January 2026

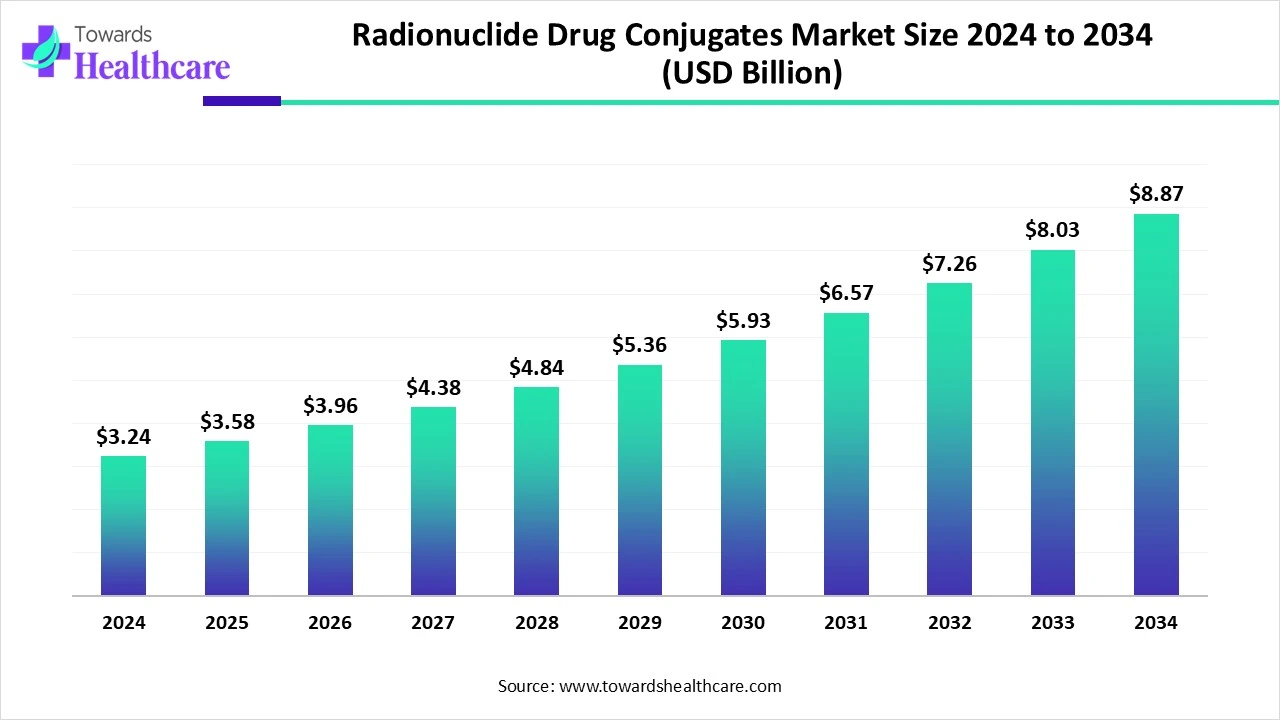
The global radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market size is calculated at US$ 3.24 billion in 2024, grew to US$ 3.58 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach around US$ 8.87 billion by 2034. The market is expanding at a CAGR of 10.54% between 2025 and 2034.
Targeted medicines are more important than ever as cancer rates continue to climb globally. The promise for better patient outcomes and treatment plan personalisation is driving the market for radionuclide drug conjugates (RDCs). Developments in molecular targeting and medical imaging have been crucial in driving this sector. The relevance of radionuclide-based therapies in contemporary cancer therapy has been further validated by the FDA's approval of a number of these treatments. For the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market, emerging markets provide substantial prospects.
| Metric | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 3.58 billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 8.87 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 - 2034) | 10.54% |
| Leading Region | North America Share 43% |
| Market Segmentation | By Type of Targeting Moiety, By Radioisotope Payload, By Therapeutic Area, By Mechanism of Targeting, By End Use/Site of Administration, By Phase of Development, By Route of Administration, By Region |
| Top Key Players | Novartis AG, Bayer AG, Fusion Pharmaceuticals, Telix Pharmaceuticals, Lantheus Holdings, Inc., Curium Pharma, RayzeBio, Inc., Actinium Pharmaceuticals, ITM Isotope Technologies Munich SE, POINT Biopharma, Orano Med, Alpha Tau Medical, Noria Therapeutics, RadioMedix, Inc., Clarity Pharmaceuticals, NorthStar Medical Radioisotopes, Perspective Therapeutics, ImaginAb, Inc., Molecular Targeting Technologies, Inc. (MTTI), Cardinal Health |
Radionuclide drug conjugates (RDCs), also known as radioligand therapies or targeted radiopharmaceuticals, are precision oncology therapeutics that deliver radioactive isotopes directly to cancer cells using a targeting molecule, such as a ligand, peptide, or antibody. The mechanism integrates three critical components: Targeting Moiety (e.g., somatostatin analogs, PSMA ligands), Radionuclide Payload (e.g., Lutetium-177, Actinium-225), and Linker Chemistry to ensure stability and targeted delivery. This innovative modality combines the selectivity of molecular targeting with the cytotoxicity of radionuclide therapy, offering an alternative to conventional chemotherapy, especially for metastatic or refractory cancers. RDCs are gaining traction due to their efficacy in tumor reduction, tolerability, and synergy with other oncology therapeutics such as immunotherapies and hormonal agents.
AI is transforming the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market by improving cancer therapy effectiveness, safety, and accuracy. For radiopharmaceutical treatments like alpha-emitting radionuclides for targeted therapy and lutetium-177 PSMA for prostate cancer, precise dosimetry, biodistribution modelling, and real-time personalisation are necessary to optimise therapeutic efficacy while reducing toxicity. By facilitating accurate dosage prediction, enhancing therapy response tracking, and optimising patient stratification, AI-driven approaches such as machine learning and deep learning models are revolutionising these procedures.
Rising Demand for Precision Medicine
The rising demand for precision medicine in cancer therapy is driving the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market. In order to create more effective cancer treatments, scientists work to comprehend how malignancies change over time and interact with other cells in their surroundings. This allows them to customise treatments for each patient, a process known as precision medicine. By focusing on the medications that are most likely to help each patient, the precision medicine approach can save the patient money and potential negative side effects by avoiding the use of medications that are unlikely to help.
Supply Chain and Logistics Limitations
RDCs can be difficult to build, despite their great promise. There is a limited supply of radioactive nuclides, and their usage is governed by stringent regulations and environmental safeguards. Their limited half-life, which restricts their usage to hours or days, also presents a logistical difficulty. They must thus be manufactured and delivered promptly from a local site, with distribution catered to the urgent need of medical personnel.
Rising FDA Approvals
There are several phases in the FDA clearance process for RDCs that are designed to guarantee quality, safety, and effectiveness. Several FDA centres, including the Centre for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) and the Centre for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), must coordinate on this. Developers must take into account a number of parameters that go beyond those needed for traditional small-molecule medicines in order for RDCs to receive FDA clearance. In addition to being a technological and regulatory accomplishment, the launch of nine RDCs and the FDA's subsequent approval of them mark a significant shift in the field of targeted cancer treatment. The use of these treatments is influencing the paradigms of therapy today and pointing to potential avenues for future study and advancement in the field of radionuclide therapeutics.
By type of targeting moiety, the peptide-based RDCs segment held the largest share of the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market in 2024. Radiolabeled short peptides for diagnostic imaging and radionuclide treatment in nuclear oncology have advanced significantly in recent years. This appearance can be explained by the fact that many tumour cells express more peptide receptors than normal tissues do. Targeted radiotherapy using radiolabeled peptides and tumour imaging may both use these receptors as molecular targets.
By radioisotope payload, the lutetium-177 segment led the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market in 2024. A radioisotope called 177Lu has gained popularity as a treatment agent for a number of ailments, such as metastatic prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumours. The fact that 177Lu-based radioligand therapies may be used for both primary tumours and metastatic malignancies is one of its many important advantages. Treatments based on 177Lu also have the benefit of typically having low toxicity. Unlike conventional chemotherapy, the 177Lu-based treatment does very little harm to healthy tissues.
By therapeutic area, the prostate cancer segment held the major share of the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market in 2024. More than 1,460,000 cases and 396,000 deaths are predicted for prostate cancer (PC) in 2022, making it the second most prevalent disease diagnosed and the fifth leading cause of cancer mortality among men globally. By 2040, the PC burden is expected to have grown to almost 2.4 million cases and 712,000 deaths due to the world's ageing and expanding population alone. The estimated number of life-years lost is expected to rise most sharply in Africa, Asia, and Latin America/Caribbean, with this increase in mortality translating to almost 7.5 million life-years lost.
By targeting mechanism, the PSMA-targeted RDCs segment held the largest share of the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market in 2024. Since prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is overexpressed in cancerous cells, it has become a crucial biomarker in the pathophysiology of prostate cancer and a desirable target for diagnostic imaging as well as treatment. According to clinical research, PSMA-directed treatments can raise radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS), lower PSA levels dramatically, and improve patient-reported quality of life.
By end-use, the hospitals segment was dominant in the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market in 2024. Hospitals are equipped with advanced systems to provide high-quality care. They are also equipped with a multidisciplinary team that provides expertise in different fields, leading to enhanced care. Due to this majority of people prefer hospitals for cancer care, especially for personalized care.
By phase of development, the commercialized segment held the largest share of the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market in 2024. A rise in cancer cases can be seen, and it is a growing increase in the future. This has led to a growing demand for personalized medicine. To meet the growing demand, pharmaceutical companies are focusing on developing RDCs on a large scale. As the demand increases in the future, the commercial development of RDCs is expected to increase.
By route of administration, the intravenous segment captured a revenue of 85% in 2024. Since the medications are injected straight into the vein to reach the bloodstream immediately, the intravenous route of drug administration is the most often used method during cancer chemotherapy. Anti-cancer drugs used intravenously offer treatment plan adaptability and flexibility.
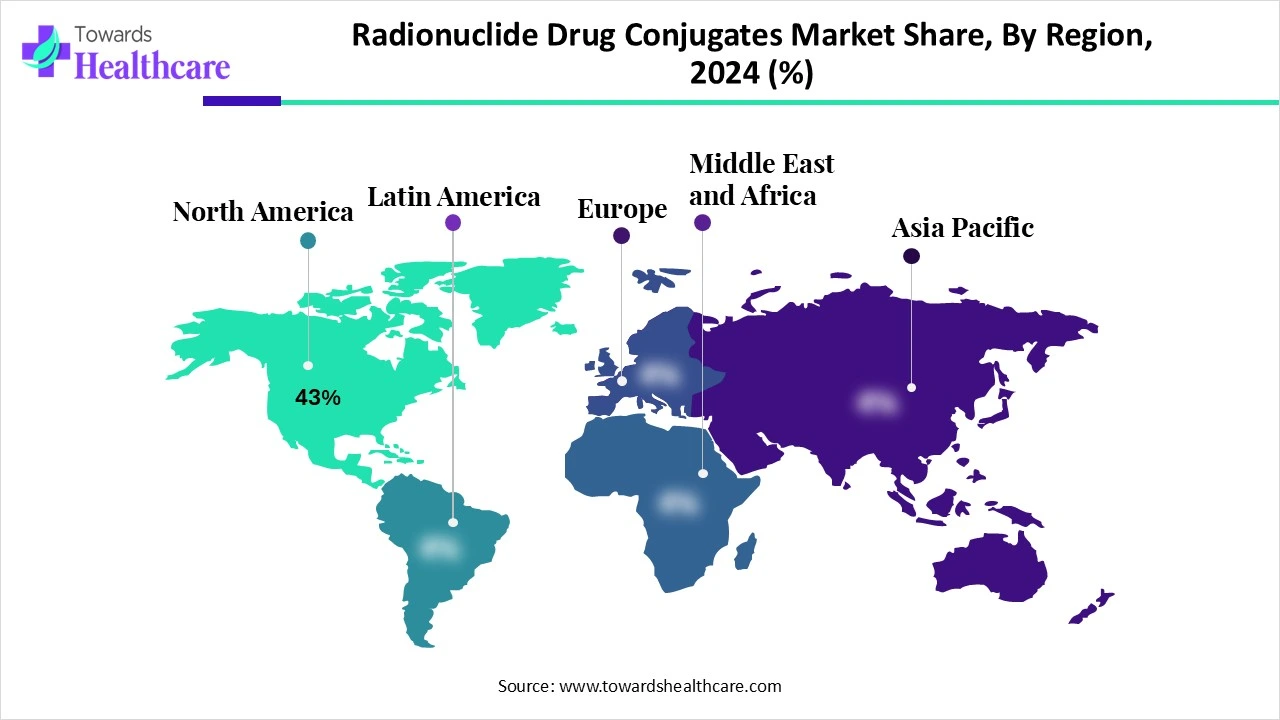
North America dominated the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market share by 43% in 2024. a climate that is conducive to research and development because of a strong product pipeline and a rise in regulatory approvals for targeted cancer medicines. The area is renowned for its rapid uptake of cutting-edge cancer therapies, especially in the U.S., and RDCs are predicted to follow suit. Additionally, this dominance is strengthened by the presence of significant pharmaceutical corporations such as Novartis, Lantheus, and Curium Pharma. When combined with a strong healthcare system that facilitates the commercialisation of innovative treatments, these elements put North America at the forefront of the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market.
The U.S. Congress provides NCI with its funding because it is a government agency. In fiscal year 2025, the NCI received $7.22 billion in funding from the Full-Year Continuing Appropriations and Extensions Act, 2025 (H.R. 1968) at levels equivalent to fiscal year 2024. Managing a wide range of research, training, and information dissemination programmes that span the whole nation, NCI is the largest financier of cancer research worldwide and the head of the cancer research enterprise, collectively known as the National Cancer Programme.
CCS invests millions of dollars annually in cutting-edge and significant cancer research, achieving quantifiable advancements in the four long-term objectives. $1.99 million was allocated by the Canadian Cancer Society to research aimed at prevention and/or risk reduction. Research on biomedicine received $1 million of that $1.99 million, clinical research received $196K, health services/systems research received $253K, and social, cultural, environmental, and population health research received $537K.
Asia Pacific is estimated to host the fastest-growing radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market during the forecast period. Significant demand is being created by nations like China, India, and South-east Asia's rapid industrialisation, population development, and growing metropolitan centres. New market entrants and expansion plans are encouraged by the region's lower production costs and growing infrastructural developments.
In China, cancer has become one of the most significant public health threats due to its increasing incidence and significant regional and population-level variations. China spends an estimated 221.4 billion RMB annually on cancer treatment, which represents 5.4% of total medical costs in the country. Additionally, the annual productivity losses resulting from early cancer-related deaths were estimated to be USD 28 billion. China's emphasis on RDC research is driving the country's market expansion for radionuclide drug conjugates (RDCs).
For instance,
Cancer is a significant public health issue in India, with a predicted substantial rise in incidence. In India, about 100 people out of every 1 lakh are diagnosed with cancer. In 2023, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) predicts that there would be more than 14 lakh cancer cases in India. The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has been given a total of Rs 99,858.56 crore, of which Rs 3,900.69 crore has been set aside for the Department of Health Research and Rs 95,957.87 crore for the Department of Health and Family Welfare.
Europe is expected to grow significantly in the radionuclide drug conjugates (RDC) market during the forecast period. Europe maintains a significant market share because to its strong healthcare systems and regulatory frameworks. Innovation is fueled by extensive research partnerships across European nations. RDCs and other sophisticated therapy alternatives are in high demand due to the increasing incidence of cancer.
The German Cancer Research Centre (DKFZ) is a premier cancer research centre and the country's largest biomedical research facility. With five research emphasis areas, a vast network of regional sites, and more than 3,400 people, the DKFZ establishes the groundwork for ground-breaking breakthroughs.
For instance,
Dr. Scott Arthur (Labour) introduced the Rare Cancers Bill 2024-25, his private member's bill (PMB), to the House of Commons in October 2024. According to the bill's lengthy title, it would provide incentives for investment and research into the treatment of uncommon cancers, among other related goals. The bill would establish three provisions aimed at promoting further research if it were approved.

In July 2024, through a licencing agreement, SK Biopharmaceuticals purchases a radiopharmaceutical therapeutic candidate from Full-Life Technologies; the deal is for $571.5 million. We are happy to work together in the biotech industry, which has seen the most international investments, acquisitions, and partnerships in recent years, through this international licencing agreement with Full-Life Technologies, stated Lee Dong-hoon, CEO of SK Biopharmaceuticals and its U.S. subsidiaries SK Life Science and SK Life Science Labs.
By Type of Targeting Moiety
By Radioisotope Payload
By Therapeutic Area
By Mechanism of Targeting
By End Use/Site of Administration
By Phase of Development
By Route of Administration
By Region
January 2026
January 2026
January 2026
January 2026