February 2026

The global cell-based vaccine market is on an upward trajectory, poised to generate substantial revenue growth, potentially climbing into the hundreds of millions over the forecast years from 2025 to 2034. This surge is attributed to evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements reshaping the industry.
A cutting-edge method of immunotherapy, cell-based vaccinations activate the immune system to prevent or treat illness by using live or altered cells. Infectious illness prevention and cancer treatment are two areas where these vaccinations show the most promise. Through the use of immune cells innate capacity to display antigens and trigger unique immune responses, cell-based vaccinations provide a highly selective and individualised method of disease prevention. Research on increasing the efficacy of cell-based vaccines, such as boosting immune cell activation, optimising antigen loading, and guaranteeing long-term protection, is still ongoing. In addition to being at the forefront of immunotherapy, cell-based vaccinations have the potential to completely transform personalised medicine.
Rising disease prevalence, developments in personalised medicine, and continuing research are driving expansion in a number of different areas of the worldwide cell-based vaccines market, such as cell-cultured flu vaccines, dendritic cell cancer vaccines, and personalised cancer vaccines. To satisfy the growing need for efficient and scalable cell-based treatment solutions for a range of indications, industry leaders are concentrating on technological innovation, strategic alliances, and extending clinical trials.
Cell-based vaccines are vaccines manufactured by growing viruses or recombinant proteins in cultured cells (mammalian, insect, or other cell lines) rather than in embryonated chicken eggs. This platform, used for seasonal and pandemic influenza and for several other viral vaccines and recombinant protein vaccines, offers cleaner, scalable production, avoids egg-adaptation of viruses, and can shorten ramp-up times during outbreaks.
Gove ment Investments: Various gove ments are investing in vaccine development due to rising cases of infectious diseases and cancer. Cell-based vaccines can provide personalized and high-level immune support, due to which more and more gove ments are investing and collaborating with private organizations as well.
For instance,
The conventional vaccine development method has been completely transformed by artificial intelligence (AI), which has recently become a potent tool in antigen selection and immunogen creation. Potential vaccine candidates are quickly identified by AI-driven methods that use sophisticated computer algorithms to evaluate enormous volumes of genetic data, protein structures, and immune system interactions. In this effort, machine lea ing methods like random forest and deep lea ing have been essential because they make it easier to anticipate antigenic epitopes and evaluate immunogenicity with previously unheard-of efficiency and precision.
Personalized Vaccine is the Future of the Cell-Based Vaccine market
A novel approach to immunotherapy, personalised vaccines are designed to improve treatment results by tailoring vaccinations to each patient unique genetic and biological traits. By concentrating on antigens specific to the tumour, personalised vaccinations provide a more focused and potent immune response against cancer cells, opening up new therapy options for a variety of maladies, from infectious disorders to cancer. In addition, by tailoring the vaccination to a person unique immunological weaknesses and past exposure to pathogens, personalised vaccines have the potential to combat infectious illnesses.
What are the Challenges in the Cell-Based Vaccine Market?
Limitations of cell-based vaccines include the possibility of contamination, the high cost and complexity of manufacture, and difficulties scaling up production. Furthermore, a restricted host range for viral generation and the possibility of virus evasion or mutation away from the targeted antigens might affect the efficacy of cell-based vaccinations.
Cell-Based Vaccine for Cancer
For decades, researchers have been studying therapeutic cancer vaccines, and many strategies have been employed to create vaccine structures for anti-cancer treatment. One benefit of tumour cell-based vaccines is that they can use a variety of neoantigens, therefore target antigens do not need to be identified in advance. Future research may be able to realise the potential of this fascinating area of anti-cancer therapy as our knowledge of cancer immunology continues to advance and cell-based vaccination technology develops.
By care setting/end-user, the hospitals segment held the largest share of the cell-based vaccine market in 2024. Hospitals provide unmatched immunisation services and patient care. Hospitals provide patients with high-quality care because they house world-class doctors and state-of-the-art equipment. Hospitals provide vaccination and immunisation services with the goals of preventing disease outbreaks, protecting patients from serious diseases, and offering convenience and education.
By care setting/end-user, the ambulatory surgery centers/day clinics segment is estimated to grow at the highest rate during the upcoming period. Health care facilities known as ambulatory surgical centres (ASCs) provide patients with the option to receive vaccines conveniently outside of a hospital. ASCs have proven to have a remarkable potential to lower costs while simultaneously improving quality and customer service since its founding more than 40 years ago. ASCs stand out as an exception to the rule at a time when the majority of advancements in health care services and technology are generally more expensive.
By sterility, the sterile vaccines segment was dominant in the cell-based vaccine market in 2024. A crucial stage in the production process that guarantees the finished product is safe to use and free of impurities is vaccine sterilisation. The type of vaccination, its makeup, and the equipment at hand all influence the sterilisation technique selection. Heat sterilisation, filtration, radiation, and chemical sterilisation are a few of the often employed sterilisation techniques in vaccine production. Strict regulations for vaccination sterilisation are set by regulatory bodies including the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the World Health Organisation (WHO).
By distribution channel, the direct sales to hospitals/GPOs segment led the cell-based vaccine market in 2024. Hospital supply expenditures are on the rise, making them the second-highest area of spending after employment. More than 95% of hospitals purchase drugs, equipment, and supplies utilised in their institutions through pooling alliances called Group Purchasing Organisations (GPOs) in an effort to reduce supply costs. Through lower negotiated pricing and less administrative work, the GPOs may save hospitals money.
By distribution channel, the e-commerce/B2B marketplaces segment is expected to witness the highest growth during 2025-2034. B2B buyers that need to swiftly and efficiently investigate, compare, and assess the market now use digital platforms. They frequently choose to carry out their whole purchasing process online. Today top B2B businesses leverage automation and cutting-edge sales technology, and they sell through a variety of digital channels.
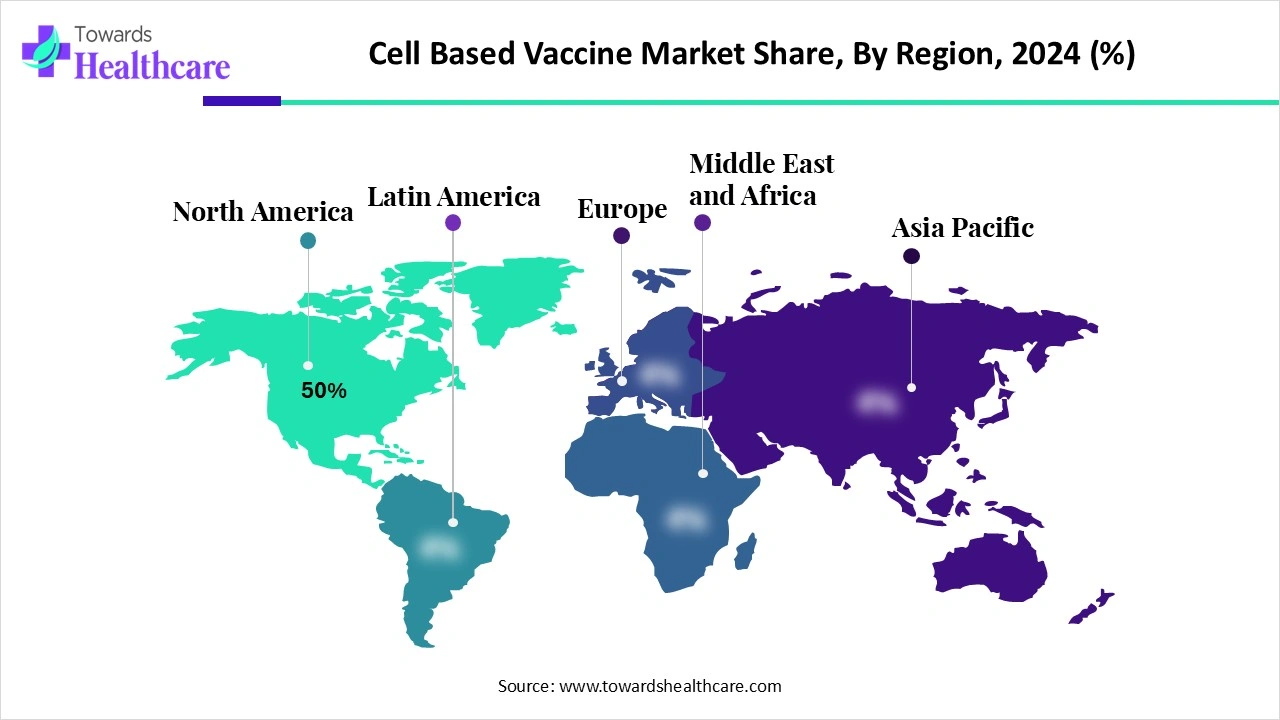
North America dominated the cell-based vaccines market share 50% in 2024. Demand is primarily driven by the increasing incidence of infectious illnesses and the requirement for efficient preventative measures. One important factor is more knowledge of the advantages of vaccination, especially in halting large-scale epidemics. Further propelling market expansion are continuous developments in vaccine technology, such as mRNA-based vaccines and enhanced vaccine delivery systems. Market expansion is also supported by gove ment programmes like immunisation campaigns and research and development funding.
The majority of vaccine development in the U.S. is carried out by private businesses, while gove ment and other public organisations may also be engaged. To ensure the safety of vaccinations in the U.S., the CDC collaborates with many organisations. They collaborate with gove ment organisations such as the NIH, which conducts research on novel vaccinations, and the FDA, which inspects vaccines before they are administered to humans. Additionally, they collaborate with academic institutions, business organisations interested in vaccine research and safety, vaccine makers, and non-gove mental organisations like the Immunisation Action Coalition.
In October 2024, a new scientific initiative is being started by Canadian experts to see whether they can expedite the production of essential vaccine ingredients in order to assist respond more quickly to potential pandemic and epidemic threats. If successful, this optimised cell line could aid in the quicker availability of vaccine doses for clinical trials and initial emergency use during future outbreaks. This would support CEPI objective, which has been adopted by Canada and other G7 and G20 countries, to respond to a novel virus with a new vaccine within 100 days of its discovery and prevent the spread of disease.
Asia Pacific is estimated to host the fastest-growing cell-based vaccines market during the forecast period. Its sizable population, rising health consciousness, and improved healthcare system are its main drivers. In order to produce, distribute, and sell vaccines, nations like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are making significant investments. Growing gove ment-led immunisation programmes, increased demand for adult and travel-related vaccines due to urbanisation and inte ational mobility, and robust domestic producers like Serum Institute of India, Bharat Biotech, Sinovac, and SK Bioscience that are pushing the boundaries of innovation and production capacity all contribute to the region continued growth.
Cell-based vaccine research and development (R&D) includes discovery (finding the target antigen and adjusting the cell system), proof-of-concept (evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine in labs and animal models), pre-clinical development (adjusting cell lines, growth conditions, and bioreactors for large-scale manufacturing), clinical trials (evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine in humans), regulatory approval (review by authorities prior to widespread use), and continuous post-approval monitoring.
Top Companies: CSL Seqirus for influenza vaccines, Serum Institute of India for its large-scale manufacturing using cell-based technology, and several biotechs like BriaCell Therapeutics and NexImmune
A multi-phase process that includes laboratory studies, animal testing, and human clinical trials (Phases 1, 2, and 3) to evaluate safety and efficacy is used for clinical trials and regulatory approval of cell-based vaccines. Following successful trials, a comprehensive application is submitted to regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States and the CDSCO in India for marketing approval.
To preserve potency and boost the immune response, the purified antigen is combined with adjuvants, stabilising agents, and preservatives in the formulation of cell-based vaccines. Following sterile packing into individual vials or syringes under aseptic conditions, the final dose preparation is diluting this vaccine formulation to the proper concentration for administration.
To guarantee safety and effectiveness, cell-based vaccines are packaged and serialised according to recognised good manufacturing procedures (GMP). The vaccine is stabilised, put into main containers, such as vials, and sealed under sterile circumstances throughout the formulation and filling steps of the process. The filled units are then serialised and labelled, which entails adding pertinent product and regulatory information along with unique IDs to each unit to facilitate tracking and traceability across the supply chain.
Top Companies: Companies like Almac, Catalent Biologics, Cryoport Systems, Saint-Gobain, Thermo Fisher Scientific, West Pharmaceuticals, and Yourway offer specialized packaging and serialization services for cell-based therapies
In order to distribute cell-based vaccines to hospitals and clinics, it is necessary to make sure that they are properly stored at particular temperatures (sometimes requiring a "cold chain"), transported in a way that maintains these conditions, and then administered to patients by medical staff at the hospitals and clinics.
With an emphasis on patient safety, education, and handling any possible adverse effects, patient support and services in cell-based vaccine procedures mainly include pre-vaccination evaluation, vaccine delivery and monitoring, and post-vaccination follow-up.
In November 2024, according to a news release from CellVax CEO Fe ando Kreutz, up to 30% of patients may still develop recurrent prostate cancer following prostatectomy, even with recent advancements in radiation, surgery, and other treatments. Furthermore, salvage radiation and/or androgen deprivation treatment (ADT) are now the standard of care following such a recurrence, and both may result in a lower quality of life for individuals in terms of their health. FK-PC101 may be able to postpone, if not completely avoid, the need for such therapies.
By Care Setting/End User
By Sterility
By Distribution Channel
By Region
February 2026
February 2026
January 2026
January 2026
