March 2026

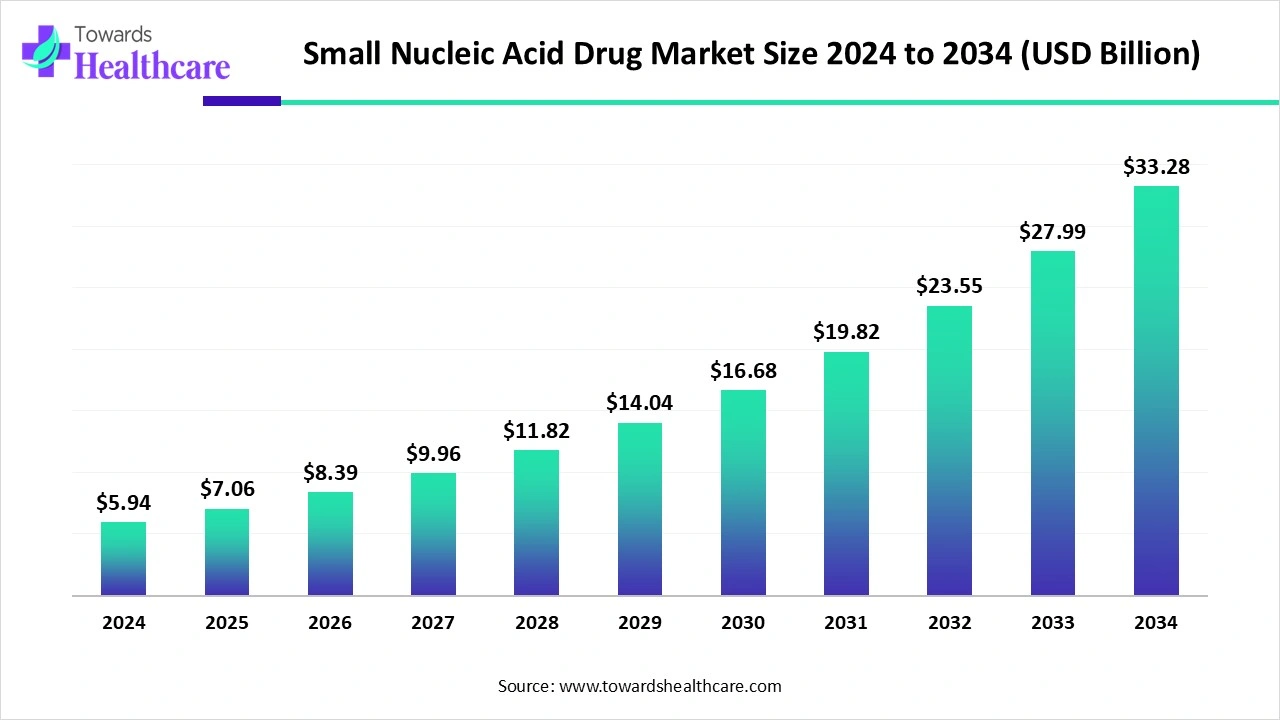
The global small nucleic acid drug market size is calculated at USD 5.94 billion in 2024, grew to USD 7.06 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach around USD 33.28 billion by 2034. The market is expanding at a CAGR of 18.84% between 2025 and 2034.
The small nucleic acid drug market is primarily driven by growing research and development activities and the burgeoning genomics and proteomics sectors. The increasing demand for personalized medicines encourages researchers to develop novel small nucleic acid drugs (SNADs). Government organizations launch initiatives to create awareness about screening and early diagnosis of chronic diseases. Artificial intelligence (AI) revolutionizes the design and development of SNADs. The future looks promising, with the increasing number of clinical trials.
| Table | Scope |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 7.06 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 33.28 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 - 2034) | 18.84% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Market Segmentation | By Molecule Type, By Therapeutic Area, By Route of Administration, By End-User, By Distribution Channel, By Region |
| Top Key Players | Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Sarepta Therapeutics, Biogen, Moderna, Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Silence Therapeutics, Dicerna (Novo Nordisk), Wave Life Sciences, Stoke Therapeutics, Arbutus Biopharma, Apellis Pharmaceuticals, OliX Pharmaceuticals, Sirnaomics, Genevant Sciences, BioNTech, Exicure, Roche |
The small nucleic acid drug market refers to therapeutics based on short strands of nucleic acids such as antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and aptamers. These drugs work by regulating gene expression, silencing disease-causing RNA, or modulating protein translation. They have emerged as targeted approaches for genetic, oncological, cardiovascular, neurological, infectious, and metabolic diseases.
Several factors influence market growth, including the rising prevalence of chronic disorders. With several FDA/EMA approvals (e.g., patisiran, nusinersen, golodirsen) and a growing pipeline, small nucleic acid drugs represent a rapidly expanding category of precision medicines supported by advances in delivery systems (lipid nanoparticles, conjugates) and expanding research collaborations.
Increasing Collaboration: Major players collaborate to share proprietary technologies, expertise, and infrastructure to expand their product pipelines.
FDA Approval: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provides market authorization for various SNADs based on their preclinical and clinical trial data.
AI can revolutionize the market by assisting researchers in designing novel SNADs. AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and predict the 3D protein structures from amino acid sequences. They enable researchers to develop stable, safe, and more effective SNADs. AI and ML can also suggest drug delivery systems that are compatible with the molecule, reducing toxic effects. They help in chemical modifications of mRNA to influence gene processing, mRNA stability, and protein production.
Personalized Medicines
The major growth factor for the small nucleic acid drug market is the increasing need for personalized medicines. Personalized medicines are developed based on the genetic profile of a patient. They work by modifying the genetic information of a patient and providing the desired therapeutic effect. SNADs, such as ASOs, regulate gene expression by blocking the function of RNAs. Aptamers can recognize, bind, and subsequently block target molecules. Additionally, siRNA and miRNA silence gene expression. Regulatory agencies derive favorable policies to support the development and launch of SNADs.
High Cost
The development of SNADs is expensive and time-consuming, as it requires specialized equipment. Several research institutions and companies, especially in low- and middle-income countries, lack such complex equipment, limiting the development of SNADs.
What is the Future of the Small Nucleic Acid Drug Market?
The market future is promising, driven by the increasing number of clinical trials. Clinical trials are conducted to assess the safety and efficacy of SNADs for different chronic disorders. They are a result of growing research activities. Apart from their therapeutic properties, SNADs are also assessed for their diagnostic properties. miRNAs are currently being investigated in clinical trials as potential biomarkers for the early detection, diagnosis, and follow-up of patients with Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The increasing clinical trials presents the future scope of SNADs.
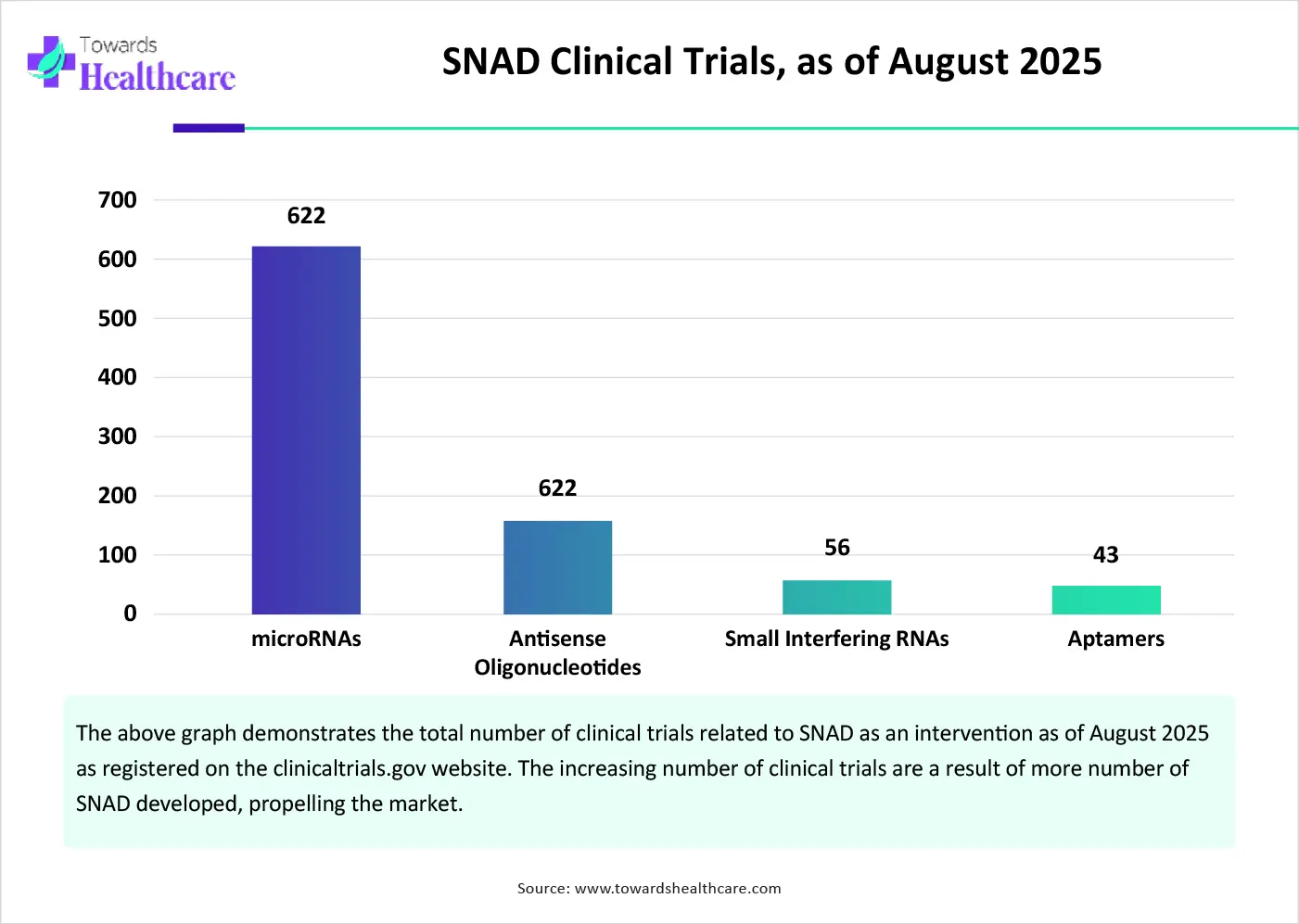
By molecule type, the antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) segment held a dominant presence in the market in 2024. This is due to the ability of ASOs to bind to RNA in a target-specific manner and ultimately modify protein expression. The rising prevalence of rare disorders potentiates the demand for ASOs. As of 2024, the FDA has approved a total of 14 ASO drugs. Researchers have demonstrated advances in the stability and binding affinity of ASOs. They also study the potential of ASOs for extended applications.
By molecule type, the small interfering RNA (siRNA) segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR in the market during the forecast period. siRNA is a double-stranded RNA that regulates the expression of genes. It offers numerous benefits, such as safety, efficiency, and specificity. It does not interact with DNA, avoiding the harmful risks of mutations and teratogenic effects. The demand for siRNA is also increasing due to its multi-functionality, as it can target multiple genes simultaneously. Moreover, siRNA is easy to synthesize and cost-effective.
By therapeutic area, the neurology segment held the largest revenue share of the market in 2024. This is due to the rising prevalence of neurological disorders and the growing need for targeted treatment. SNADs are designed based on the sequences of target genes, ultimately inhibiting their response. They provide long-lasting therapeutic effects by addressing the root cause of neurological disorders. They overcome several challenges of conventional drugs, such as BBB permeability, cellular uptake, and timely drug release.
By therapeutic area, the oncology segment is expected to grow with the highest CAGR in the market during the studied years. Current research studies focus on assessing the genes involved in cancer progression. It is estimated that about 10-20% of all cancer types are caused by an inherited genetic mutation. SNADs are designed to initiate or enhance anti-tumor responses, making them vital for cancer immunotherapy. Safe and efficient gene delivery systems are developed to facilitate targeted delivery directly into tumor cells.
By route of administration, the intravenous (IV) segment contributed the biggest revenue share of the market in 2024. The segmental growth is attributed to high bioavailability and drug delivery throughout the body. The intravenous (IV) route delivers the drug directly into the bloodstream, thereby leading to passive targeting of tissues with high blood supply. The need for immediate and prolonged therapeutic effects of SNADs necessitates healthcare professionals to deliver them through the IV route.
By route of administration, the subcutaneous (SC) segment is expected to expand rapidly in the market in the coming years. The SC route is preferred as it allows patients to self-administer medications, eliminating the need for trained professionals. Drugs delivered through the SC route also do not result in injection site side effects, such as redness and swelling. The SC route results in reduced systemic exposure compared to the IV route, providing more efficient local effect.
By end-user, the hospitals segment accounted for the highest revenue share of the market in 2024. This segment dominated because hospitals have skilled professionals to prescribe and deliver SNADs based on the conditions of a patient. They provide multidisciplinary expertise to patients. The increasing number of hospitalizations is due to favorable reimbursement policies, which enhance the accessibility and affordability of advanced therapeutics. In hospitals, healthcare professionals can continuously monitor a patient and their responses towards novel SNADs.
By end-user, the specialty clinics segment is expected to witness the fastest growth in the market over the forecast period. Specialty clinics possess suitable capital investment and skilled professionals to provide personalized treatment and care to patients. Specialty clinics have specialized infrastructure to facilitate the delivery, targeting, and monitoring of SNADs among the patients.
By distribution channel, the direct hospital sales segment led the market in 2024. SNADs are directly sold to hospitals due to the increasing number of hospital admissions. Hospitals have their own pharmacies to store and manage novel drugs for providing personalized treatment. Pharmaceutical and biotech companies directly provide SNADs to hospitals, as it reduces the extra cost of wholesalers. Thus, hospitals get SNADs at affordable rates.
By distribution channel, the specialty pharmacies segment is expected to show the fastest growth over the forecast period. Specialty pharmacies offer medications for rare and other complex chronic disorders. They have suitable facilities for special handling, administration, and patient support for SNADs. Patients prefer purchasing SNADs from specialty pharmacies due to numerous services, including patient education, financial assistance, and home delivery.
North America dominated the market in 2024. Favorable regulatory support, the availability of state-of-the-art research and development facilities, and the presence of key players are the major growth factors for the market in North America. The increasing demand for personalized medicines and the rising healthcare expenditure augment the market. Prominent pharma & biotech companies focus on expanding their product pipeline owing to increased competition. People are becoming aware of screening and early diagnosis of chronic disorders.
As of August 2025, a total of 23 SNADs have been approved by the FDA, including 14 ASOs, seven siRNAs, and two aptamers. Companies like Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals develop and manufacture SNADs for U.S. patients. The Precision Medicine Initiative by the U.S. government supports the development of personalized medicines.
About 1 in 12 people live with a rare disease in Canada. In March 2025, the Government of Canada announced a collaboration with Quebec and invested over $305 million to support access to new and existing drugs, early diagnosis, and screening for rare diseases. The investment also supports the Action Plan on Rare Diseases 2023-2027.
Asia-Pacific is expected to host the fastest-growing small nucleic acid drug market in the coming years. The burgeoning genomics and proteomics sector and venture capital investments augment the market. Government organizations support the development of novel SNADs through funding and initiatives. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are emerging as global hubs for clinical trials, potentiating the development of SNADs. The rising adoption of advanced technologies also contributes to market growth.
The demand for SNADs is increasing in China with increasing investments and business deals. In 2023, 20 funding events were reported in China related to SNADs, including siRNAs and ASOs. Apart from this, companies like Sanegene Bio, Ribo Life Science, and Argo Biopharma collectively raised USD 4 billion, highlighting the significance of SNADs in China.
The National Policy for Rare Diseases provides incentives to patients of up to Rs 50 lakh for rare disease treatment. The Indian government also launched a nationwide NCD and cancer screening initiative for the prevention, control, and screening of NCDs and three common cancers. The GenomeIndia project was recently announced to understand the genetic identity of the Indian population.
The research activities for SNADs include designing and evaluating novel SNADs for diverse diseases. Scientists also develop novel drug delivery systems for the targeted delivery of SNADs.
Key Players: Axolabs GmbH, AstraZeneca, and Ionis Pharmaceuticals
Clinical trials are conducted to either find expanded applications for existing SNADs or study the safety and efficacy of novel SNADs against a particular disease.
Key Players: Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Isarna Therapeutics GmbH, Bio-Path Holdings, Inc.
The final drug product of SNADs is distributed to hospitals and specialty or retail pharmacies by manufacturers or wholesalers.
Healthcare professionals provide personalized care to patients by prescribing SNADs. They also educate patients about the dosage regimen and therapeutic benefits of SNADs.

Daniel J. Siegwart, Co-founder & Chief Scientific Advisor at SignifyBio, commented that their modular platform, Signal Peptide Engineered Nucleic acid Design (SEND), offers an unprecedented opportunity to engineer personalized protein therapeutics directly within the body, addressing long-standing challenges in drug production, delivery, and efficacy. The company lays the groundwork for a new generation of precision medicine across a wide range of chronic and genetic disorders with its versatility and adaptability.
By Molecule Type
By Therapeutic Area
By Route of Administration
By End-User
By Distribution Channel
By Region
March 2026
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
