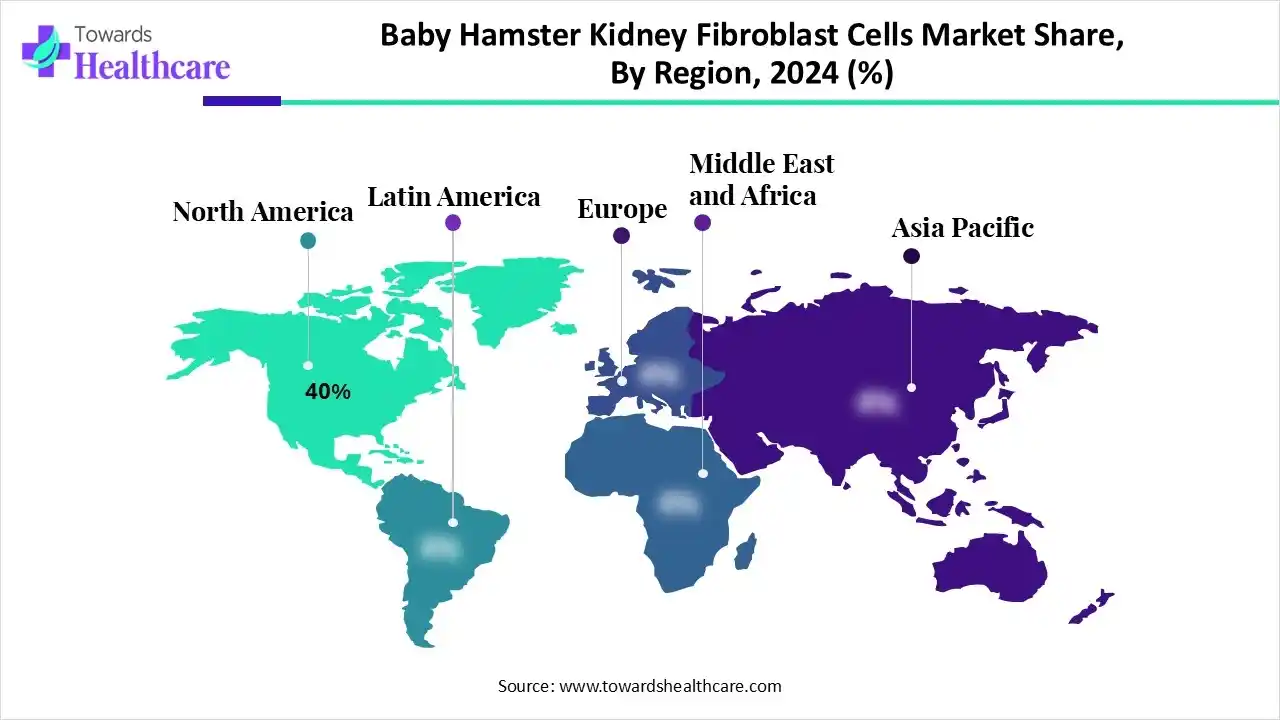
North America captured a revenue of 40% of the baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market in 2024. propelled by substantial expenditures in R&D and a firmly developed biopharmaceutical sector. The region's dominant position is partly a result of its sophisticated healthcare system and advantageous regulatory framework. The need for BHK cells in this area is further increased by the existence of significant biotechnology and pharmaceutical businesses as well as research facilities in the U.S. and Canada.
After possible exposure, almost 100,000 Americans are vaccinated against rabies annually. Although there are less than 10 rabies-related deaths in the United States each year, the illness kills over 70,000 people worldwide, with dogs accounting for more than 95% of fatalities outside of the country. The CDC has further information.
In August 2025, to stop the spread of racoon rabies into the American heartland, the Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) of the U.S. Department of Agriculture will start distributing RABORAL V-RG®, an oral rabies vaccination (ORV) bait, in a few locations in the eastern U.S.
Asia Pacific is estimated to host the fastest-growing baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market during the forecast period. Geographically, the Asia Pacific area especially China and India, is becoming a major development engine thanks to rising R&D expenditures and growing biopharmaceutical production capacities. In addition, biotechnology investment is increasing, and genetic research is becoming more and more important.
China has one of the worst rabies epidemics in the world; the country has the second-highest incidence of rabies and it is the third most common cause of sickness that has to be reported in China. As is the case in the majority of nations with a high rabies burden, dogs are the main disease reservoirs and rabies transmission vectors. The tremendous increase in the number of dogs in Beijing, the capital of China, since the turn of the twenty-first century has made dog-mediated rabies management in the city an unprecedented problem.
Europe is expected to grow at a significant CAGR in the baby hamster kidney fibroblast cells market during the forecast period. Strong industrial bases in Germany and the UK, strict quality and safety regulations, and rising interest in sustainable solutions are driving Europe's steady development. Expansion is also supported by EU cross-border commerce and government incentives.
Significant public funds have been pledged by the German government, which has allocated €1.75 billion into a "Future Fund" designed especially for biotech and related enterprises. The goal is for at least the equal level of private investment to match this governmental spending. With important innovation hubs in Berlin, Munich, and Heidelberg, a robust network of BioRegions links business and academics. These hubs draw funding and have robust academic and research infrastructure.
In order to maximise cell growth and product production, the R&D process has changed from using standard adherent cultures to large-scale, serum-free suspension cultures. To achieve reliable, economical, and large-scale manufacturing, researchers modify adherent BHK-21 cells to grow in suspension using serum-free media.
Clinical trials and regulatory clearances for Baby Hamster Kidney (BHK-21) fibroblast cells are complicated processes that mostly pertain to the vaccines or other products made with the cells. The BHK-21 cell line is not a medicinal product that is tested on humans; rather, it is a commonly used cell substrate for viral culture. In order to guarantee the quality, safety, and effectiveness of the finished product, the production process is very closely regulated.
Fibroblast cells from baby hamster kidneys (BHK-21) are essential for the production of biopharmaceuticals, especially viral vaccinations. The distribution of BHK-21 cells and their products is mostly a business-to-business activity for vaccine producers, research institutes, and labs, as opposed to distribution to hospitals for clinical use. To guarantee quality and safety, this procedure is subject to stringent regulatory requirements.
By Product Type
By Cell Line/Strain
By Application
By End-User
By Region
March 2026
October 2025
